Comparing Ceramic and Coated Insulated Bearings
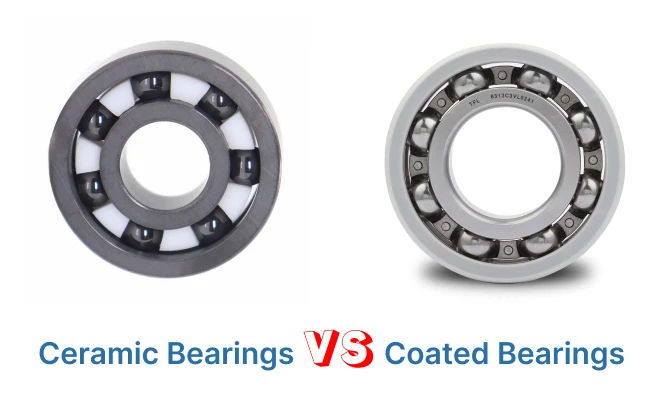

Explore key differences in performance, cost, and applications.
Features | Ceramic Bearings | Coated Insulated Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silicon nitride balls with steel rings | Steel rings coated with alumina layer |
| Electrical Insulation | Inherent insulation via ceramic balls | Insulation from alumina coating on ring |
| Durability | High wear resistance, long-lasting | High, depends on coating quality |
| Speed Capability | Supports very high-speed operation | Standard speed, like steel bearings |
| Weight | Lighter due to ceramic balls | Similar weight to steel bearings |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent, up to 2200°C | Good, up to 150°C |
| Maintenance Needs | Reduced wear, less maintenance | Coating requires regular inspection |
| Dimensional Compatibility | May need design changes | Matches standard bearing sizes |
| Applications | High-speed, hot, corrosive environments | Electric motors, generators, insulation focus |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials | More cost-effective, easier replacement |
Choosing between ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings depends on what your job needs. Ceramic bearings work best in tough places, like very fast or hot spots. Coated insulated bearings are good for stopping electricity from passing through. They also save money in machines like industrial motors. New market data shows ceramic coated isolating bearings are used the most around the world. They are popular in electric motors and green energy.
| Market Segment | 2024 Value (USD Billion) | 2033 Value (USD Billion) | Largest Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coated Insulated Bearings | 0.78 | 1.3 | Electric motors |
| Ceramic Coated Isolating Bearings | 1.25 | 2.00 | Electric motors, generators |
If you need help picking the right bearing, TFL Beaings can help you. We want to help you find what works best for you.
Key Takeaways
- Ceramic bearings work well in fast and hot places. They lower friction and stop wear. Their ceramic balls also block electricity.
- Coated insulated bearings have a special coating. This gives strong electrical insulation and stops rust. They fit into machines without changing the size.
- Hybrid ceramic bearings use steel rings and ceramic balls. They are good for high speed and heat. They last a long time and work well in hard jobs.
- Coated bearings are a cheaper way to get insulation and strength. They are used in electric motors, generators, and machines that need easy replacement.
- Picking the right bearing depends on your machine’s speed and heat. You should also think about insulation and how much care it needs. Experts can help you choose the best one.
Overview
Main Differences
Ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings are used for different jobs in factories. Ceramic bearings have silicon nitride balls. These balls stop electricity and make less friction. They work well in machines that go very fast or get very hot. These bearings are light, so machines can run faster and use less power. Ceramic bearings last a long time and can handle very hot or cold places.
Coated insulated bearings are also called coated bearings. They have a steel base with an alumina coating on the ring. This coating blocks electricity from passing through. Coated bearings are the same size and shape as regular steel bearings. This makes them easy to swap in old machines. How long they last depends on how good the coating is. They work well in electric motors and generators. Coated bearings do not get damaged by water or tough conditions, so they last a long time.
Both types of bearings help lower the need for repairs. Ceramic bearings are best for fast and hot jobs. Coated bearings are better when you need to stop electricity. You should pick the bearing that fits your job, like speed, insulation, or easy replacement.
Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | Ceramic Bearings | Coated Insulated Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silicon nitride balls, steel rings | Steel rings with alumina coating |
| Insulation | Inherent via ceramic balls | Provided by alumina coating on ring |
| Durability | High, with excellent wear resistance | High, depends on coating integrity |
| Speed Capability | Very high, supports fast operation | Standard, similar to steel bearings |
| Weight | Lighter due to ceramic balls | Similar to conventional steel bearings |
| Maintenance | Reduced due to less wear and no current erosion | Similar to steel bearings, coating needs checks |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent, handles extreme heat and cold | Good, coating supports high temperatures |
| Dimensional Compatibility | May need design changes for hybrid structure | Matches standard bearings, easy replacement |
| Applications | High-speed, high-temperature, electrical risk | Electric motors, generators, insulation focus |
| Cost | Higher due to ceramic materials | Cost-effective for insulation needs |
If you need help picking coated bearings or insulated bearings, TFL Bearings can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Ceramic Bearings
Construction
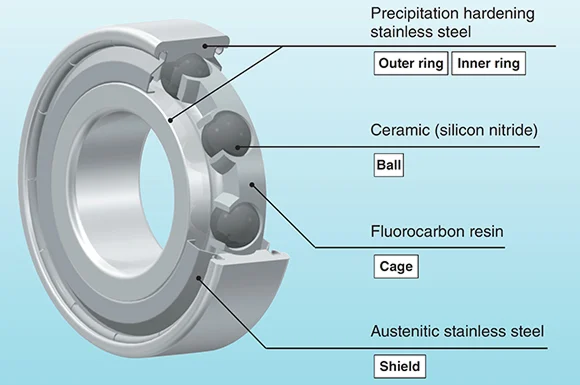
Ceramic bearings are made with special materials and careful methods. Most of the time, makers use silicon nitride or alumina ceramic for the rolling parts. Alumina ceramic comes from bauxite. It is shaped by different ways like injection molding, die pressing, isostatic pressing, slip casting, or extrusion. These ways make strong and even parts. The parts can work well in tough places.
Properties
There are two main kinds of ceramic bearings. One kind is full ceramic bearings. These have rings and balls made from ceramic. The other kind is hybrid ceramic bearings. These use ceramic balls and steel rings. The ceramic balls are rounder, lighter, and harder than steel balls. This design lets hybrid ceramic bearings take the place of steel bearings in many machines. This makes it easy to upgrade for some uses.
Ceramic bearings are special because of their strong physical and chemical features. They are very hard, light, and do not rust easily. These things help them last longer and lower friction better than steel bearings. The light ceramic balls help machines go faster and use less energy.
Hybrid ceramic bearings give both electrical insulation and long life. They do not get damaged by acids, alkalis, or other harsh chemicals. This makes them good for places where strength is important. The low friction in ceramic bearings means less heat and less energy loss. This helps them last longer and work better.
The table below shows how ceramic and steel bearings are different:
| Property | Ceramic Bearings (Silicon Nitride) | Steel Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Much higher | Lower |
| Density | Lower (lighter) | Higher |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very low (insulating) | Conductive |
| Temperature Tolerance | High (up to ~800°C) | Lower (~180°C) |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Coefficient of Friction | Lower | Higher |
Ceramic bearings are great for wear resistance, less friction, and lasting a long time. They are a smart pick for fast, hot, or harsh places.
If you want to know more about ceramic bearings or hybrid ceramic bearings, TFL Bearings can help you find the best one for your needs.
Coated Insulated Bearings
Coated Bearings: Features
Coated bearings use new technology to help electric motors work better. Makers put a special layer on the outside ring of these bearings. This layer stops electricity from passing through the bearing. The most used coating is ceramic, like aluminum oxide. It gives strong insulation and keeps the bearing from rusting. Some coated bearings use polymer coatings like PPS. These can save money and still give good insulation.
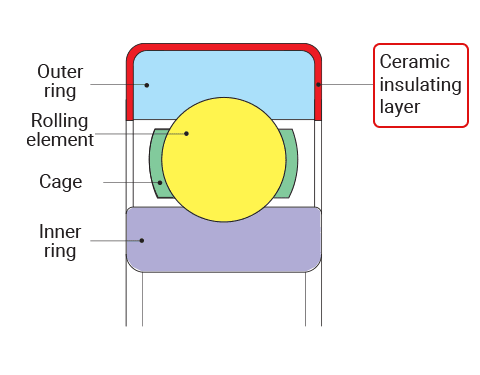
The coating can be put on in different ways:
- Physical vapor deposition (PVD) and plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition (PACVD) make thin, even layers.
- Chemical ways include electroless deposition, dipping, and spraying.
- Molten state ways, like thermal spraying and laser cladding, make thicker layers for more protection.
These ways help coated bearings keep their size and shape. This means you can easily swap them into old machines. The coating also helps stop rust and wear.
Properties
Coated insulated bearings give both insulation and strength. The ceramic or polymer layer blocks stray currents that can hurt bearings in motors. Coated bearings give good insulation, but ceramic bearings give even more. This is because ceramic bearings have insulation all over the ball, not just the ring. So, ceramic bearings are better when you need the most insulation.
Coated bearings are great at stopping rust and working in tough places. The coating keeps water and chemicals away from the steel rings. This lowers the chance of rust. These bearings also resist wear, so they last longer in hard jobs. Coated insulated bearings are the same size as regular bearings. This lets engineers use them without changing the machine.
Note: Coated insulated bearings are a smart and cheap choice for many motors and generators. They give insulation, stop rust, and are easy to put in.
If you need help picking coated bearings or insulated bearings, TFL Bearings can help you choose the right one.
Performance
Electrical Insulation
Ceramic bearings and coated bearings both stop electricity, but they do it differently. Ceramic bearings use special balls that do not let electricity pass. Coated bearings have a layer, usually alumina, on the ring to block current. Lab tests show they work in different ways.
| Parameter | Ceramic Bearing Analog (Wire A) | Coated Insulated Bearing Analog (Wire B) |
|---|---|---|
| Partial Discharge Inception Voltage (PDIV) (V) | 119 | 328 |
| Breakdown Voltage (V) | 173 | 540 |
| Insulation Resistance (Rp, MΩ) | 2.47 | 1.74 |
| Dielectric Losses (tan δ) | 0.099 | 0.206 |
| Mechanical Stability (Bending Radius) | Critical issue (cracking, porosity) | No critical issue (thicker insulation) |
Coated bearings can handle higher voltages before breaking down. Their coating is thick, so it does not crack easily. Ceramic bearings have higher insulation resistance, but their insulation can crack or have holes. So, coated bearings give stronger and more steady insulation in most factories.
Speed and Load
Ceramic bearings are great for fast and heavy jobs. Their silicon nitride balls are lighter and harder than steel. This means less spinning force and less heat. They also lower friction and help machines move better.
| Aspect | Ceramic Bearings (Silicon Nitride) | Steel Bearings | Notes/Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 40% of steel | Baseline (100%) | Lower density reduces centrifugal loads, improving dynamic behavior and speed capability. |
| Thermal Expansion | 29% of steel | Baseline (100%) | Smaller thermal expansion leads to less preload increase due to temperature differences, enhancing stability. |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 151% of steel | Baseline (100%) | Higher modulus increases bearing stiffness by ~10% static, more at high speeds due to better dynamic behavior. |
| Hardness (HV10 at 20°C) | 1700 | 700 | Greater hardness improves wear resistance and service life. |
| Centrifugal Load (example) | 71 N (normal size ball, 12.7 mm at 15,000 r/min) | 174 N | Ceramic balls experience significantly lower centrifugal loads, reducing stress and temperature rise. |
| Radial Stiffness at 40,000 r/min | 70% of static stiffness (hybrid bearing with ceramic balls) | 61% of static stiffness (steel balls) | Ceramic bearings maintain higher stiffness at high speeds, beneficial under high-load conditions. |
| Service Life | Longer than steel bearings under grease lubrication | Baseline | Improved durability under operating conditions. |
| Temperature Rise | Lower compared to steel bearings | Higher | Reduced temperature rise improves reliability and reduces preload increase risks. |
| Application Examples | High-speed CNC lathes, machining centres, internal grinding spindles | Common in general applications | Ceramic bearings are increasingly preferred for demanding high-speed, high-load applications. |
Ceramic bearings are used more for speed and heavy loads. There is not much data about coated bearings in these jobs. Coated bearings work like steel bearings for speed and load. They are good for many electric motors.
Wear and Durability
Both types of bearings are made to last and fight wear. Ceramic bearings, especially with SlipCoat, last a long time and resist damage. Coated bearings are also strong, especially where there is electricity.
| Bearing Type | Wear Duration (hours) | Failure Mode / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Uncoated Ceramic (ZrO2) Rings | ~200 | Failure due to severe spalling after initial wear |
| TDC-Coated 100Cr6 Steel Rings | >2000 | Durable but produces contaminating black powder residue |
| SlipCoat-Treated Steel Rings | >6000 (test stopped) | No visible damage, raceways appear as new |
| SlipCoat-Treated Ceramic Rings | 14x longer than untreated ceramic (~2800) | Significant durability improvement over untreated ceramic |
SlipCoat-treated steel rings with ceramic balls last the longest and look new. Coated bearings also last long, but some coatings leave black dust. Both types stop rust, but ceramic bearings are even better at fighting rust.
Temperature Resistance
How well bearings handle heat is important. Coated bearings, like INSOCOAT, keep their insulation even in very hot or wet places. They work from –40°C to +150°C and stay strong in high humidity.
- New coated bearings keep insulation steady in tough places.
- At over 90% humidity and 30°C, coated bearings keep resistance above 2,000 MΩ.
- Coatings can take high voltage up to 6 kV DC and still work well.
Ceramic bearings can handle even higher heat. The table shows how hot each ceramic material can get:
| Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m.K) | Key Properties and Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Nitride | 1900 | 40-60 | Lightweight, high rigidity; used in aerospace and semiconductor |
| Zirconium Oxide | 2200 | 10-20 | High strength and toughness; chemical and medical applications |
| Aluminium Oxide | 2000 | 18-35 | High melting point and stability; used in capacitors, resistors |
Ceramic bearings can work in places up to 2200°C. This makes them great for space and other very hot jobs. Coated bearings work well in most factories, but ceramic bearings are best for extreme heat.
Maintenance
Both ceramic and coated bearings need care to last long. Makers say you should:
- Use the right oil or grease to stop friction and heat.
- Clean bearings to get rid of dust and dirt.
- Check bearings for damage or wear.
- Store bearings in a cool, dry place and keep them flat.
- Use the right tools when putting them in to avoid harm.
- Watch the temperature and load to stop early failure.
How often you add oil depends on how fast and hot the job is. Fast or hot jobs need more oil. Both types last longer if you follow these steps.
Tip: Keep dirt and water away from both ceramic and coated bearings. Use sealed bearings and clean areas before installing. This helps bearings work well and last longer.
Bearings can fail from dirt, rust, or electricity. Ceramic bearings do not rust or get water damage easily. Coated bearings use their layer to block electricity and stop fluting. Using sealed bearings, cleaning, and careful installation lowers these risks.
If you want help picking the right bearing, TFL Bearings can help you find the best one for your job.
Cost
Purchase Price
When people compare ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings, they look at the first price. Coated insulated bearings can cost very little or a lot. If you buy many insulated bearings, each one can be as cheap as ten cents. Most deep groove ball bearings with insulation cost between $30.80 and $300. The price changes with the size and how many you buy. Some really good insulated bearings cost $142 each if you buy just a few. Special sets can cost up to $2,500.
Ceramic bearings, like hybrid ceramic bearings, usually cost more money. Small ceramic insulated bearings start at about $76. Bigger or fancier ones can cost up to $1,600 each. The higher price is because they use special materials and need careful work to make. These bearings are made to last longer and fight rust.
| Product Type / Description | Price Range (USD) | Minimum Order Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Electrically Insulated Deep Groove Ball Bearings | $30.80 – $300 | 10 to 500 pieces |
| High Quality Deep Ball Bearing Insulated Bearings | $142 | 2 pieces |
| Electrically Insulated Bearings (various models) | $2 – $9.90 | 2 pieces |
| Insulated Bearings (bulk) | $0.10 – $0.20 per piece | 10 pieces |
| Specialized Electrical Insulated Bearing Sets | Up to $2,500 | 1 set |
| Bearing Model | Dimensions (mm) | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| MR6313CCT-ZZ/C3/IS/1000V/NS7 | 65 x 140 x 33 | $1,554.53 |
| MR6313CCT-2RS/C3/IS/1000V/NS7 | 65 x 140 x 33 | $1,554.53 |
| MR6313CCT-M/C3/IS1000V LD | N/A | $1,607.11 |
| MR6314CCT-ZZ/C3/IS/1000V/NS7 | N/A | $1,554.53 |
| MR3724CCT-2RS/C3 #3 NS7 | 24 x 37 x 7 | $76.41 |
Long-Term Value
Ceramic bearings cost more at first but can save money later. They are tough and do not wear out fast. They help machines run longer without breaking. Ceramic materials do not rust, so you do not have to replace them as often. Hybrid ceramic bearings last even longer, so they are good for jobs where you need them to work well for a long time.
Coated insulated bearings are a good deal for many motors and generators. Their alumina coating keeps them safe from rust and electricity. This helps stop early damage from stray currents. Coated bearings are the same size as regular bearings, so you can swap them easily. Many people like them because they cost less and are simple to put in.
Tip: Pick ceramic bearings if you need them for fast, hot, or rusty places. They may cost more at first but can save money over time. For most motors that need insulation and rust protection, coated bearings are a good choice for the price.
If you want to get the most for your money and pick the right bearing, TFL Bearings can help you find what you need.
Applications
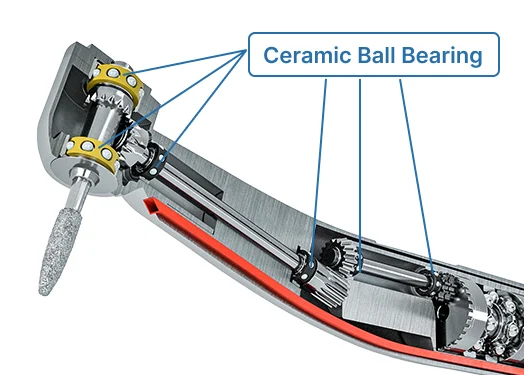
Ceramic Bearings Uses
Ceramic bearings are used in many tough jobs. Engineers pick them for fast machines like CNC spindles and tools. These bearings help cut down friction and stay steady when hot. Hybrid ceramic bearings have ceramic balls and steel rings. They work well in electric motors and generators. The insulation keeps them safe from electric current. Aerospace companies use ceramic bearings because they are light and last long. Medical tools use them because they are safe for the body and have low friction. Factories that make semiconductors use ceramic bearings. They need bearings that stay stable in high heat and vacuum.
| Industrial Application | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|
| High-speed machinery | Great at fighting wear, can run very fast |
| Corrosive environments | Very good at not rusting |
| High-temperature environments | Keeps working even when it is very hot |
| Medical equipment | Safe for people, low friction |
| Semiconductor manufacturing | Stays steady and precise in hot and vacuum places |
| Aerospace | Light, handles heat, fights wear |
| Hybrid ceramic bearings | Faster, less friction, blocks electricity, lasts longer, helps machines work better |
These uses show ceramic bearings are strong and reliable in hard places.
Coated Insulated Bearings Uses
Coated bearings are important in electric motors, especially with variable frequency drives. They stop electric current from hurting the bearing. Many jobs use coated bearings, like wind turbines, generators, and train or car motors. Machines in factories, like pumps and fans, also use coated bearings. These bearings block current, make less noise, and help save on repairs. Their coating stops rust and wear, so they work well in rough places. Coated bearings come in normal sizes, so engineers can swap them easily.
| Industry/Application Area | Primary Reasons for Using Coated Insulated Bearings |
|---|---|
| Electric Motors (especially VFD-driven) | Stops electric damage, helps motors last longer, cuts repair time and cost |
| Generators (all types) | Blocks stray current, keeps power machines working well |
| Wind Turbines | Handles tricky electric jobs, makes them more reliable |
| Traction Motors (Rail & EV) | Stops bearing currents, needed for trains and electric cars |
| Industrial Machinery | Stops electric wear, keeps machines running and lowers breakdowns |
| Power Transmission Equipment | Gives insulation, stops electric damage, helps machines last longer |
Selection Guide
Picking ceramic or coated bearings depends on the job. Ceramic bearings are best for fast, hot, or rusty places. They lower friction and block electricity, so they are good for planes, medical tools, and making chips. Coated bearings are best for motors, wind turbines, and machines that need insulation and easy swaps.
Tip: For fast or very hot jobs, ceramic bearings are often best. For motors and machines that need insulation and easy setup, coated bearings are a smart pick.
We at TFL Bearings can help you choose the right bearing for your job. Contact us for advice and solutions made just for you.
Recommendations
Decision Factors
Picking between ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings depends on a few big things. Engineers and buyers look at what their machines need before they choose. Here are the main things to think about:
- Full ceramic bearings have rings and balls made from ceramic. Hybrid ceramic bearings have steel rings and ceramic balls. This makes them stiff, stops electricity, and keeps them from rusting.
- Hybrid ceramic bearings have much less friction than steel bearings. This means they make less heat and move smoother.
- Both ceramic and hybrid ceramic bearings can work with little or no oil. This helps in places where oil or grease is hard to use.
- Ceramic materials like silicon nitride are not magnetic. They can go very fast and get very hot. They also last a long time in tough places.
- Coated insulated bearings have a special layer, usually alumina, to stop electricity. This keeps motors and generators safe from electric damage.
- Coated bearings are the same size as regular bearings. This makes them easy to swap in old machines.
- Both types need to be strong and fight wear. Ceramic-coated bearings are extra tough and last longer, so you do not have to fix them as much.
- The best choice depends on speed, weight, heat, and if you need insulation. For fast or hot jobs, hybrid ceramic bearings are often best. For motors and generators that need insulation and easy swaps, coated insulated bearings are a smart pick.
Tip: Always pick the bearing that fits your job. Think about speed, weight, heat, and if you need to block electricity.
Expert Advice
Experts say you should follow steps when picking bearings for hard jobs:
- Use hybrid ceramic bearings if you need speed, heat resistance, and insulation. These have ceramic balls and steel rings for extra strength.
- Pick coated insulated bearings with alumina coatings to stop electric damage in high-voltage machines. This keeps stray currents away and helps bearings last longer.
- Match the bearing to the job. Deep groove ball bearings are good for motors. Tapered roller bearings are for heavy loads. Cylindrical roller bearings hold up big side forces. Hybrid ceramic bearings are best for fast jobs and insulation.
- Make sure the bearing can handle more force than your machine gives. Check the speed rating so it does not get too hot or break early.
- Use the right oil or grease. Synthetic grease helps lower friction and wear, especially when things go fast or get hot.
- Think about space and weight. Thin-section or hybrid ceramic bearings can make machines lighter without losing strength.
- Test bearings in real jobs before using them everywhere. Ask suppliers for help and special answers.
Note: Hybrid ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings both fight rust, block electricity, and last a long time. The best one depends on your job and where the bearing will work.
We at TFL Bearings can help you pick the best bearing for your needs. Our team can show you the choices and help you find the right one. Contact us today for advice and good bearing solutions.
Ceramic bearings are very good at fighting wear and rust. They also help machines run smoother by lowering friction. These bearings last a long time, even when things move fast or get hot. Coated bearings, like insulated bearings, stop electricity from passing through. They also keep the bearing safe from rust. Hybrid ceramic bearings are best when you need both strength and insulation. People should pick ceramic bearings for really tough places. Coated bearings are better for electric motors or generators. If the job is tricky, it is smart to ask experts for help. We at TFL Bearings want you to reach out for advice and answers.
FAQ
What are the main differences between ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings?
Ceramic bearings have ceramic balls that help stop electricity and lower friction. Coated insulated bearings use a special layer to block electricity. Ceramic bearings are better at fighting wear and rust. Coated bearings are the same size as regular ones, so they are easy to swap in machines.
Which bearing type offers better durability and long-lasting performance?
Hybrid ceramic bearings last longer and work better in fast or hot places. Coated insulated bearings also last a long time, mostly in electric motors. The best one depends on what you need, like insulation or stopping rust.
How do coated insulated bearings and ceramic bearings handle corrosion?
Ceramic bearings do not rust because of their material. Coated insulated bearings have a layer that keeps rust away. Both types work well in tough places, but ceramic bearings are even better at stopping rust in hard jobs.
In which applications should engineers choose coated insulated bearings over ceramic bearings?
Engineers pick coated insulated bearings for electric motors, generators, and machines that need insulation and easy swaps. Ceramic bearings are better for fast, hot, or rusty places. The right choice depends on what the job needs and how the bearing will be used.
Do both bearing types help with friction reduction?
Both ceramic bearings and coated insulated bearings help lower friction. Ceramic bearings are best at cutting down friction and wear, so they are great for fast jobs. Coated bearings also help lower friction, especially in electric motors.
Need help picking the right bearing? We at TFL Bearings can help you find the best one for your job.




