Railway Bearings
Locomotives, passenger cars, freight wagons (railcar), and track maintenance equipment operate under demanding conditions, including high speeds, heavy loads, constant vibration, and exposure to diverse weather. Industrial bearings are critical components throughout railway systems, enabling motion, supporting loads, and ensuring the operational integrity of everything from the wheel assembly parts on rolling stock to sophisticated track infrastructure.

Home / Industries / Railway Bearings
Key Bearing Applications in the Railway Sector

Railway Bearings
Axle Bearings: Wheelset bearings, axle box bearings.
Traction Motor Bearings: Electric motor bearings, rotor bearings.
Gearbox Bearings: Transmission gearbox bearings, pinion bearings.
Bogie Bearings: Bogie pivot bearings, suspension bearings.
Coupler Bearings: Draft gear bearings, coupling mechanism bearings.
Pantograph Bearings: Current collector bearings, actuator bearings.
Brake System Bearings: Brake actuator bearings, caliper bearings.
Compressor Bearings: Air compressor bearings for pneumatic systems.
Fan Bearings: Cooling fan bearings, HVAC blower bearings.
Door System Bearings: Sliding door bearings, hinge bearings.
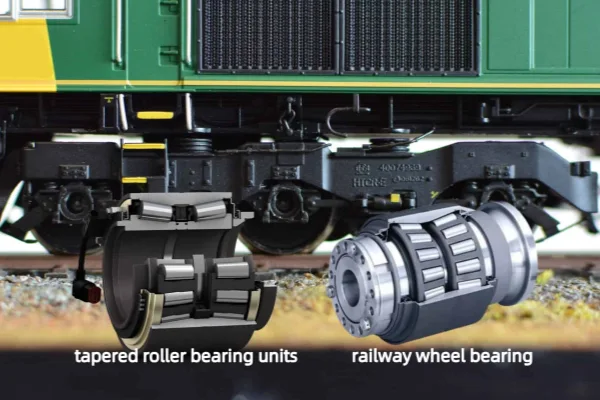
Axle Boxes / Wheelset Bearings
Railroad car wheel bearings (also known as railcar wheel bearings or train wheel bearings) are housed within axle boxes and support the entire weight of the vehicle while allowing the wheels to rotate freely.
These are typically specialised heavy-duty roller bearings, often tapered roller bearing units (TBUS) or cylindrical roller bearing units, designed as sealed and pre-lubricated bearing assembly units for maximum reliability and long maintenance intervals.
They must withstand immense static and dynamic loads, high speeds, shock impacts, and varying temperatures, making their design and manufacturing quality absolutely critical for safety.


Traction Motors and Gearboxes
Electric and diesel-electric locomotives and multiple units rely on powerful traction motors and associated gearboxes to drive the wheels. Bearings within these systems support the motor armature shaft bearings and gear shafts.
They operate under conditions of high rotational speeds, significant torque loads, vibration, and, in the case of motor bearings, potential electrical currents. Cylindrical roller bearings and deep groove ball bearing types are commonly used.
In some cases, electrically insulated bearings are required to prevent damage from stray currents. Durability and precision are essential for efficient power transmission and reliability.
Linear Motion Systems
Modern passenger trains incorporate numerous systems requiring smooth and reliable linear movement. Automatic door systems, adjustable seating mechanisms, and accessibility ramps all rely on linear bearing technology.
Linear rails and linear guide rail systems, often incorporating linear slide bearings or linear ball bearing blocks (linear bearing block), ensure precise, low-friction motion. These linear bearings and rails must be robust enough to handle frequent use and vibration while often fitting into compact spaces.
The reliability of these linear motion bearing components directly impacts passenger experience and safety. We supply various linear rail system components for these applications.

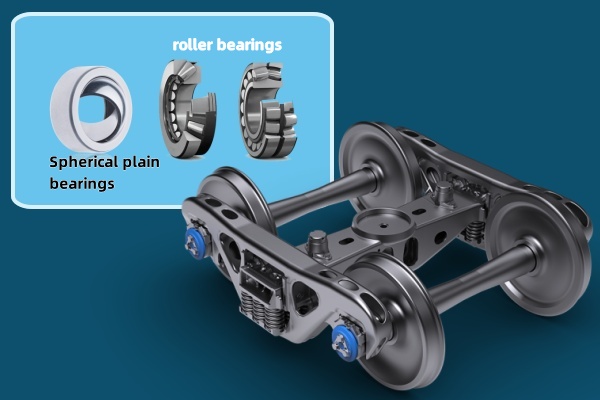
Bogie Components and Suspension Systems
The bogie (or truck) is the structure underneath a railway vehicle to which the axles and wheels are attached. It incorporates suspension elements and pivot points that utilize various bearings.
These include bearings for linkages, damper attachments, and pivot points which accommodate complex movements and absorb vibrations between the wheel hub assembly and the car body.
Spherical plain bearings, robust roller bearings, and sometimes specialized bearing assembly units are employed here. They must endure constant vibration and environmental exposure while maintaining the stability and ride quality of the railcar.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS

What makes railway wheel bearing units different from standard industrial bearings?
Railway wheel bearings, specifically railroad car wheel bearings, are engineered for exceptionally high safety standards and reliability under severe operating conditions. They face unique challenges like extreme dynamic loads, high mileage requirements between maintenance intervals (long average life of wheel bearings expected), impact forces from track irregularities, and the need for failsafe performance. They are typically designed as sealed, pre-lubricated cartridge units (bearing hub assembly style) for easy mounting and maximum protection.
What types of bearings are used in train traction motors?
Traction motors typically use a combination of cylindrical roller bearings to handle high radial loads and speeds on the main shaft, and deep groove ball bearings for positioning and lighter loads. Due to the electrical environment, one or both bearings might feature ceramic rolling elements or insulating coatings to prevent electrical current damage.
Why are Insulated bearings necessary in railway traction motors?
Electric traction motors can generate stray electrical currents that may seek a path to ground through the motor shaft bearings. Without insulation, this current can cause electrical discharge machining (EDM) damage to the bearing raceways and rolling elements, leading to premature failure. Insulated bearings have a non-conductive coating that breaks this electrical circuit, protecting the bearing and enhancing the reliability of the traction system.
Are linear bearings commonly used on actual train wheels or bogies?
No, the primary load-bearing components for train wheels are rotational bearings housed in axleboxes (railway wheel bearing units). Linear bearing systems (linear bearings and rails, linear guide rail system) are typically used in auxiliary railway applications, such as maintenance equipment, specialized machinery functions, or potentially automated door systems, rather than the core running gear of the train itself.
RELATED ARTICLES

Discover the different ball bearing types like deep groove, angular contact, self-aligning, thrust, and linear. Learn their unique structures and specific uses....

Discover the unmatched advantages of super precision angular contact ball bearings that boost performance in high-demand applications. Learn more at TFL....