Slewing bearings help machines carry heavy things. They let machines turn and move back and forth. These bearings can handle different types of forces. They are very important in building, mining, and clean energy work. It is important to choose the right bearing for each job. This helps the bearing last longer and not break.

| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2024) | USD 4.5 billion |
| Market Size (2034) | USD 8.2 billion |
| CAGR | 6.2% |
The market is getting bigger. This means it is important to pick the right slewing bearing for each job.
Key Takeaways
- Slewing bearings help machines turn and lift heavy things. They are used in many jobs like building and clean energy. Picking the right bearing type and gear helps machines work better. It also makes them last longer and easier to fix. There are different bearing types for different jobs. Four-point contact ball, double-row ball, crossed roller, and three-row roller bearings fit different loads and needs. The materials and seals change how strong the bearing is. They also help stop rust and make the bearing last longer. It is important to pick them for the place where the machine works. You should take care of bearings often. Oil them and check the seals every three months. This keeps them working well and helps them last longer.
Structure
Components
Slewing bearings have many important parts. These parts work together to help carry heavy things and turn smoothly. The main parts are bearing rings, rolling elements, integral gearing, mounting structures, seals, bolts, and shrouding. Bearing rings hold the rolling elements. The rolling elements can be balls or rollers. Integral gearing spreads out forces and helps the bearing hold more weight. Mounting structures like steel plates, gussets, and channels make the bearing strong and flat. These parts stop too much stress in one spot and help spread the load. Gussets near the holes make the bearing even stronger. Making the mounting surface just right keeps the rolling elements safe. Seals stop dirt and dust from getting inside. Bolts keep all the parts together. Tight bolts help the bearing stay lined up and work better.
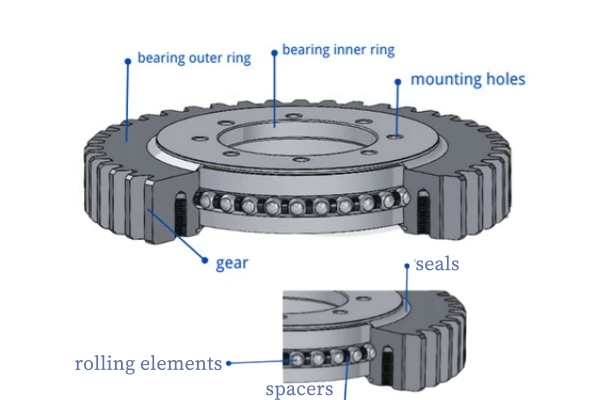
A good slewing bearing design makes machines more stable. It also lowers friction and helps them work well in tough jobs like building, clean energy, and flying.
Materials
The materials used for slewing bearings change how strong and long-lasting they are. They also affect how well the bearing fights rust. Makers pick materials based on what the bearing needs to do. Aluminum is light and strong, so it is good when weight matters. Rolling elements can be made from ceramics, chromium steel, or stainless steel. These materials help the bearing last longer and work better. The table below lists common materials and what is good about them:
| Bearing Part | Common Materials | Advantages / Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Rings | 50Mn steel, 42CrMo, 40Cr | These steels are strong and hard. 42CrMo is good for heat treating. 50Mn is used a lot. |
| Rolling Elements | GCr15, GCr15SiMn bearing steels | These steels have lots of carbon and chromium. They are hard and last a long time. |
| Cages | Steel, Aluminum alloy, Brass, Bronze, Polymers | Steel cages are tough. Aluminum alloy is light and does not rust. Polymers help stop wear and heat. |
| Sealing Rings | Nitrile rubber, Silicone rubber, Fluorine rubber, EPDM, PTFE | These rubbers fight oil, acid, and base. The best one depends on where the bearing is used. |
Gear Options
Slewing bearings can have different gear types for different jobs. Internal gears have teeth inside the ring. This makes the bearing smaller and helps it turn with the right force. External gears have teeth outside the ring. This makes fixing the bearing easier and lets it work with more drive systems. Some bearings do not have any gear teeth. These use other ways to turn, like drive-plate coupling. Other choices are external belt drives, which use belts to turn the bearing. Worm gear drives use a worm gear and shaft to help the bearing turn to the right angle. Drive-plate coupling lets a motor connect right to the bearing for more power.

Picking the right gear type helps the bearing send power better. It also makes it easier to fix and helps it last longer, especially in hard jobs.
| Gear/Drive Option | Description | Operational Impact/Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Gear | Teeth are on the inside ring of the bearing. | Works with outside gears. Small size. Turns with the right force. |
| External Gear | Teeth are on the outside ring of the bearing. | Works with belts or worm gears. Easier to fix. Can be used in many ways. |
| No Gear | The bearing has no gear teeth. | Uses other ways to turn. Simple design. May not work with all drives. |
| External Belt Drive | Belts turn the bearing from the outside. | Flexible way to turn. Cost, noise, and space can change. |
| Worm Gear Drive | Uses a worm gear and shaft with the bearing. | Can be used flat or upright. Helps measure the turning angle. |
| Drive-Plate Coupling | Motor connects right to the bearing ring. | Easy to connect. Can handle more force for bigger bearings. |
Classification
By Structure
Slewing bearings have different structures. The structure changes how much weight they hold. It also affects how they fit machines. Engineers check the type and size of rolling elements. They also look at the raceway shape. Some common structures are single-row four-point contact ball, double-row ball, and crossed roller types.
- Single-row four-point contact ball bearings are simple. They can hold big axial forces and overturning moments.
- Double-row ball bearings have two rows of balls. This makes them stronger for heavy jobs.
- Crossed roller bearings are stiff and precise. They work well in machines that need exact movement.
- Changing the number of rolling elements or raceway curve helps. It can make the bearing hold more weight and shake less.
- Picking the right structure helps the bearing last longer. It also helps the bearing do its job better.
By Rolling Element
The rolling element type changes how the bearing works. There are two main types: ball bearings and roller bearings. Each type is good for different things.
| Feature/Aspect | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Element Shape | Spherical balls | Cylindrical, conical, or barrel-shaped rollers |
| Contact Type | Point contact | Line or surface contact |
| Load Capacity | Lower, best for lighter loads | Higher, handles heavy and shock loads |
| Speed Performance | High-speed, low friction | Medium/low speed, higher friction |
| Vibration & Noise | Low vibration and noise | May produce more vibration and noise |
| Maintenance | Easier installation and maintenance | Needs careful lubrication and higher maintenance |
| Applications | Precision tools, motors | Construction, cranes, heavy machinery |
Ball bearings are best for fast and precise machines. Roller bearings are good for heavy machines that carry more weight.
By Gear Position
Slewing bearings have different gear positions. The gear can be inside, outside, or not there.
- Internal gear means teeth are inside the ring. This saves space and keeps dirt out.
- External gear means teeth are outside the ring. This makes fixing easier and gives more drive choices.
- No gear means the bearing turns in other ways. It can use belt drives or direct coupling.
Picking the right gear position helps the bearing fit the machine. It also helps the bearing work well.
Types of Slewing Bearings
Four-Point Contact Ball
Four-point contact ball slewing bearings have a special raceway shape. The raceways look like a gothic arch. This makes four contact spots for each ball. These bearings can hold up different forces at once. They handle axial, radial, and tilting moment loads together. The split raceway helps with putting the bearing together and fixing it. Strong seals keep dirt out and oil in. Engineers can pick internal or external gear types. This lets power move right through the bearing. You can adjust preload to make the bearing work better and last longer. There are many ways to mount these bearings, like using bolted holes. This helps them fit big machines.
These bearings use a double half inner ring. This design lets the balls touch in more places. It lowers stress and helps the bearing last longer. The split inner ring lets you add more balls. This makes the bearing stronger.
| Load Type | Typical Load Capacity Range | Example Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Axial Load | 30–50 kN (small) / up to >5000 kN (large) | Industrial robots, tower cranes |
| Radial Load | 10–20 kN (small) / up to 50 kN (large) | Rotating worktables, general equipment |
| Tilting Moment Load | Up to >50000 kN·m | Port cranes, heavy lifting |
These bearings are used in many machines. You can find them in cranes, excavators, wind turbines, and port cranes. They are good for tight spaces and can hold many kinds of loads.
Double-Row Ball
Double-row ball slewing bearings have two rows of balls. This makes them stronger and more stable. The two rows help spread out the weight. This lowers shaking and keeps the bearing in the right spot. The bearing is wider, so it bends less. Even though they are strong, they do not take up much space. The two rows also help stop friction and heat. This makes the oil last longer and helps the bearing work well.
- These bearings can hold axial, radial, and overturning moment loads. This means they work for tough jobs.
- The design makes the bearing stiff and stops it from bending.
- Gears, seals, and oil holes are built in for easy use.
- You need to check and oil these bearings often. You may also need to change the seals.
| Industry | Reasons for Use |
|---|---|
| Construction Machinery & Lifting Equipment | High load-bearing capacity and rotational precision enable efficient lifting and loading tasks. |
| Excavation and Earthmoving Machinery | Stability and high rotational precision ensure accurate and safe excavation operations. |
| Wind Power Industry | Critical for blade adjustment and positioning due to load capacity and precise rotation. |
| Aerospace and Aviation | Used for controlling aircraft surfaces, ensuring smooth maneuvering and high reliability. |
You can find these bearings in wind turbines, cranes, robots, telescopes, and radar antennas. They are small, easy to care for, and work well in factories.
Crossed Roller
Crossed roller slewing bearings use rollers set at right angles. The rollers cross each other in the bearing. This helps the bearing hold big forces and turn with care. The bearing has two rings and one row of crossed rollers. There is a cage or spacer block and seals too. Spacers keep the rollers apart and stop them from rubbing. This lowers friction and keeps the rollers in place.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Roller Arrangement | Short cylindrical rollers crossed at 90°, each bearing axial force in opposite directions |
| Load Capacity | Handles loads in all directions: axial, radial, and overturning moments |
| Rigidity | 3 to 4 times higher than double-row angular contact ball bearings |
| Precision | High rotation accuracy, even under preload |
| Functional Advantages | Stable torque, easy installation, withstands large overturning moments, used in robots and heavy machinery |
These bearings are very stiff and turn with high accuracy. They are used in robots, CNC machines, port cranes, and automatic machines. The design helps the bearing last longer and work well with heavy loads. Good materials and seals help them work in tough places.
Crossed roller slewing bearings are great for jobs that need strong support and careful movement.
Tapered Roller
Tapered roller slewing bearings have an inner ring, outer ring, tapered rollers, and a cage. The rollers and raceways are shaped like cones. All the cone points meet at one spot on the center line. This shape lets the bearing hold both radial and axial loads. The cage keeps the rollers apart and stops them from moving at high speeds. The tapered shape helps the bearing hold more weight and lowers stress.
These bearings work well for heavy jobs. They roll smoothly, lower friction, and can hold many kinds of loads. Some have more than one row for extra strength. You need to keep them oiled and sealed for a long life.
- Cranes
- Excavators
- Stackers and reclaimers
- Heavy mill equipment
These bearings are good for machines that need to be stiff and hold heavy loads.
Three-Row Roller
Three-row roller slewing bearings have three rings for the raceways. There are three rows of rollers between the rings. The top and bottom rows hold axial loads. The middle row holds radial loads. This design spreads out the weight and lets the bearing hold loads from many sides. Spacers keep the rollers apart. Cages hold the rollers in place.
- Inner ring: Has a raceway and holes for mounting
- Outer ring: Has a round raceway, sometimes with gear teeth
- Three rows of rollers: Hold both radial and axial loads
- Spacers and cages: Help spread out the weight and keep things steady
- Seals and oil: Keep parts safe and lower wear
- Mounting holes: Make it easy to put in the machine
Three-row roller slewing bearings are the strongest type. They are used in big machines for building, mining, wind turbines, ships, radar, steel mills, kilns, and tunnel machines.
Three-row roller slewing bearings are the best for tough jobs. They last a long time and work with very heavy loads.
Comparison
Features
There are different types of slewing bearings. They are not all the same. Each type has its own structure and use. Some are better for heavy loads. Others are good for high accuracy. The table below shows how they are different:
| Slewing Bearing Type | Structure & Rolling Elements | Load Capacity & Types Supported | Key Feature Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Four-point contact ball | Compact, balls contact at four points | Axial, radial, tilting moment loads | Versatile, compact, variable contact angle |
| Crossed roller | Rollers in 90° cross pattern | High axial, radial, and tilting moment loads | High accuracy, high capacity, stiff |
| Double-row ball | Two rows of balls, open assembly | Large axial and tilting moment loads | Convenient assembly, strong, stable |
| Three-row roller | Three raceways, separate rollers | Largest capacity, all load types | Firm structure, heavy-duty, long life |
Single-row ball bearings are easy to take care of. They can hold a medium amount of weight. Crossed roller bearings can hold more weight. They are also more exact but need more care. Three-row roller bearings are the strongest. They can hold the most weight and are very tough.
Applications
Each slewing bearing type is used for certain machines. They are picked for different jobs:
- Four-point contact ball: Used in cranes, excavators, and building machines.
- Double-row ball: Found in tower cranes, wind turbines, and big machines.
- Three-row roller: Used in port cranes, tunnel machines, and large wind turbines.
- Crossed roller: Used in robots, precise platforms, and military tools.
Picking the right bearing helps machines work safely and well.
Selection
Engineers look at many things when picking slewing bearings:
- Load capacity: Check how much weight the bearing can hold.
- Rotation accuracy: Needed for robots and tools that must be exact.
- Working environment: Think about heat, wetness, and dirt.
- Lubrication: Pick a bearing that matches the oil and care plan.
- Seal quality: Stops dust and water from getting inside.
- Installation: Make sure the bearing fits and is held tight.
- Cost: Find a balance between price, how well it works, and how long it lasts.
It is important to take care of bearings often. Add oil as the maker says. Check seals every three months. Change broken parts fast. Good care stops damage and keeps bearings working longer.
Slewing bearings have different structures. Some types are single-row ball, double-row ball, crossed roller, and three-row roller. Each type works best in certain machines. For example, cranes and wind turbines use different types. Picking the right bearing helps machines stay safe and work well. It also saves money.
| Classification | Examples | Application Contexts |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Four-point, double-row | Cranes, excavators, robots |
| Load Capacity | Light, medium, heavy duty | Construction, industry |
If you need help picking a slewing bearing, you can ask TFL Bearings. Their experts can help you choose the best one for your project.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a slewing bearing?
A slewing bearing lets machines turn and hold heavy things. It helps with both spinning and carrying weight at once.
Engineers put slewing bearings in cranes, wind turbines, and robots.
How does a four-point contact ball slewing bearing work?
Four-point contact ball slewing bearings have balls that touch the raceway in four places. This lets them handle different forces at the same time. They are good for machines that do not have much space.
When should someone choose a three-row roller slewing bearing?
Three-row roller slewing bearings are best for very heavy jobs. They are used in big cranes, mining machines, and wind turbines.
These bearings are the strongest and last the longest.
How often should slewing bearings receive maintenance?
Engineers need to check and add oil to slewing bearings every three months. Doing this often stops damage and keeps machines working well.
Can slewing bearings be customized for special applications?
Yes, companies like TFL can make slewing bearings for special jobs. Custom choices include different materials, gear types, and seals.




