Rolling bearings have a few main types. These are cylindrical, needle, tapered, spherical, and thrust roller bearings. Each type has a special roller shape. This helps them handle loads in different ways. For example, cylindrical roller bearings have ribs. The ribs help keep the inside space steady when things change. Tapered roller bearings react more to endplay. This means each roller bearing type has its own benefits. The best choice depends on how you use it.
Picking the right rolling bearing makes machines work better and last longer. Rolling bearings are not like ball bearings. They can carry heavier loads. They also work well in hard places. Studies show that changes in design and how they are made can change how long bearings last and if they fit the job.

Key Takeaways
- There are five main types of roller bearings. These are cylindrical, needle, tapered, spherical, and thrust. Each type handles loads in its own way. Each one fits certain machines best.
- Picking the right roller bearing helps machines work better. It lowers friction and helps machines last longer. You must match the bearing to the load and alignment needs.
- You need to do regular maintenance. This means checking oil quality and keeping things clean. This helps roller bearings work well and stops them from breaking early.
- Cylindrical bearings are good for heavy radial loads and fast speeds. Tapered and spherical bearings handle both radial and axial loads. They also work well when things are not lined up perfectly.
- Needle roller bearings save space and hold heavy loads in small areas. Thrust roller bearings support strong forces along the shaft. Each type is important for different machine parts.
Roller Bearings Overview
Construction
Roller bearings are a kind of rolling bearing. They use rollers to help moving parts slide easier. These bearings have two rings, rollers, and a cage. The inner ring goes on the shaft. The outer ring fits inside the housing. The rollers are between the rings. The cage keeps the rollers apart. This stops them from touching each other.
- The inner ring turns with the shaft.
- The outer ring stays still in the housing.
- The cage keeps the rollers in their spots.
The rings and rollers are made from strong steel. This steel is very hard and does not wear out fast. The cage can be made from steel, brass, or plastic. Making these bearings uses careful cutting, heating, grinding, and smoothing. These steps make the bearing strong and dependable.
| Component / Parameter | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Definition of roller bearing | A part that helps machines by lowering friction and letting parts move as needed. |
| Bearing type | Spherical roller bearing (model 22212E) |
| Internal diameter | 60 mm |
| Outer diameter | 110 mm |
| Average outer diameter of inner ring | 72.7 mm |
| Average inner diameter of outer ring | 96.5 mm |
| Average roller diameter | 14.20 mm |
| Length of roller | 10.20 mm |
| Number of rollers | 17 |
| Maximum load on single roller | 3637.75 N |
| Contact stress reduction | Hollow rollers lower stress and pressure by up to about 325.8 MPa and 453.5 MPa at 60% hollowness |
| Friction reduction mechanism | Hollow rollers spread out the force and bend more, so they lower pressure and stress, making the bearing last longer and hold more weight |
Function
Rolling bearings are important in machines. They hold up shafts and help things move smoothly. The rollers lower friction by rolling, not sliding. This helps machines use less energy and stay cooler.
- Rolling bearings use new designs, smaller sizes, and oil to lower friction.
- Most bearing problems happen because of bad oil or dirt.
- Using the right oil and smooth materials helps bearings last longer.
Rolling bearings have low friction, usually between 0.013 and 0.032. This means they do not wear out fast and help machines last longer. Special systems can find bearing problems early with over 94% accuracy. Hybrid roller bearings with ceramic rollers can lower friction and wear even more. The right bearing setup helps machines work better and need less fixing.
A good bearing setup also keeps the rollers in the right place. This spreads out the weight and lowers stress. When the bearing is set up right, the machine works better and lasts longer.
Tip: Check your bearings often and use the right oil to keep them working well and stop them from breaking early.
Common Types of Roller Bearings
Roller bearings come in a few main types. Each type has its own roller shape and inside design. These differences help each bearing hold weight in its own way. The most common types are cylindrical, needle, spherical, taper, and thrust roller bearings. Knowing about these types helps people choose the right one for their machines.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings have rollers shaped like cylinders. The rollers go between two rings. They touch the rings along their whole length. This gives the bearing a big contact area. Cylindrical roller bearings can hold heavy radial loads. They have a simple shape and fit many setups. Some have one row of rollers. Others have two rows for more strength.
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings use long, thin rollers. These rollers look like needles. Their small width and long length help them fit in tight spots. Needle roller bearings can hold a lot of weight for their size. They work best when there is not much space. The thin rollers also help lower friction.
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings use rollers shaped like barrels. The rollers sit in rings with a curved path. This lets the bearing hold both radial and axial loads. Spherical roller bearings can adjust if the shaft and housing do not line up. This makes them good for setups where things move or shift. The barrel shape spreads out the weight and lowers stress.
Taper Roller Bearings
Taper roller bearings have rollers shaped like cones. Both the rollers and the paths are tapered. This lets the bearing hold both radial and thrust loads at once. Tapered roller bearings work well when they need to hold heavy mixed loads. The angle of the rollers helps guide the load’s direction.
Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust roller bearings use rollers to hold weight in the axial direction. These bearings come in different shapes, like cylindrical, spherical, or tapered thrust types. The rollers go between flat or curved rings. Thrust roller bearings work best when they need to hold force along the shaft. The roller shape and setup decide how much weight the bearing can hold.
Note: The main types of rolling bearings are different because of the roller shape and how they are set up. Each type has its own setup. This changes how much weight it can hold and how it moves. Engineers use special math to pick the right bearing for each job.
| Bearing Type | Roller Shape | Main Load Direction | Typical Bearing Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical | Cylinder | Radial | Single/Double Row |
| Needle | Needle | Radial | Compact, Space-Saving |
| Spherical | Barrel | Radial & Axial | Self-Aligning |
| Tapered | Cone | Radial & Thrust | Adjustable, Combined Loads |
| Thrust | Cylinder/Barrel/Cone | Axial | Flat/Curved Rings |
The main types of roller bearings each have a special design. The roller shape and setup decide how the bearing works. These differences help people pick the right bearing for their machines.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Single Row
Single row cylindrical roller bearings have one row of rollers. These rollers sit between the inner and outer rings. This setup gives strong support for radial loads. The rollers touch the raceways along their whole length. This spreads out the force and lowers stress. Some designs, like full complement, use more rollers. This lets them hold more weight in small spaces. But more rollers can make extra friction and heat. So, it is important to use the right oil. How well the bearing works depends on its design and materials. It also depends on how well it fits. These bearings are used in gearboxes and heavy machines.

| Performance Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Radial Load Capacity | Very high; types N and NU support only radial loads. |
| Higher Capacity Roller Set (Suffix E) | Improved roller set design increases load capacity. |
| Toroidal Crowned Roller End Face (TB design) | Reduces friction torque by up to 50%, lowers operating temperature. |
| Axial to Radial Load Ratio (Fa/Fr) | Maximum 0.4 for standard; up to 0.6 for TB design. |
| Minimum Radial Load | P > C0r/60 during continuous operation. |
Double Row
Double-row roller bearings have two rows of rollers. This makes them able to hold even more weight. They can also handle some axial loads. The extra row gives more strength and keeps things steady. These bearings are used in big machines that run fast and carry heavy loads. Full complement double-row types use more rollers for extra strength. But this also makes more friction and heat. People pick these bearings because they last long and work well in tough jobs.
- Two rows of rollers give more support.
- Good for heavy-duty and high radial load jobs.
- Full complement types use more rollers for more strength.
| Manufacturer | Max Radial Load (kN) | Max Speed (rpm) | Temperature Range (°C) | L10 Life Rating (hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFL N Series | 850 | 15,200 | -40 to +200 | 60,000 |
| TFL ECP Series | 720 | 14,800 | -30 to +150 | 55,000 |
| TFL Xtreme® | 890 | 13,900 | -45 to +175 | 65,000 |
| TFL DYNABEARINGS® | 780 | 16,300 | -20 to +220 | 58,000 |
Features
Cylindrical roller bearings have many important features. They can hold heavy radial loads and spin fast. The rollers touch the raceways in a straight line. This spreads out the weight and helps the bearing last longer. These bearings are simple to put in and take out. Some types let the shaft move a little, which helps with alignment. But they do not hold much axial load unless they have special ribs. Double-row types are stiffer for machines that need to be very exact.
| Feature Aspect | Description / Specification |
|---|---|
| Roller Tolerances | Precise measurements ensure consistent roller geometry. |
| Roller Ring Standards | Surface finish and clearance tolerances keep performance high. |
| Cage Styles Comparison | Different cage designs affect reliability and performance. |
| Roller Retention Methods | Cage manufacturing methods influence strength and reusability. |
Applications
Cylindrical roller bearings are used in many fields. They help hold heavy loads in gearboxes, motors, pumps, and rolling mills. Car makers use them in transmissions and wheel hubs. This helps lower friction and makes cars work better. As more electric cars are made, these bearings help drivetrains run smoothly. Big machines in factories also use them for strength and long life.
Tip: Always check if your bearings fit well and have enough oil. This helps them work better and last longer.
Taper Roller Bearings
Taper roller bearings have rollers shaped like cones. The raceways are also cone-shaped. This shape lets them hold both radial and axial loads. The rollers touch the raceways along their whole length. This spreads out the force and makes the bearing last longer. The contact angle can change to handle more radial or axial load. These bearings are used in gearboxes, wheels, and big machines.

Single Row
Single row taper roller bearings have one row of tapered rollers. The cone shape gives a big area for contact. This helps them hold heavy radial and thrust loads. The design lets the shaft move a little under load. Single row bearings are simple and cannot be taken apart. They work best when the load comes from one direction or changes just a bit. Engines and gearboxes use these bearings because they last long and hold high loads.
Double Row
Double-row roller bearings have two rows of tapered rollers. This makes them stronger and more stable. The two rows share the load and keep the shaft steady. These bearings can hold bigger combined loads than single row types. They also help lower vibration and wear. Double-row roller bearings are found in heavy vehicles, rolling mills, and big motors.
Four Row
Four row taper roller bearings have four sets of tapered rollers. This gives extra support for both radial and axial loads. The four rows make a bigger contact area. This spreads out the force and lowers wear. These bearings stay lined up even with heavy loads. They save space by putting four rows in one bearing. Steel mills and big machines use four row bearings for strength and stability.
- Four row bearings hold heavy radial and axial loads at once.
- The design keeps machines steady and accurate.
- They save space and help build machines more easily.
Features
Taper roller bearings have some important features:
| Feature | Description / Statistic |
|---|---|
| Load Handling Mechanism | Conical rollers and raceways spread out radial and axial loads along the roller |
| Contact Angle Effect | Bigger angles help with axial loads; smaller angles help with radial loads |
| Load Contact Type | Line contact (tapered rollers) gives more strength than point contact (ball bearings) |
| Load Capacity Advantage | Can hold up to 15% more radial and 20% more axial load than ball bearings of the same size |
| Performance Advantages | Handles both radial and axial loads at the same time; matched sets share the load evenly |
| Limitations | Not good for very high speeds; needs to be lined up right; needs pairs for loads in both directions |
The contact angle can be between 10° and 29°. Steeper angles help with axial loads. Smaller angles help with radial loads. The line contact between rollers and raceways gives more strength and makes the bearing last longer.
Applications
Taper roller bearings are used in many machines that need to hold both radial and axial loads. They are found in engines, gearboxes, wheels, axles, turbines, and propellers. These bearings work well in cars, trucks, heavy equipment, and factory machines. Their strong design and ability to hold different loads make them a good choice for hard jobs.
Tip: Always check if taper roller bearings are lined up right and have enough oil. This helps them work better and last longer.
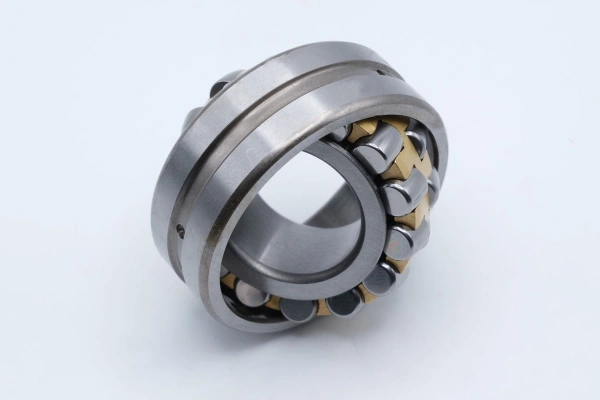
Spherical Roller Bearings
Standard
Standard spherical roller bearings have two rows of barrel-shaped rollers. These rollers sit in a curved outer ring. The inner ring can tilt a little. This helps the bearing work if the shaft and housing are not lined up. Machines keep running well even if parts move during use. Standard types use strong steel cages and long rollers. This spreads out the weight and helps the bearing last longer. It also makes the bearing work better.

Note: Engineers use many tests to check how well these bearings work. The table below lists some common tests and rules.
| Test Type | Purpose | Test Description | Test Runs / Samples Required | Standards Referenced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frictional Torque & Temperature Testing | Checks friction and temperature, power loss, and quality | Measures frictional torque and temperature under different conditions | 3 runs per group | ISO 281, DIN 51819 (FE8) |
| Endurance Testing (Life Tests) | Validates supplier and product quality | Tests bearing life under load; must last up to twice the theoretical life | 5 runs for validation; 5 runs to failure | ISO 281, DIN 51819 (FE8) |
| Accelerated Performance Tests | Compares endurance quickly | Increases load to speed up failure; uses automated rigs | 1 test, 1-4 weeks | DIN 51819 (FE8) |
| Continuous Quality Control Tests | Checks batch quality | Quick tests on small samples at tough conditions | 4 samples per batch, ~5 days | ISO 281 |
Split
Split spherical roller bearings come in two pieces. This makes them easy to put in and take out. Workers can put split bearings around a shaft without moving other parts. This saves time and helps fix machines faster. Split types are good for big machines where it is hard to reach the bearings.
Features
Spherical roller bearings have many helpful features. The curved outer ring lets the inner ring tilt. This helps the bearing work if the shaft is not straight. Strong steel cages and long rollers help spread out the weight. This makes the bearing last longer. Engineers use math to figure out how much weight the bearing can hold. They look at the size and strength of the race. Some new bearings have smart sensors. These sensors watch the bearing and find problems early. This helps stop sudden breakdowns and keeps machines working longer.
Applications
- Heavy machines, mining tools, and wind turbines use these bearings because they are strong.
- The self-aligning feature helps when big machines are not lined up right.
- These bearings can hold heavy loads from the side and some from the end.
- They work well in tough places like gearboxes, mining belts, and big fans.
- Some types can work in heat up to 500°F if treated right.
- Strong cages and hard guide rings help them handle shocks and moving loads.
- Newer models with higher ratings can last up to 60% longer and let you use smaller bearings for the same job.
Tip: Always make sure the bearing has enough load and good oil. This stops damage and helps the bearing last longer.
Needle Roller Bearings
Drawn Cup
Drawn cup needle roller bearings have a thin steel outer ring. This makes them very small and good for tight spaces. You can press them into place easily. Most do not need extra snap rings or collars. These bearings are used in gearboxes and planetary gears where space is tight. They can hold a lot of weight, especially the full complement types. But they are only somewhat stiff.
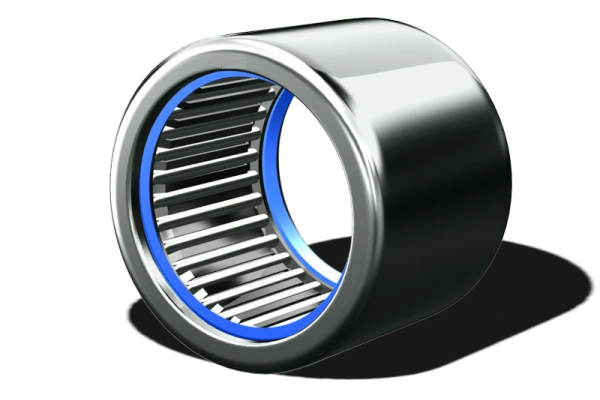
Solid
Solid needle roller bearings have a strong outer ring made by machines. The ring is made from special steel that is very strong. This makes the bearing stiff and able to handle heavy hits. Some types use the shaft as a raceway, which helps them be more exact. These bearings work well in fast machines that need to be very accurate. Solid types cost more, but they last longer and work better.
| AspectDrawn Cup Needle Roller BearingsSolid Needle Roller Bearings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Outer Ring | Thin, drawn cup type with smallest cross-sectional height | Solid outer ring, made from vacuum-degassed or carburized steel |
| Load Capacity | High load capacity, especially full complement designs | Maximum load capacity, suitable for heavy and impact loads |
| Rigidity | Moderate rigidity, supports downsizing and space-saving designs | High rigidity, withstands heavy and impact loads |
| Speed Capability | High limiting speeds, especially caged models | High precision for high-speed rotation under heavy loads |
| Mounting | Easy axial mounting with press fit, no snap rings or collars | May require more precise mounting, some types use shaft as raceway |
| Precision | Suitable for general industrial applications | High precision, ideal for machine tools requiring accuracy |
| Applications | Planetary gears, constant mesh gearboxes, industrial machinery | High-speed machine tools, planetary gears, constant mesh gearboxes, industrial machinery |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, easy to use | Higher cost due to precision and rigidity |
Features
Modern needle roller bearings use long, thin rollers. These rollers help them hold a lot of weight in a small space. The bearings are made from strong steel and are treated with heat. Their smooth surface helps them last longer and lowers friction. Many types run quietly and do not get too hot. This saves energy. Some, like X-life, have better shapes and inside parts. These changes help them hold more weight and last longer. Their small size makes them easy to add to machines.
Tip: Needle roller bearings do not need much oil. They can go longer without needing care. This helps machines keep running.
Applications
Needle roller bearings are used in many machines that need to save space and hold heavy loads. They are found in gearboxes, pumps, and other machines. Fast machine tools use solid types for strength and accuracy. Drawn cup types fit in small places and help make machines smaller. Their small size and strength make them a good choice for many jobs. They can handle heavy forces and spin fast, so engineers use them a lot.
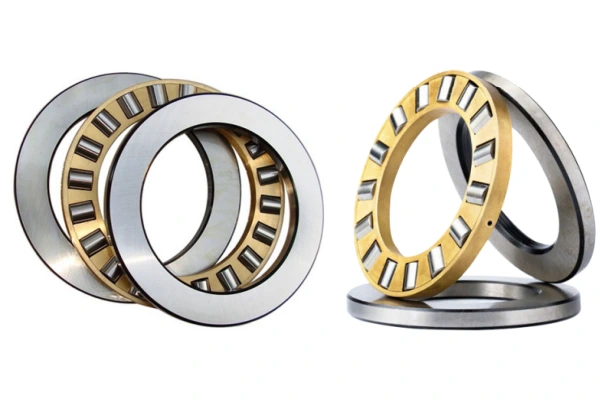
Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust bearings help hold up forces that push along the shaft. They use rollers, not balls, so they can handle bigger forces. There are different types of thrust roller bearings. Each type has its own design for special jobs.
Cylindrical Thrust
Cylindrical thrust bearings have straight rollers between flat washers. This setup lets them hold very strong forces in one way. The rollers and washers touch in a big area. This spreads out the force and helps stop wear. These bearings work best in slow or medium-speed machines that need strong support.

Spherical Thrust
Spherical thrust bearings use rollers shaped like barrels. The raceway is curved, so the bearing can adjust if things are not lined up. These bearings can hold heavy forces and some misalignment. You often see them in machines like cranes or big gearboxes that move or bend.
Tapered Thrust
Tapered thrust bearings have cone-shaped rollers and matching raceways. This shape helps them hold both pushing and some sideways forces. The tapered rollers stay in place and keep the load steady. Big machines that face changing forces, like rolling mills, use these bearings.
Features
Thrust bearings have many helpful features:
- Special washers with grooves guide the rollers and keep them in place.
- Some types hold force in one way, others in both ways.
- Aligning seat washers help if the bearing is not mounted perfectly.
- Shaft and housing washers help distribute the force and strengthen the bearing.
- Engineers use ratings to see how much force the bearing can take before it wears out.
- Tests and models check if the bearing can really hold up under real work.
Newer thrust bearings use better materials and oil. Some have sensors to watch how they work in real time. These changes help them last longer and work better, even in tough places. Picking the right oil and space inside the bearing helps lower shaking and makes them more reliable.
Applications
Thrust roller bearings are used in many jobs. They are found in mining, building, paper mills, pumps, motors, machine tools, and cranes. These bearings work well where machines get strong pushes along the shaft. Some types hold force in one way, others in both ways. You can take them apart to change parts without removing the whole bearing. They do not spin as fast as thrust ball bearings, but they can hold more weight and are easy to fix.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Bearing Design | Cylindrical rollers hold more force than thrust ball bearings |
| Load Handling | Hold heavy forces in one or both ways |
| Industrial Applications | Used in mining, building, paper mills, pumps, motors, cranes |
| Installation | Parts come apart for easy fixing |
| Speed/Load Limits | Spin slower, but hold more weight |
| Maintenance | Change parts without taking out the whole bearing |
Tip: Always make sure the bearing is lined up right and use the best oil. This helps thrust bearings work well and last longer.
Roller bearings and ball bearings are not the same. They handle loads and alignment in different ways. Spherical roller bearings are good for heavy loads and when things are not lined up. Cylindrical roller bearings work best with radial loads and can spin very fast. Tapered roller bearings can handle both radial and axial loads at the same time. Needle roller bearings are better than ball bearings for small, tight spaces. The table below shows how each bearing type matches with load, speed, and alignment needs.
| Bearing Type | Load Handling | Speed Suitability | Alignment Capability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical Roller | Heavy, misalignment | Slow to moderate | Good | Gear boxes, steering columns |
| Cylindrical Roller | Radial | High speeds | Limited | Driven wheels |
| Tapered Roller | Axial and radial | High speeds | Moderate | Non-driven wheels |
| Needle Roller | Compact, friction | Compact spaces | Limited | Transmissions, compressors |
A new study found that checking vibration helps find bearing wear. Picking the right bearing type makes machines last longer and work better. TFL Bearings has many roller and ball bearings for different jobs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between roller bearings and ball bearings?
Roller bearings use cylinders or needles to hold weight. Ball bearings use balls instead. Roller bearings can carry heavier loads. Ball bearings are better for fast spinning. Each type works best for certain machines.
How does a user know which roller bearing type to choose?
Users should look at the load direction, speed, and space. Cylindrical types are good for high radial loads. Spherical types help if things are not lined up. Tapered types can hold both radial and axial loads.
Can roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads?
Some roller bearings, like tapered and spherical types, can hold both radial and axial loads. Others, like cylindrical and needle types, mostly hold radial loads.
How often should roller bearings get maintenance?
Most roller bearings need regular checks for oil, dirt, and wear. Users should follow the machine’s plan. Clean oil and good setup help bearings last longer.
Tip: Checking bearings often and using clean oil helps stop early problems.




