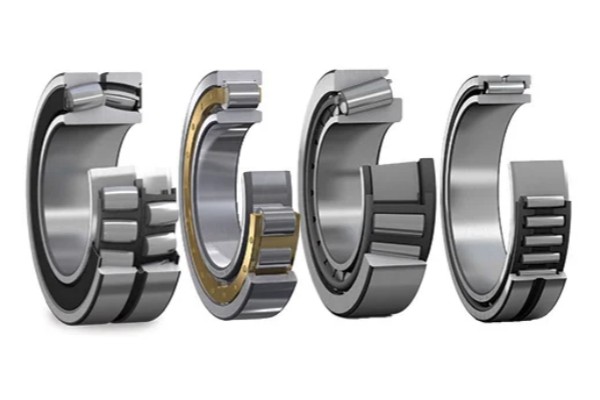
Roller bearings are a critical component in modern mechanical and industrial systems, designed to support heavy loads while minimizing friction and wear. Unlike ball bearings, which rely on spherical rolling elements, roller bearings use cylindrical, tapered, spherical, or needle-shaped rollers to distribute loads across a larger contact area. This structural advantage allows roller bearings to perform exceptionally well in demanding environments where high radial loads, axial forces, or shock loads are present. Understanding the different types of roller bearings and their applications is essential for engineers, procurement specialists, and maintenance professionals seeking reliable and efficient motion solutions.
What Are Roller Bearings and How Do They Work
Roller bearings are anti-friction bearings that use rolling elements in the form of rollers positioned between an inner ring and an outer ring. The rollers rotate as the bearing operates, reducing sliding friction and improving load-carrying capacity. Because the contact area between the rollers and raceways is larger than that of ball bearings, roller bearings can support significantly heavier loads and operate more reliably under stress. They are widely used in industrial machinery, automotive systems, power generation equipment, mining operations, and material handling applications.
Importance of Selecting the Right Type of Roller Bearing
Selecting the correct roller bearing is not simply a matter of size or load rating. Each type of roller bearing is engineered for specific operating conditions, including load direction, speed, alignment tolerance, and environmental exposure. Improper selection can lead to premature failure, increased downtime, and higher maintenance costs. By understanding the characteristics of different roller bearing types, users can optimize equipment performance and extend service life.
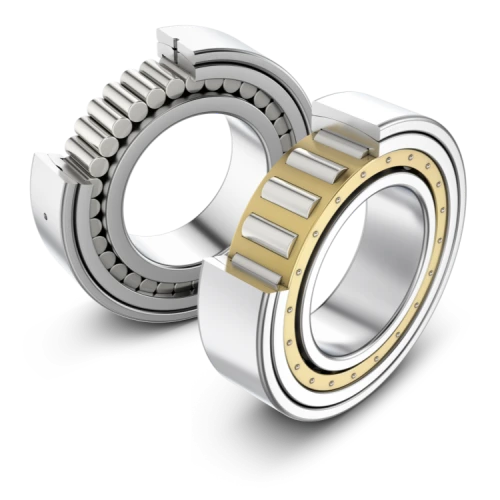
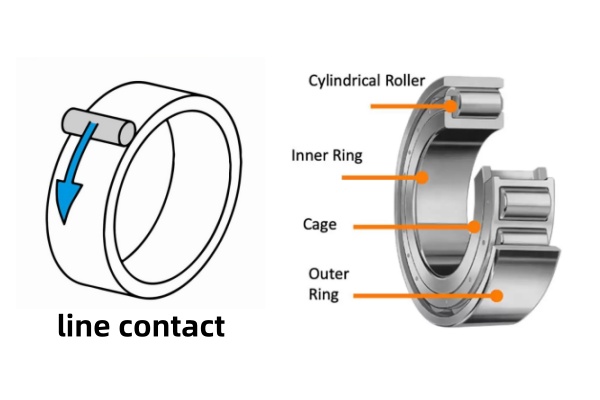
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings are among the most commonly used roller bearing types in industrial applications. They feature cylindrical rollers that provide line contact with the raceways, enabling them to carry heavy radial loads while operating at relatively high speeds. These bearings are often used in electric motors, gearboxes, pumps, compressors, and industrial transmissions.
One of the key advantages of cylindrical roller bearings is their high radial load capacity combined with low friction. Some designs allow axial displacement between the shaft and housing, making them suitable for applications where thermal expansion occurs. Due to their versatility and performance, cylindrical roller bearings are a standard choice in many manufacturing and automation systems. A detailed overview of cylindrical and other roller bearing designs can be found at SDTFL Bearing through their technical resources on roller bearing types.
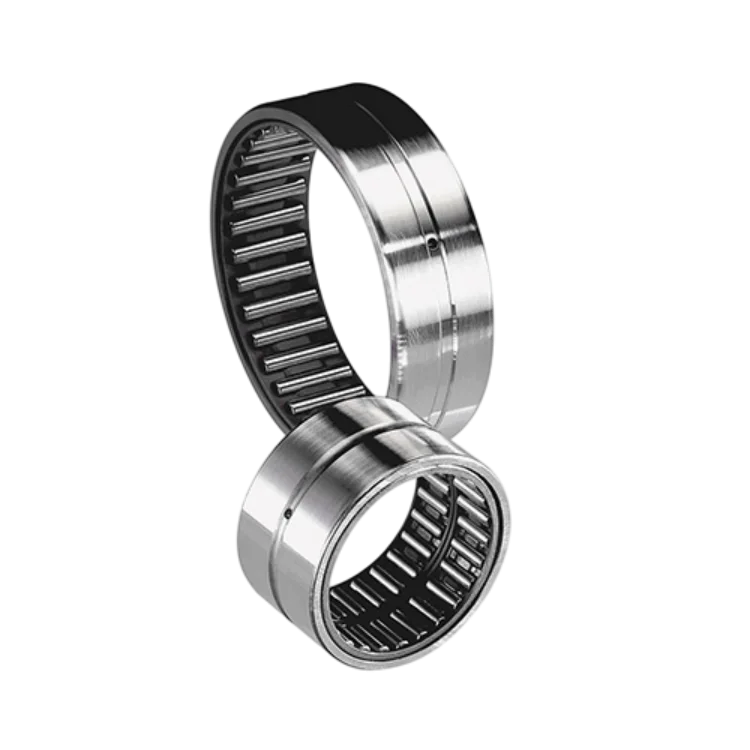
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings use long, thin cylindrical rollers with a small diameter relative to their length. This design allows them to provide high load capacity within a compact envelope, making them ideal for applications with limited installation space. Needle roller bearings are commonly used in automotive transmissions, compressors, power tools, and compact industrial equipment.
Despite their small size, needle roller bearings can handle significant radial loads. They are particularly effective in applications where weight reduction and space efficiency are critical. However, because they typically have lower speed limits than other roller bearing types, careful consideration must be given to operating conditions during selection.
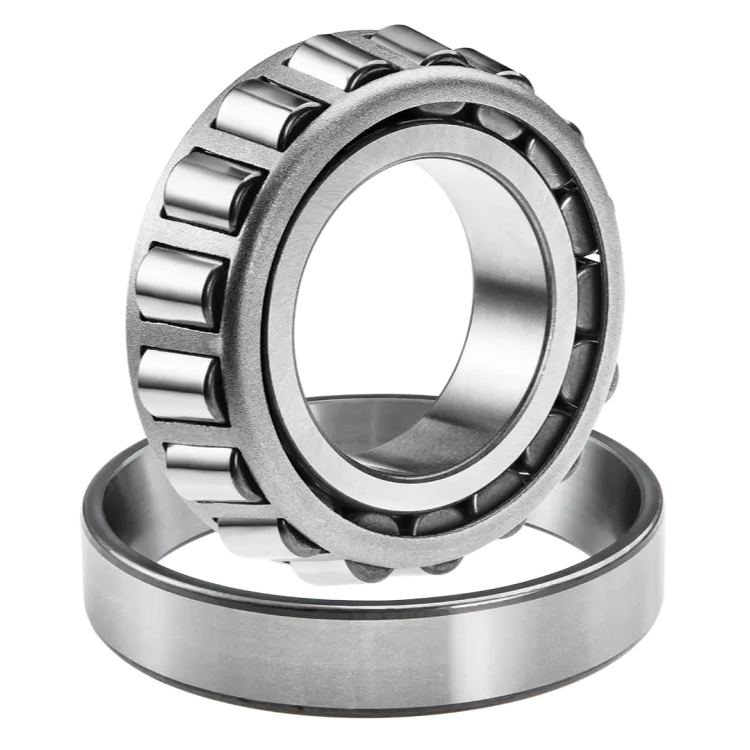
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are designed to handle combined radial and axial loads. Their tapered rollers and raceways converge toward a common point on the bearing axis, enabling them to manage heavy loads in both directions simultaneously. This makes tapered roller bearings especially suitable for automotive wheel hubs, gearboxes, rolling mills, and heavy-duty industrial machinery.
One of the defining characteristics of tapered roller bearings is their ability to be adjusted for preload or clearance during installation. Proper adjustment enhances rigidity and improves load distribution, which is essential in high-precision or high-load applications. Due to their strength and reliability, tapered roller bearings are widely used in industries where durability is a priority.
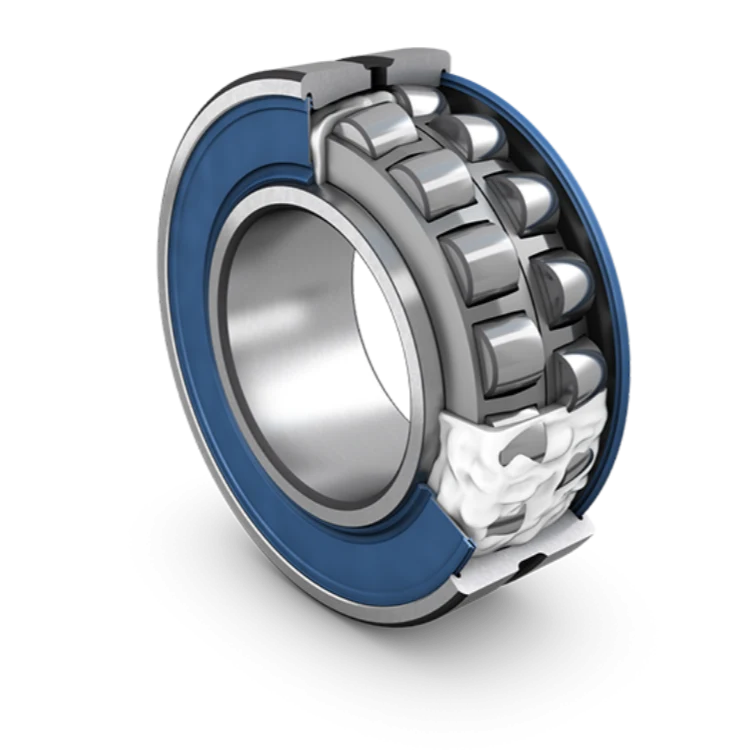
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings are designed to accommodate heavy radial loads as well as moderate axial loads while tolerating misalignment between the shaft and housing. They feature barrel-shaped rollers arranged in two rows, with a common spherical raceway in the outer ring. This self-aligning capability makes spherical roller bearings ideal for applications where shaft deflection, mounting errors, or structural deformation may occur.
Common applications include mining equipment, vibrating machinery, wind turbines, paper mills, and heavy conveyors. Spherical roller bearings are known for their robustness and long service life, even under harsh operating conditions such as high vibration, shock loads, and contamination.
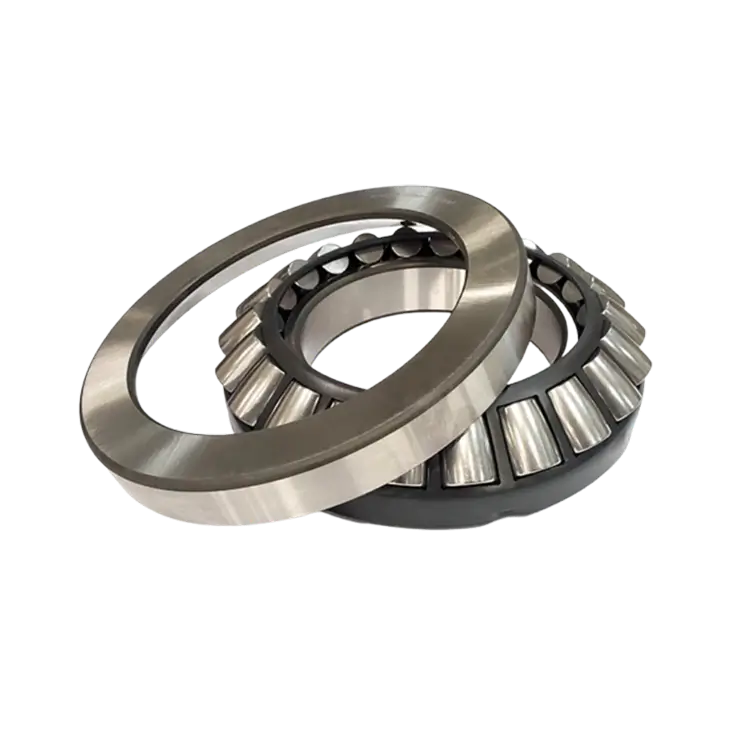
Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust roller bearings are specifically designed to support axial loads, either in one direction or both directions, depending on the configuration. Unlike radial roller bearings, thrust roller bearings are not intended to carry significant radial loads. They are commonly used in applications such as crane hooks, marine propulsion systems, vertical pumps, and heavy-duty gear assemblies.
Different designs, including cylindrical thrust roller bearings and spherical thrust roller bearings, are available to suit varying load requirements and alignment conditions. Selecting the appropriate thrust bearing is essential for ensuring stability and preventing axial movement in rotating systems.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Roller Bearings
When selecting from the various types of roller bearings, several factors should be evaluated to ensure optimal performance. Load characteristics, including magnitude and direction, are among the most important considerations. Operating speed, temperature, lubrication conditions, and environmental exposure also play a significant role in bearing selection.
Alignment tolerance is another critical factor. In applications where misalignment is unavoidable, spherical roller bearings may offer the best solution. For compact designs with high load demands, needle roller bearings are often preferred. Consulting detailed technical guidance, such as the comprehensive explanations available in this roller bearing overview, can help users make informed decisions based on real-world operating conditions.
Applications of Roller Bearings Across Industries
Roller bearings are used across a wide range of industries due to their versatility and performance advantages. In the automotive sector, they are essential for transmissions, wheel hubs, and differentials. In industrial manufacturing, roller bearings support conveyors, gearboxes, rolling mills, and heavy machinery. Energy and power generation industries rely on roller bearings for turbines, generators, and large rotating equipment.
Material handling, mining, construction, and agriculture also depend heavily on roller bearings to ensure reliable operation under challenging conditions. The ability of roller bearings to handle heavy loads, resist wear, and operate efficiently makes them indispensable in modern engineering systems.
Advancements in Roller Bearing Design and Manufacturing
Advances in materials, heat treatment processes, and precision manufacturing have significantly improved the performance of modern roller bearings. Enhanced steel alloys, optimized roller profiles, and advanced surface treatments contribute to increased load capacity, reduced friction, and longer service life. Improved sealing solutions also help protect bearings from contamination, further enhancing reliability.
Manufacturers continue to invest in research and development to meet the evolving demands of industrial automation, renewable energy, and high-performance machinery. As a result, today’s roller bearings offer higher efficiency and durability than ever before.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of roller bearings is essential for selecting the right solution for industrial and mechanical applications. Cylindrical, needle, tapered, spherical, and thrust roller bearings each offer unique advantages tailored to specific load and operating requirements. By carefully evaluating application conditions and performance needs, users can ensure reliable operation, reduced maintenance, and extended equipment life.
For those seeking deeper technical insights into roller bearing designs and applications, this detailed guide on types of roller bearings provides valuable information to support informed decision-making in industrial bearing selection.
Which Roller Bearing Fits Your Application?
Navigating the differences between Types of Roller Bearings—from Cylindrical to Spherical—can be complex. Incorrect selection often leads to premature machinery failure.
At SDTFL Bearings, our engineering team helps you match the perfect bearing geometry to your load and speed requirements.
Explore Cylindrical BearingsGet Expert Selection Advice
Technical Support: 📧 info@sdtflbearing.com | 📞 +86 15806631151










