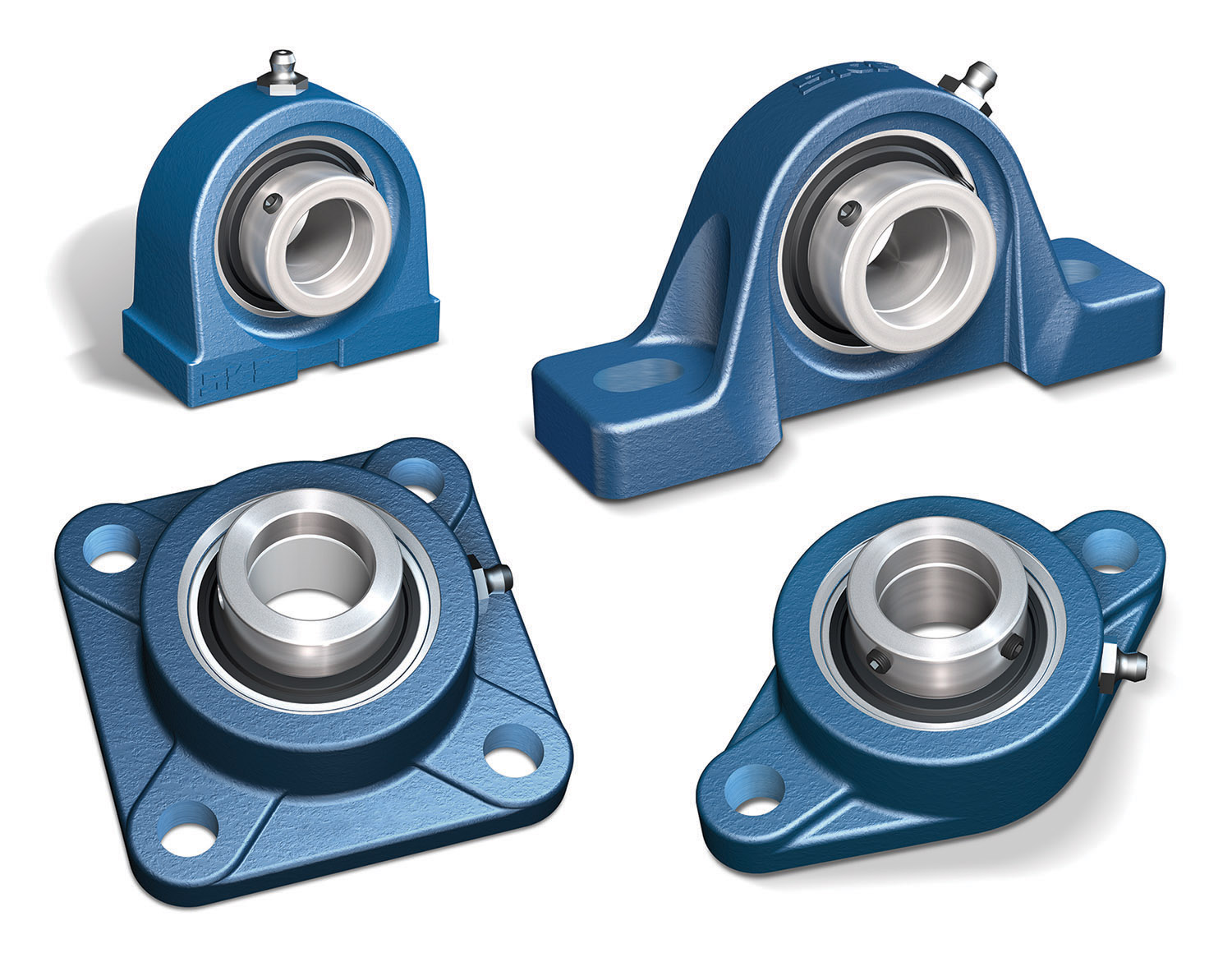
Mounted bearings appear in many forms, each serving a unique purpose. Pillow block bearings support rotating shafts in conveyor systems. Flange mounted bearings work best when the shaft sits perpendicular to the mounting surface. Take-up bearings help adjust tension in conveyor belts. Thrust and sliding bearings handle axial loads, while suspension and insert bearings offer flexibility for different machines. Corrosion-resistant units protect equipment in harsh settings.
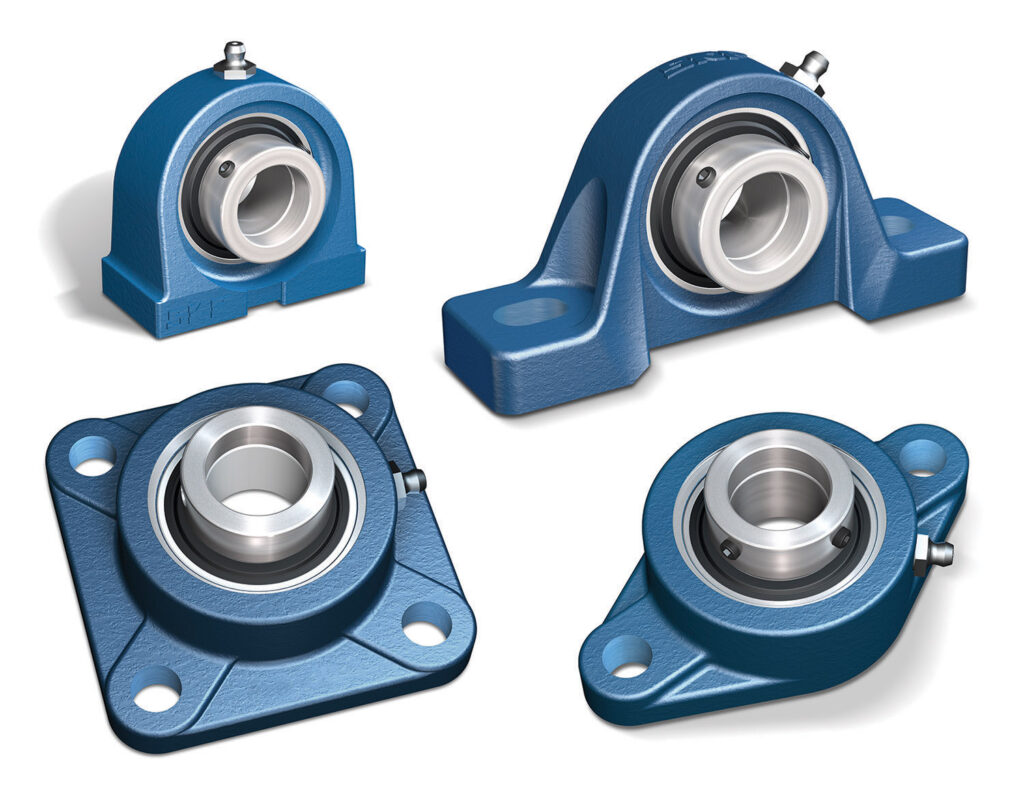

The market for mounted ball bearings reached $1.54 billion in 2024, serving industries like heavy machinery, automation, and robotics. Ball bearings with housing simplify installation and boost durability. The housing shields the bearing, making mounted units reliable and easy to maintain.
Metric | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Industry Market Size | $6 billion | Total ball bearing manufacturing |
| Number of Facilities | 160 | Manufacturing plants worldwide |
| Employees | 20,037 | Industrial workforce |
Key Takeaways
- Mounted ball bearings come pre-assembled in housings, making installation quick and reducing errors.
- Different types of mounted bearings, like pillow block and flange units, fit specific needs and environments.
- Good seals and durable materials protect bearings from dirt, moisture, and corrosion, extending their life.
- Regular maintenance and proper lubrication greatly increase bearing performance and reduce downtime.
- Mounted bearings support many industries, including automation, food processing, and heavy machinery.
Overview of Mounted Ball Bearings
Definition and Structure of Mounted Ball Bearings
Mounted ball bearings are special rolling element bearings that come pre-assembled in a housing. This design makes installation easy and protects the bearing from dust and moisture. A mounted bearing unit often includes a ball bearing with housing, which supports a rotating shaft and keeps it aligned. These units can handle both radial and axial loads, making them useful in many machines. The housing can be made from materials like cast iron, stainless steel, or thermoplastic, depending on the environment. Mounted ball bearing units are common in conveyor systems, agricultural equipment, and industrial machinery.
The global market for mounted bearings is growing fast. Experts expect a 5-7% growth rate through 2033, with a market size of about $10 billion by 2025. Growth comes from new infrastructure, automation, and better bearing designs.
| Bearing Unit Type | Structural Features | Materials Used | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pillow Blocks | Rigid housing, easy mounting | Cast iron, steel, stainless steel | Conveyors, transport equipment |
| Flanged Units | Flange housing, simple bolt-on installation | Same as pillow blocks | Roll support, machinery |
| Set Screw Bearings | Multiple mounting options, secure fit | Spherical or straight outer rings | Wide industrial use |
Main Components of Mounted Ball Bearings
A mounted bearing unit has several key parts:
- The rolling element bearings (balls) reduce friction and allow smooth rotation.
- The housing supports and protects the bearing.
- Seals and shields keep out dirt and hold in lubricant.
- The cage keeps the balls spaced and prevents them from rubbing together.
Using 400 series stainless steel in the race rings and balls gives corrosion resistance and hardness. Seals, like triple lip FKM, help keep out water and dust, which extends the life of the bearing. The load a bearing carries affects its lifespan. If the load doubles, the life drops by eight times, so choosing the right bearing is important.
How It Differs from Standard Ball Bearings
Standard ball bearings do not come with a housing. They need careful mounting and alignment, which takes more time and skill. Mounted ball bearings, such as a housed ball bearing or insert bearing with housing, arrive ready to install. The housing makes them easier to use and protects them from harsh conditions. Mounted units also offer more options, like self-aligning or rigid ball bearings, and can include hybrid ceramic ball bearings for special needs. Roller bearings, including radial ball bearings, are also available in mounted forms for heavy loads. This flexibility makes mounted bearings a top choice for many industries.
- Construction machinery leads demand for mounted bearing units.
- North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are the main regions using these products.
- Agricultural and transportation sectors also use many types of ball bearings.
Types of Mounted Bearings
Mounted bearings come in several types, each designed for specific tasks and environments. The right choice depends on the application, load, and installation needs. The following sections explain the main types of mounted bearings and their advantages.
Pillow Block Bearings
Pillow block bearings are one of the most common types of mounted bearings. These units feature a deep groove ball bearing or a roller bearing inside a solid housing. The housing, often made from cast iron or stainless steel, supports the shaft and keeps it aligned. Pillow block bearings handle both radial and axial loads. They work well in conveyor systems, industrial machinery, and farming equipment.
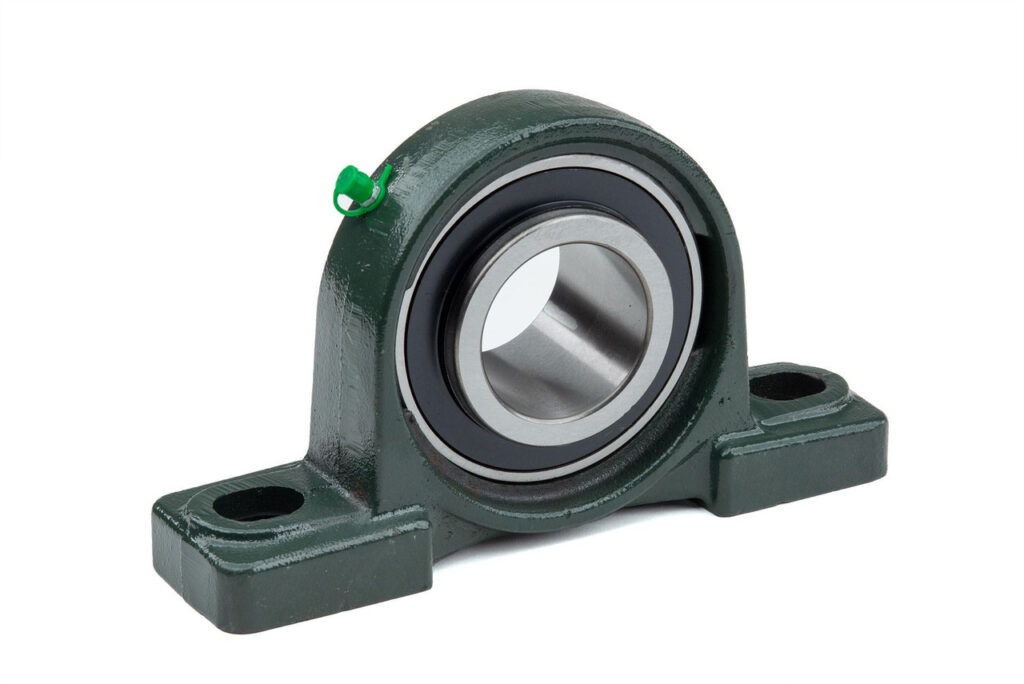

Pillow block bearings maintain shaft alignment, reduce vibration, and resist contamination. Their design allows for easy installation and replacement, which helps reduce downtime in heavy-duty settings.
| Material | Key Performance Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Strong, durable, withstands heavy loads | Industrial machinery, conveyors, farming |
| Bronze | Handles high loads at low speeds, excellent wear resistance | Cranes, lifts, harsh conditions |
Self-lubricating plastic pillow block bearings also exist. These reduce maintenance and contamination risks. The use of permanent bearing protection, such as advanced seals, increases the operational life of the bearing unit.
Flange Mounted Bearings
Flange mounted bearings are another popular type of mounted bearing unit. These bearings have a housing with a flange, which allows for easy bolt-on installation. The flange can have two, three, or four holes, depending on the design. Flange mounted bearings support shafts that run perpendicular to the mounting surface.
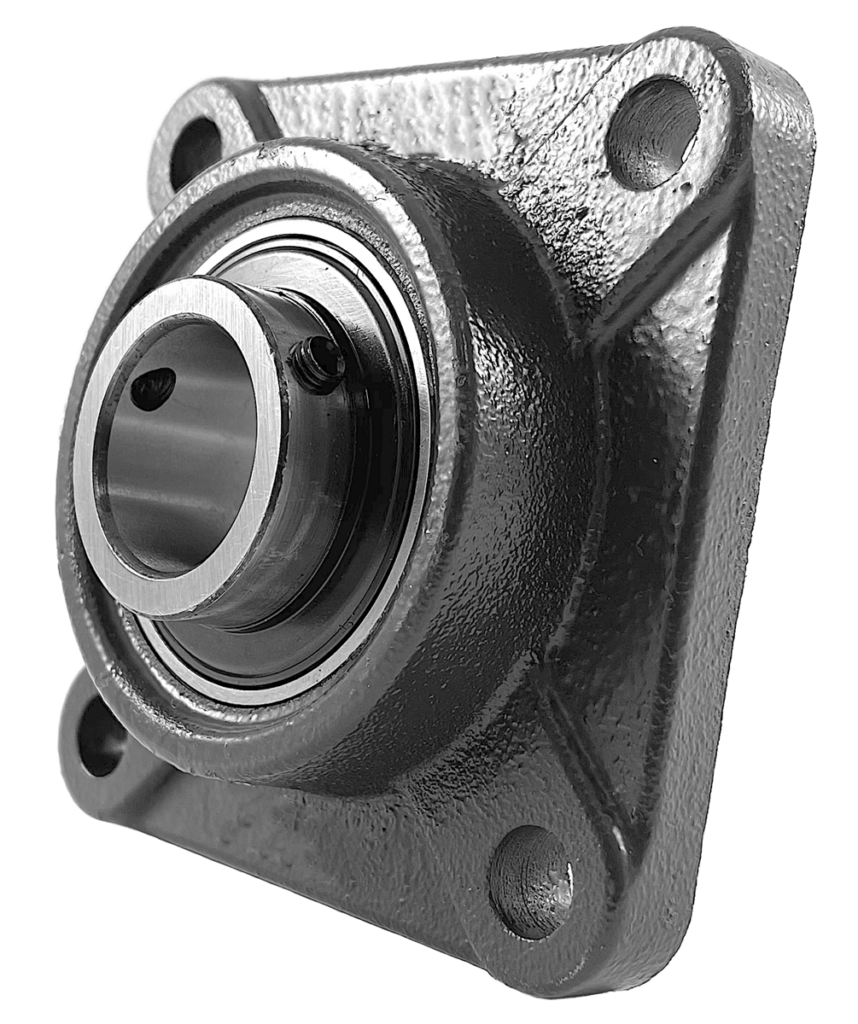

These units often use deep groove ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings. They provide stability in space-constrained areas, such as fans, blowers, and material handling equipment. Flange mounted bearings are common in commercial and industrial settings.
| Statistic Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Valuation (2024) | USD 4.23 Billion |
| Projected Market Size (2033) | USD 6.98 Billion |
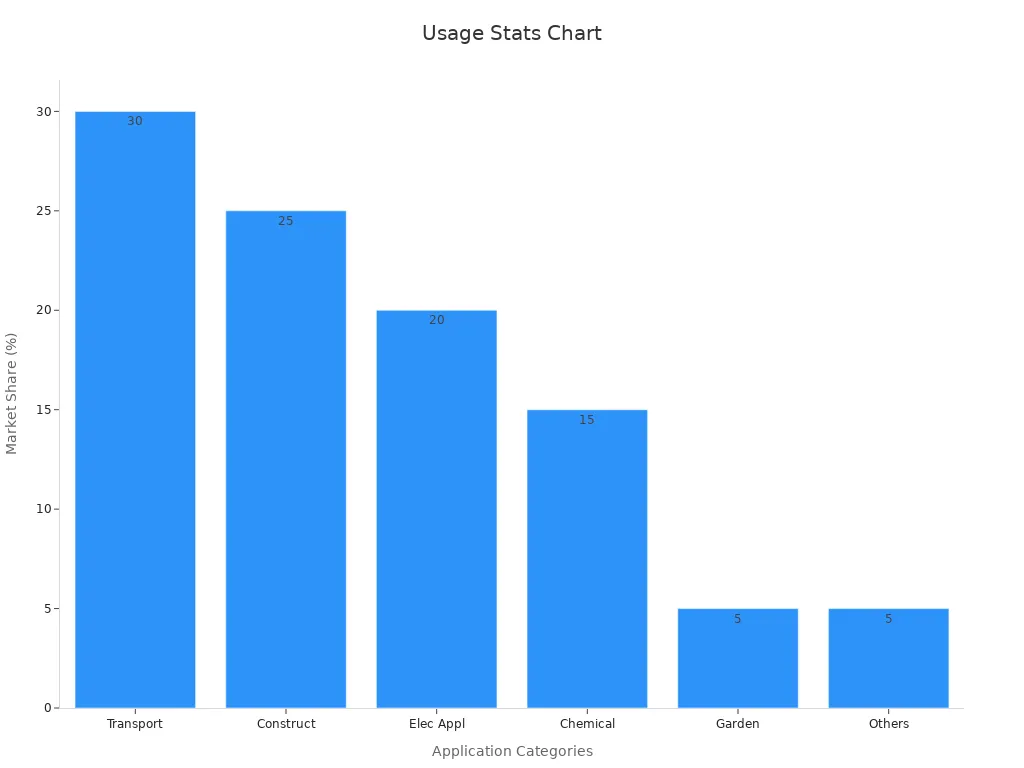
| Market Share by Bearing Type (2023) | Ball Bearings: 40%, Needle Roller Bearings: 15%, Plain Bearings: 25%, Roller Bearings: 20% |
Flange mounted bearings offer high load capacity and easy alignment. Their design helps prevent shaft movement and misalignment, which is important for reliable operation.
Take-Up Bearings
Take-up bearings are a special type of mounted bearing used to adjust shaft tension. These units slide along a guide or frame, allowing for precise tension control in conveyor belts and similar systems. Take-up bearings often use deep groove ball bearings or roller bearings for smooth operation.

Take-up bearing units include features like relubrication points and reliable seals. These help reduce maintenance and extend the life of the bearing. Proper alignment is crucial for take-up bearings to prevent premature wear.
- Mounted bearings, including take-up types, withstand heavy loads and demanding conditions.
- Sealed designs and quality materials, such as chrome steel or stainless steel, improve durability and corrosion resistance.
- Scheduled lubrication and clean operating environments help maximize bearing life.
Industry standards define load ratings and fatigue life for take-up bearings. Adjustments in material and design can increase operating life by more than double.
Thrust and Sliding Bearings
Thrust bearings and sliding bearings are types of mounted bearings designed to handle axial loads. Thrust bearings support forces parallel to the shaft, while sliding bearings allow for smooth movement between surfaces.
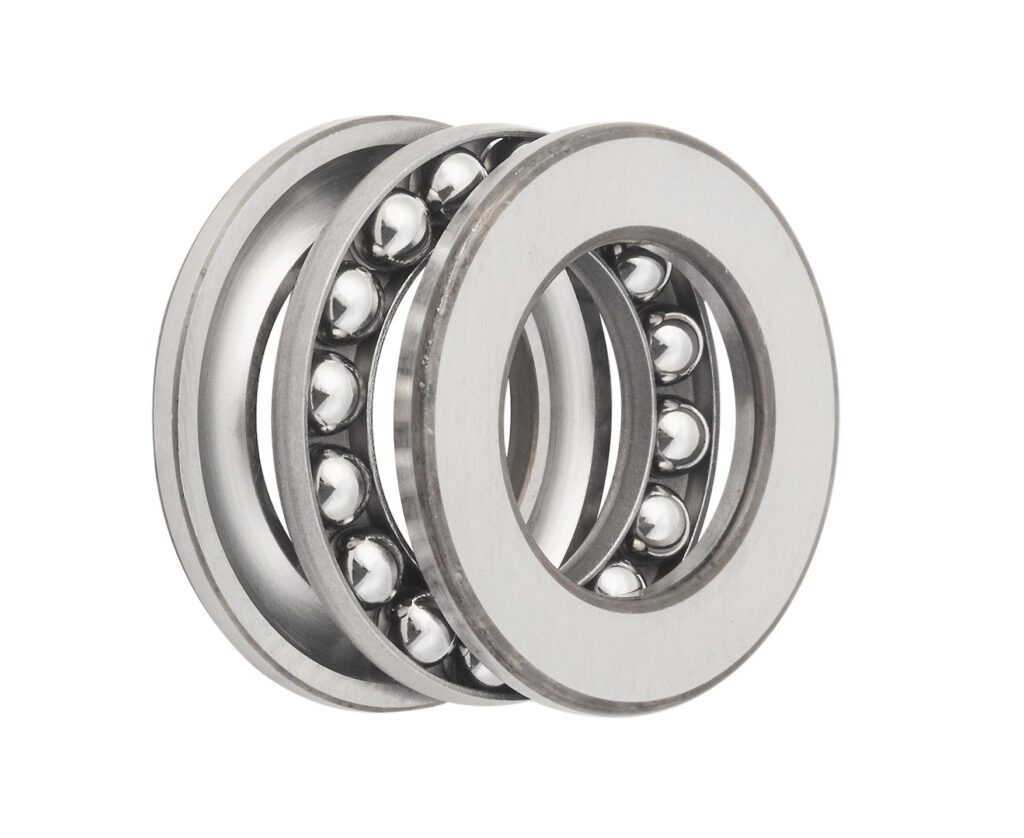

Thrust bearings often use angular contact ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings. These types provide high load-carrying capacity and stability. Enhanced thrust bearings with cooling features can operate at higher pressures and lower temperatures.
| Performance Aspect | Conventional Thrust Bearing | Enhanced Thrust Bearing (with cooling, recesses, texturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Reduction | N/A | 18°C lower temperature |
| Load-Carrying Capacity (Pressure) | 5.8 MPa | 6.8 MPa |
| Operating Conditions | Axial load 1–10 kN, 600–3000 rpm | Same |
| Lubrication | SAE 30 oil, 0.25–5 L/min | Same |
| Thermal Deformation | Higher | Significantly reduced |
Sliding bearings rely on material choice for performance. PTFE and tin compositions offer low friction, while aluminum bronze provides good wear resistance. These types are used in applications where smooth, low-friction movement is needed.
Suspension and Insert Bearings
Suspension bearings and insert bearings are types of mounted bearings that provide flexibility and stability. Suspension bearings support shafts in hanging or suspended positions. Insert bearings fit into standard housings and can be replaced easily.

These bearing units often use deep groove ball bearings, spherical ball bearings, or cylindrical roller bearings. They tolerate minor misalignments and reduce stress on the shaft. Advanced sealing mechanisms protect against dust and moisture, while lubrication systems extend bearing life.
| Technical Parameter | Description | Example Values / Details |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Sustains significant loads, improves conveyor system function | Dynamic Load Rating, Static Load Rating |
| Misalignment Tolerance | Accepts minor shaft misalignments without stress or wear | Use of rotation alignment tools, H7/g6 fits |
| Sealing Mechanisms | Prevents ingress of contaminants | Advanced seals protecting against dust, moisture |
| Lubrication System | Reduces friction and heat, extends bearing life | Grease fittings, self-lubrication, oil-filled designs |
| Maintenance Features | Simplified access, easy replacement, reduced downtime | Two-piece designs, modular structure |
Pipe insert bearings often include grease fittings and self-lubrication. Their modular construction allows for quick replacement, reducing downtime in conveyor systems and other machinery.
Corrosion-Resistant Units
Corrosion-resistant units are types of mounted bearings designed for harsh environments. These bearing units use materials like stainless steel or special coatings to resist rust and chemical damage. They are common in food processing, marine, and chemical industries.

| Evidence Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Rating Life Definition | Number of revolutions reached or exceeded by 90% of identical bearings before fatigue. |
| Impact of Harsh Environments | Extreme conditions can reduce bearing rating life by up to 90%. |
| Material Improvement: Vacuum Degassed Steel | Bearings made from this steel show a 2.2 times increase in operating life and 1.3 times load capacity. |
| Corrosion Resistance Enhancement | Nitrogen-enhanced martensitic stainless steel offers 5 times the corrosion resistance of standard stainless steel. |
Design adjustments, such as improved seals and lubricants, help maintain the life expectancy of corrosion-resistant mounted bearings. These units ensure reliable operation and long service life, even in extreme conditions.
Mounted bearings, including corrosion-resistant types, play a vital role in industries where equipment faces moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures.
Prevalence and Application Table
| Category | Segments / Details | Prevalence / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Ball bearings, Roller bearings, Plain bearings | Ball bearings dominate due to versatility; Roller bearings preferred for heavy-duty, high load applications |
| Housing Type | Flanged, Pillow block, Take-up units | Pillow block most popular for ease of installation; Flanged favored in space-constrained applications |
| Equipment Type | Conveyors, Fans & blowers, Crushers | Conveyors hold significant share due to manufacturing and material handling demand |
| Material | Cast iron, Stainless steel, Others | Cast iron most common for cost-effectiveness; Stainless steel used in corrosion-sensitive industries |
| End-Use Industry | Automotive, Construction, Mining, Food & beverage, Others | Automotive leads due to use in engines, transmissions; Construction and mining significant for heavy machinery |
| Region | Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, Latin America, Middle East & Africa | Asia-Pacific dominates due to rapid industrialization; North America ~30% market share; Europe ~25% |
- Automotive and construction industries use many types of mounted bearings, including deep groove ball bearing units and spherical ball bearings.
- Industrial automation and rapid industrialization increase the adoption of mounted bearing units in conveyors, robotics, and automated systems.
The wide range of types of mounted bearings, such as pillow block, flange, take-up, thrust, sliding, suspension, insert, and corrosion-resistant units, ensures that every application finds a suitable solution. Deep groove ball bearings, spherical ball bearings, and cylindrical roller bearings are among the most widely used rolling elements in these bearing units.
Design and Function of Mounted Ball Bearings
Bearing Housing Materials
The housing in a mounted bearing unit plays a key role in protecting the bearing and supporting loads. Different materials give the housing unique properties. Cast iron, stainless steel, and thermoplastic are the most common choices. Each material offers special advantages for mounted applications.
| Material | Key Performance Characteristics | Typical Applications and Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Excellent strength, durability, cost-effective, high load-bearing capacity, wear resistance | Heavy-duty industrial machinery, construction equipment; withstands harsh conditions, long service life |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, hygiene, improved mechanical and corrosion resistance due to alloy advancements | Food, pharmaceutical, chemical industries; meets regulatory requirements, operates in corrosive environments |
| Thermoplastic | Corrosion resistant, lightweight, maintenance-free, excellent mechanical strength, stiffness, dimensional stability | Automotive, aerospace, clean operating environments; weight reduction, eco-friendly, low maintenance |
Thermoplastic housings resist corrosion and do not rust. They are interchangeable with cast iron housings and need little maintenance. These characteristics of housings with mounted bearings make them ideal for clean environments like food processing and automation.
Structure and Alignment
The structure of a mounted bearing unit ensures that the bearing stays in place and supports loads. Precision in structure and alignment is very important. Even a small misalignment between the shaft and the bearing can cause changes in oil film pressure and friction. This can lower the load-carrying ability and increase the risk of vibration.
- Misalignment can lead to uneven lubrication and higher frictional forces.
- Numerical studies show that flexible structures and rubber materials in the housing improve lubrication and prevent metal-to-metal contact.
- Experimental results confirm that poor alignment reduces bearing performance and stability.
A well-designed mounted ball bearing keeps the shaft aligned and helps decrease friction. This allows for smooth movement and longer service life.
Seals and Shields
Seals and shields protect the bearing inside the housing from dust, dirt, and moisture. They keep the lubricant inside and block out harmful particles. Good seals and shields extend the life of mounted bearings by reducing wear and preventing contamination.
Mounted bearing units often use triple lip seals or advanced shields. These features help the bearing unit work well in harsh or dirty environments. Seals and shields are key to the design and function of ball bearings, making sure the bearing stays clean and runs smoothly.
Tip: Regular inspection of seals and shields helps maintain the performance of any mounted bearing unit.
Benefits of Mounted Ball Bearings
Easy Installation
Mounted bearings offer simple and fast installation. Each bearing unit arrives pre-assembled, so workers do not need to fit the ball bearing with housing separately. This design reduces the risk of mistakes during assembly. Up to 20% of bearing failures come from poor installation, which can cause damage to the raceways or seals. Using proper tools and easy-to-mount bearing units helps prevent these problems. As a result, machines experience less downtime and run more smoothly. Maintenance teams can replace a housed ball bearing quickly, which keeps production lines moving.
Tip: Proper installation with the right tools protects the bearing and extends its life.
Protection and Durability
Mounted ball bearings provide strong protection against dirt, dust, and moisture. The housing shields the bearing insert, while seals and end caps keep out harmful particles. These features help the bearing last longer, even in tough environments. The table below shows how different design elements improve durability:
| Feature | Measured Performance / Benefit | Impact on Protection and Durability |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-rotation device | 33% increase in bearing life | Prevents outer race spinning, enhancing bearing longevity |
| Permanent lubrication | Up to 4x oil capacity vs. greased bearings | Supports seals, protects rolling elements, no regreasing |
| Flinger seal | Spins with inner race, flings contaminants away | Adds protection in dirty environments |
| Triple lip seal | Increased contact, blocks heavy contamination | Protects rolling elements |
| Wide inner rings | More shaft contact, less tilt | More stable, longer life |
These features show why the benefits of ball bearings with advanced protection are important for industrial use.
Versatility in Applications
Mounted bearings work in many industries and settings. They come in different shaft sizes, mounting styles, and sealing options. This flexibility allows them to fit a wide range of machines and environments. Some key benefits of mounted bearings include their ability to handle harsh conditions, such as high heat or washdown areas. Workers use them in food processing, material handling, construction, and even aerospace.
- Ball bearings are common in automotive, construction, and aerospace.
- Types like deep groove and self-aligning ball bearings meet different load needs.
- Bearing units can be customized for special applications.
- Mounted bearing units suit tough jobs, including food and beverage processing.
The benefits of ball bearings extend to many fields, making them a smart choice for engineers and maintenance teams.
Applications of Mounted Bearings
Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery relies on mounted ball bearings for smooth and reliable operation. Over 25% of the mounted bearing market comes from this sector. Factories use bearing units in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and manufacturing lines. Medium-sized mounted bearings, ranging from 10mm to 50mm, are the most common. These bearing units support rotating shafts, reduce friction, and help machines run longer with less maintenance. The Asia-Pacific region leads in market revenue, driven by new infrastructure and more industrial machinery production.
Mounted ball bearings play a key role in automation and heavy machinery, supporting both radial and axial loads.
Food-Grade and Harsh Environments
Food processing and chemical plants need bearings that resist corrosion and contamination. Engineers choose ball bearings with housing made from stainless steel or coated with special materials. These bearing units use advanced seals, such as triple lip FKM seals, to keep out water and chemicals. Tests show that these bearings can handle acidic and basic solutions, high-pressure washdowns, and even slurry mixtures. IP69K certification proves their ability to resist dust and water. Housed ball bearings with smooth finishes and food-grade grease help keep food safe and equipment clean.
- Corrosion-resistant materials like 400 series stainless steel extend bearing life.
- Special coatings and seals prevent contaminant ingress.
- Easy-to-clean designs reduce contamination risk.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics depend on mounted bearing units for precision and durability. The market for these applications is growing fast, with a projected CAGR of over 8%. Robots need high-quality mounted ball bearings to handle high-speed applications and heavy workloads. In 2022, factories installed 500,000 new robots, each requiring reliable bearing units. Smart factories and Industry 4.0 trends increase the need for accurate, long-lasting bearings. Mounted bearings help reduce energy use and improve machine efficiency.
- Automation equipment investments rose by 15% in 2023.
- Mounted bearings support high-speed, continuous operation in robotics.
Material Handling and Conveyors
Material handling systems, such as conveyors and forklifts, use many types of mounted bearings. Deep groove ball bearings, pillow block bearings, and self-aligning ball bearings are common choices. These bearing units provide low friction, resist contamination, and handle both radial and axial loads. Tapered roller bearings and double row bearings support heavy loads in conveyor systems. Leaf chain and mast guide bearings help forklifts lift and move materials safely.
The applications of mounted bearings span many industries, from automotive and aerospace to energy and consumer electronics. Their versatility and reliability make them essential for modern machinery.
Selecting Mounted Bearings
Load and Speed
Choosing the right mounted ball bearing starts with understanding load and speed requirements. Engineers use the ISO 281 standard to calculate the dynamic load rating. This rating considers rolling contact load, load distribution, and bearing quality. These factors help determine how much force a bearing unit can handle without failing. Vibration analysis, including kurtosis and RMS values, helps identify the best speed and load combinations. By studying these signals, teams can select a ball bearing with housing that minimizes defects and runs smoothly at the desired speed. Multi-Attribute Decision Making methods also help rank options, ensuring the chosen bearing unit performs well under real-world conditions.
Proper alignment and correct installation are essential. Misalignment can reduce bearing life and increase vibration.
Environment and Material
The operating environment plays a big role in selecting a housed ball bearing. Engineers test bearings for endurance, friction, and temperature to see how they perform in tough conditions. These tests include running bearings until failure, measuring heat, and checking for wear. Continuous quality control checks for defects that could cause early failure. Environmental factors like dust, moisture, and poor lubrication can shorten bearing life. The ISO 281 model uses these factors to predict how long a mounted bearing unit will last. Material choice matters too. Stainless steel resists corrosion in wet or chemical settings, while thermoplastic housings work well in clean environments.
- Endurance testing validates bearing life.
- Frictional torque and temperature tests show heat and wear.
- Supplier approval testing ensures batch quality.
- Comparative assessments compare different bearing types.
- Quality control detects defects early.
Maintenance Needs
Regular maintenance keeps insert bearings with housing running longer. Grease quality, amount, and relubrication schedules all affect service life. Studies show that better grease and scheduled relubrication can double the life of a mounted ball bearing. Specialized greases protect against corrosion and wear, especially in harsh environments. Maintenance teams should tailor relubrication frequency to the machine’s workload and environment. Both manual and automatic systems can deliver grease, but the schedule must fit the application.
- Scheduled lubrication prevents early failure.
- Proper maintenance reduces downtime and repair costs.
- Regular checks help spot problems before they grow.
Tip: Always follow a maintenance plan and use the right lubricant to maximize the life of any mounted bearing unit.
Mounted ball bearings, including ball bearings with housing and insert bearings with housing, offer strong support, easy installation, and long service life. Choosing the right bearing unit for each application ensures smooth operation and reduces downtime. Regular maintenance keeps machines running longer.
| Bearing Type | Key Benefits and Performance Insights |
|---|---|
| Ball Bearings (General) | Reduce friction, support loads, last up to 1 million rotations |
| Hybrid Ceramic Bearings | 20%-40% higher speeds, improved corrosion resistance |
| Self-Aligning Ball Bearings | Compensate for misalignment, reduce vibration, require little upkeep |
For expert advice and quality mounted bearing units, consult TFL Bearings.
FAQ
What is a mounted ball bearing?
A mounted ball bearing is a ball bearing with housing. The housing supports and protects the bearing. This design makes installation easy and helps the bearing last longer in machines.
How does a housed ball bearing differ from a standard bearing?
A housed ball bearing comes pre-assembled in a housing. This unit is ready to install. Standard bearings do not have a housing and need careful mounting. The housing gives extra protection and support.
Where can someone use a mounted bearing unit?
People use mounted bearing units in conveyors, industrial machines, food processing, and robotics. These units work well in places that need strong support and easy maintenance.
Why choose a corrosion-resistant bearing unit?
Corrosion-resistant bearing units use stainless steel or special coatings. These materials protect the bearing from rust and chemicals. They work best in food plants, marine equipment, and chemical factories.
How often should someone maintain an insert bearing with housing?
Maintenance depends on the environment and workload. Most experts suggest checking and lubricating the insert bearing with housing every few months. Regular care helps the bearing unit last longer.





