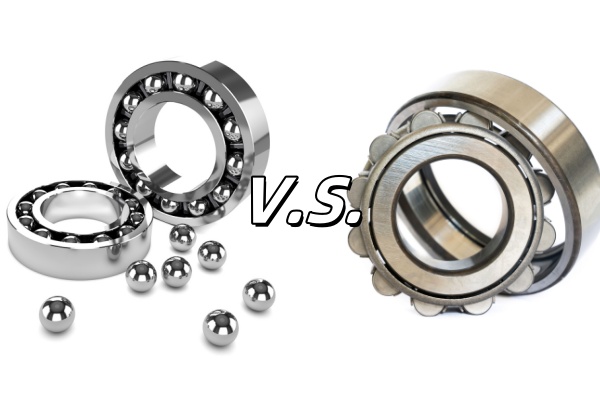
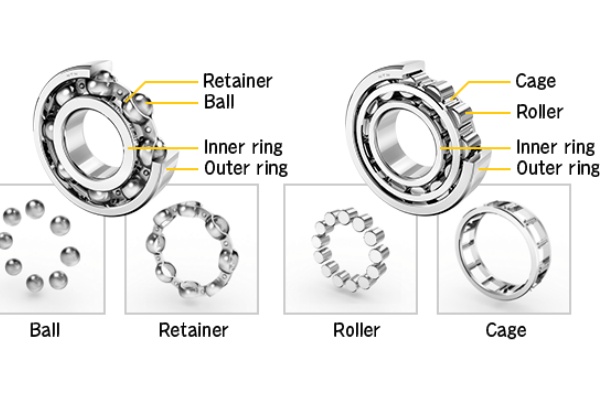
Key Features of Ball vs. Roller Bearings
Explore the differences between ball and roller bearings.
| Features | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Design and Structure | Use small balls for low friction. | Use cylinders for better load distribution. |
| Load Capacity | Good for medium loads. | Best for heavy loads. |
| Speed Performance | Excellent for high-speed applications. | Moderate speed capabilities. |
| Friction Levels | Lower friction with good lubrication. | Higher friction due to larger contact area. |
| Durability | Wear faster under heavy loads. | Stronger for heavy-duty tasks. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Simpler and require less upkeep. | Need more attention to avoid damage. |
| Environmental Suitability | Struggle in extreme temperatures. | Handle tough conditions better. |
| Applications | Used in fast-moving machines. | Ideal for heavy-duty applications. |
You see ball bearings and roller bearings in many machines. Each type has its own job. Ball bearings use round balls to lower friction. They work best for fast-moving parts and light loads. Roller bearings use cylinder shapes to carry heavy loads and handle shocks better. When picking bearings, think about the weight, speed, and surroundings of your system. Knowing these differences helps you choose the best bearing for good performance.
Key Takeaways
- Ball bearings work well for fast-moving parts. They have low friction.
- Roller bearings are best for heavy loads and absorbing shocks. Use them for strong and tough tasks.
- Think about load, speed, and environment when picking bearings. This helps them work better.
- Take care of bearings often. Clean them, add oil, and check for damage to make them last longer.
- Knowing how ball and roller bearings differ helps you choose the right one for your machines.
Key Differences Between Ball Bearings and Roller Bearings
Design and Structure
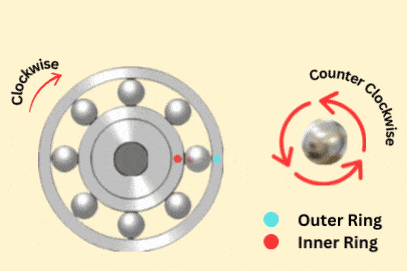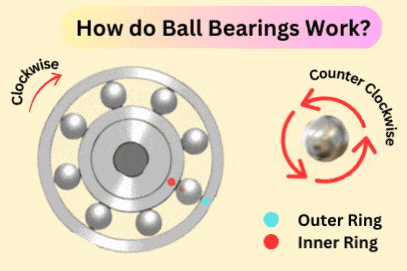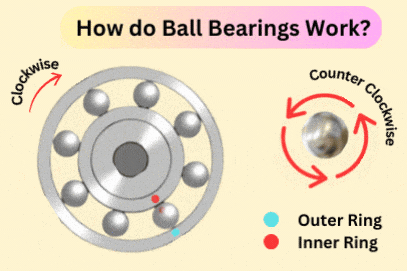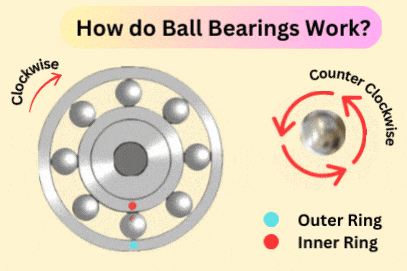
Knowing how ball bearings and roller bearings are made explains their uses. Ball bearings touch the raceway at one small point. This lowers friction and helps parts spin smoothly. But this design can affect how magnetic fields spread in the contact area.
Roller bearings, with their cylinder or cone shapes, touch a bigger area. This makes them roll better and carry heavy loads. The strength of magnetic induction in their design also impacts how well they work.
Tip: Use roller bearings for heavy loads or shock. Their bigger contact area works better.
Load Capacity and Speed
How much weight and speed bearings can handle depends on their type. Ball bearings work well for medium loads and high speeds. They are great for fast-moving machines. Roller bearings are better for heavy loads. They can handle both sideways and upward forces. Below is a table comparing load and speed abilities:
| Bearing Type | Load Capacity | Speed Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Groove Ball Bearings | Good for medium loads | Limited high-speed performance |
| Spherical Roller Bearings | Best for heavy loads | Moderate speed abilities |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Handles both load types | High speed but less load capacity |
Think about your machine’s needs when picking bearings. For speed, choose ball bearings. For weight, go with roller bearings.

Friction and Efficiency
Friction and efficiency matter when comparing these bearings. Ball bearings usually have less friction with good lubrication. This makes them better for fast-moving parts. Roller bearings have more friction because of their bigger contact area. But new methods, like SKF and LFP models, help predict friction better. This improves how roller bearings perform with different lubricants.
Keep bearings working well by using the right lubrication. This lowers friction and helps them last longer.
Performance and Maintenance
Durability and Longevity
How long bearings last depends on their design and use. Ball bearings wear out faster with heavy loads due to small contact points. Roller bearings spread weight better, making them stronger for heavy-duty tasks.
Using the right lubrication helps bearings last longer. In 1978, the first ISO standard showed how oil thickness and dirt affect lifespan. A Kappa value of 4.0 means the best lubrication for durability. Dirt or poor lubrication can shorten life quickly. This is why taking care of bearings is so important.
In 1947, the Lundberg-Palmgren model didn’t focus on lubrication. Later studies proved it’s very important. Picking the right bearing for the job helps it last longer.
Maintenance Requirements
Both types of bearings need care to work well. Ball bearings are simpler and need less upkeep. Roller bearings, with bigger contact areas, need more attention to avoid damage.
Important maintenance steps include:
- Cleaning off dirt and old grease.
- Checking for cracks or wear.
- Adding the right oil to reduce friction.
- Storing bearings safely to avoid rust or bending.
- Watching for overheating or too much weight.
Doing these things helps bearings last longer and prevents sudden breakdowns.
Environmental Suitability
Where bearings are used affects how well they work. Ball bearings are great for speed but struggle in extreme heat or cold. Roller bearings handle heavy loads and tough conditions better.
| Study | Findings | What It Means |
|---|---|---|
| Walters | High-speed ball bearings need good balance and oil | Careful design and oiling are key for speed |
| Sathtan et al. | Special cages work better in high heat | Roller bearings are better for hot places |
| Nosaka et al. | Certain designs work well in freezing cold | Ball bearings can be improved for cold areas |
Think about the environment when choosing bearings. For heat or heavy loads, roller bearings are better. For speed or precision, ball bearings are a good pick.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball Bearings and Roller Bearings
Ball Bearings: Pros and Cons
Ball bearings have many benefits for fast and precise tasks. Their design lowers friction, helping parts spin smoothly at high speeds. Steel ball bearings don’t rust easily, so they last longer. Small ball bearings work quietly and with little vibration. These features make them great for jobs needing accuracy and reliability.
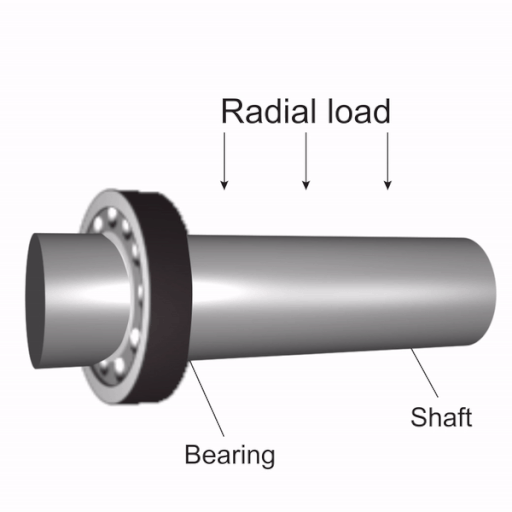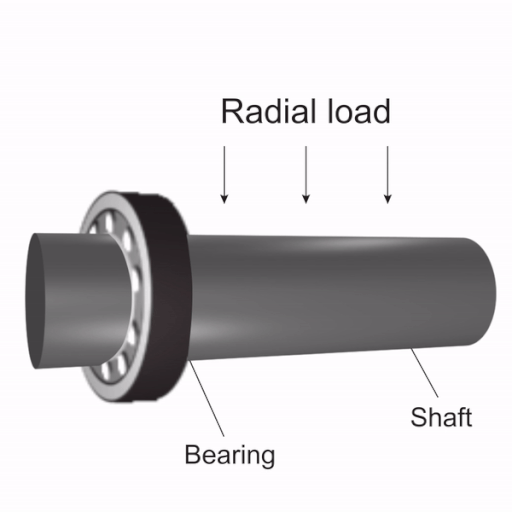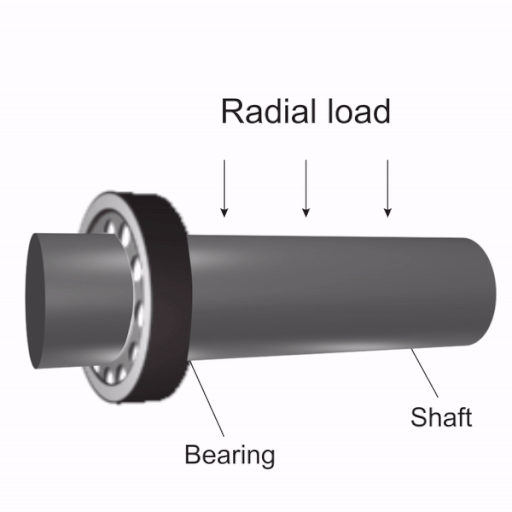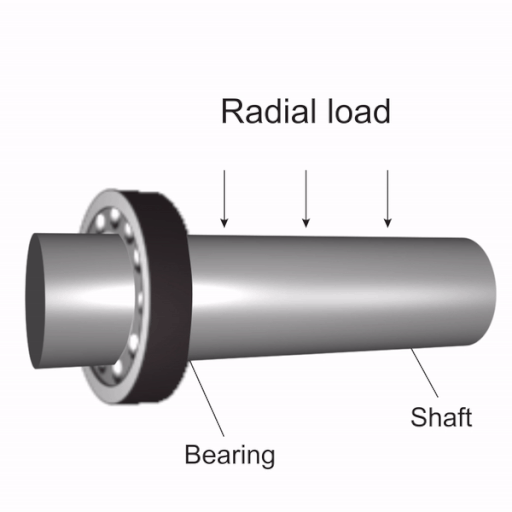
But ball bearings also have some downsides. They handle moving and sideways forces well but struggle with heavy or pushing forces. Small contact points can wear out quickly under heavy pressure. Without proper oiling or if dirt gets in, their lifespan can shorten.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Good for moving and sideways forces, not heavy pushing forces. |
| Durability | Steel ball bearings resist rust, making them last longer. |
| Resistance to Corrosion | Steel keeps them from rusting, improving their lifespan. |
| Operational Efficiency | Small bearings are quiet and reduce friction and vibration. |
| Lifespan | Can last up to a million spins with proper care. |
Tip: Pick ball bearings for fast, light jobs where accuracy is key.
Roller Bearings: Pros and Cons
Roller bearings are best for carrying heavy weights. Their bigger contact area spreads weight evenly, making them good for heavy and pushing forces. Special hollow rollers can carry more weight and last longer. Solid rollers are strong for heavy loads, while hollow ones are lighter and reduce stress.
However, roller bearings have weaknesses too. They might fail with very light loads. Solid rollers are heavier and less effective when loads change. Hollow rollers, though lighter, can break under certain conditions. Choosing the right roller bearing is important for your needs.
| Bearing Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Layered Cylindrical Hollow Rollers (LCHRs) | Great for heavy loads, lasts longer | May fail with very light loads |
| Conventional Solid Rollers | Strong for heavy weights | Heavy, less effective with changing loads |
| Hollow Cylindrical Rollers | Lightweight, reduces stress | Can break in specific situations |
Note: Use roller bearings for heavy weights and tough conditions.
What are the two common types of bearings?
Bearings help machines move by reducing friction and carrying loads. Two main types are ball bearings and roller bearings. Each type works best for specific tasks.
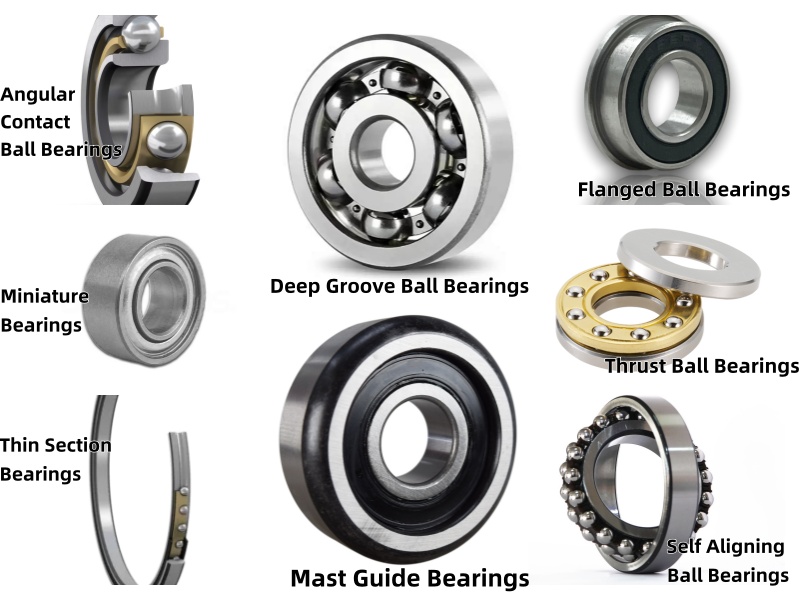
Ball Bearings Types
Ball bearings are very common in machines. They use round balls to lower friction and carry loads in different directions. These bearings are great for fast-moving and precise parts. Some types include:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: These handle loads from all directions and work well in motors and fans.
- Stainless Steel Deep Groove Ball Bearings: These resist rust, making them good for wet or chemical-filled places.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: These are strong for heavy loads and used in precise machines like CNC tools.
- Miniature Bearings: Miniature bearings are small-sized rolling-element bearings designed for precision applications in compact machinery.
- Thin Section Bearings:Thin section bearings are compact rolling-element bearings designed to save space while maintaining high performance in applications requiring minimal weight and size. These bearings are ideal for industries like robotics, aerospace, and medical equipment.
- Standard Flanged Ball Bearings:Standard flanged ball bearings feature an integrated flange that simplifies mounting and ensures precise alignment in various applications. These bearings are widely used in conveyor systems, robotics, and small-scale machinery.
- Thrust Ball Bearings:Thrust ball bearings are made especially to support axial loads in high-performance, lightweight applications. Systems needing effective load management in confined places depend on these bearings.
- Self Aligning Ball Bearings:Self-aligning ball bearings are perfect for applications where mounting mistakes or shaft deflection may occur since they are made to accept misalignment between the shaft and housing. These bearings are frequently found in conveyor systems, textile equipment, and paper mills.
- Mast Guide Bearings:Mast guide bearings are specialized bearings designed for vertical movement applications, such as forklift masts and lifting systems. These bearings provide stability, durability, and precise guidance in heavy-duty operations.
Choose ball bearings for fast-moving parts or light loads. They are also important in industries needing tough and reliable bearings.
Roller Bearings Types
Roller bearings use cylinders or cones instead of balls. This design helps them carry heavier loads and absorb shocks better. Common types include:
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: These are great for heavy loads and found in machines like conveyor belts.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: These handle loads from all directions and adjust to misaligned parts. They are used in mining and construction tools.
- Tapered Roller Bearings: These are strong for carrying loads and used in cars and gear systems.
- Needle Roller Bearings: These have thin rollers and fit into tight spaces like pumps and transmissions.
- Crossed Roller Bearings:Crossed roller bearings are designed to handle both radial, axial, and moment loads simultaneously. These bearings are ideal for applications requiring high rigidity and precision, such as robotics, medical equipment, and rotary tables. Their compact design and exceptional load-carrying capacity make them a popular choice for industries prioritizing accuracy and efficiency.
- Spherical Roller Thrust Bearings:Spherical roller thrust bearings are engineered to handle high axial loads and moderate radial loads while accommodating misalignment. These bearings are commonly used in heavy machinery, marine applications, and industrial equipment. Their robust design ensures reliable performance and long service life, even in the most demanding environments.
Pick roller bearings for heavy-duty jobs where strength and durability matter.
Tip: Think about load type, speed, and conditions when choosing bearings.
Application Selection Guide for Bearings
Factors to Consider When Choosing Bearings
Picking the right bearings needs careful thought about many things. Each point helps your machine work better and last longer. Here are the main things to think about:
- Size Restrictions: Bearings must fit the space in your design. Small spaces may need special types like needle bearings.
- Precision Requirements: Machines needing high accuracy, like in medicine or planes, need precise bearings.
- Bearing Load: Check if the load is sideways, pushing, or both. Roller bearings are great for heavy loads, while ball bearings handle lighter, multi-directional forces.
- Operating Speeds: Bearings have speed limits based on their type and oiling. Ball bearings are best for fast-moving parts, while roller bearings work well at medium speeds.
- Durability: Think about strength and heat resistance. Roller bearings are tougher for heavy jobs, while ball bearings last longer in lighter tasks.
- Maintenance: Bearings need regular checks and oiling. Easy-to-care-for bearings save time and reduce problems.
Tip: Match the bearing type to your machine’s load, speed, and conditions for the best results.
Common Applications of Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are used in many industries because they lower friction and handle forces from different directions. They are great for fast and precise machines. Here are some common uses:
Aerospace: Used in airplane engines
and spacecraft parts like gyroscopes.
- Automotive: Found in car engines, wheels, and pumps.
- Construction: Help machines run smoothly in building work.
- Energy: Wind turbines and other energy systems use them for efficiency.
- Medical Equipment: Found in machines needing precision, like imaging devices.
- Mining: Support heavy machines used in mining.
- Machine Tools: Help with accurate and smooth movements in machining.
Note: Use ball bearings for tasks needing speed, accuracy, and reliability.
Common Applications of Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are made for heavy loads and shocks, making them perfect for tough jobs. Their bigger contact area spreads weight better. Here are some common uses:
- Automotive: Found in gears, axles, and heavy-duty car parts.
- Aerospace: Support landing gear and other high-load parts.
- Construction: Used in cranes and other big machines.
- Mining: Found in conveyor belts and crushers for tough conditions.
- Marine: Used in propeller shafts and parts exposed to water.
- Oil and Gas: Found in pumps and drilling machines for reliability.
- Steel Industry: Handle heavy loads and heat in steel-making machines.
Tip: Pick roller bearings for jobs needing strength, durability, and shock handling.
Knowing how ball bearings and roller bearings differ helps you choose wisely. Ball bearings are great for fast-moving parts with light loads. They work smoothly because they reduce friction. Roller bearings are better for heavy loads and shocks. Their bigger contact area makes them stronger.
Think about three things when picking bearings: load type, speed, and surroundings. Use ball bearings for quick-moving machines. Choose roller bearings for tough jobs or harsh conditions.
Tip: Pick the right bearing for your machine to make it last longer and work better.
FAQ
What is the main difference between ball bearings and roller bearings?
Ball bearings use round balls to lower friction. They are best for fast-moving, light-load tasks. Roller bearings use cylinders or cones to spread weight better. This makes them great for heavy loads and absorbing shocks.
Which bearing type is better for high-speed applications?
Ball bearings are better for high speeds. Their design reduces friction and helps parts move faster. They spin smoothly, making them quicker than roller bearings.
Can roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads?
Yes, roller bearings can handle both radial and axial loads. Their bigger contact area makes them strong for heavy weights and steady for sideways forces.
Are ball bearings easier to maintain than roller bearings?
Ball bearings are easier to take care of because they are simpler. Roller bearings need more care since they carry heavier loads and have larger contact areas.
Which bearing type works best in extreme environments?
Roller bearings are better for tough conditions. They handle heavy weights, high heat, and shocks well. Ball bearings are good for precise tasks but not harsh environments.






