Tapered roller bearings are very important in main reducers for cars. These bearings hold up both side and straight forces. This makes them good for handling mixed loads in the drivetrain. Their special shape makes them last longer and work better. This helps stop common problems from happening. Picking the right bearing lowers problems like rough wear, surface damage, and rust. Main reducers need tapered roller bearings to keep working well when things get tough. The way they handle mixed loads means they work well and last longer.

Common bearing failure modes in automotive main reducers include:
- Abrasive wear
- Surface-initiated fatigue
- Moisture corrosion
- Adhesive wear
- Current leakage erosion
Choosing the correct tapered roller bearings lowers these dangers and helps the drivetrain work better.
Key Takeaways
- Tapered roller bearings can hold side and straight forces. This makes them great for main reducers in cars. They help handle mixed loads and last longer.
- Their special cone shape spreads force out evenly. This lowers wear, heat, and friction. It helps the drivetrain work well and saves gas.
- Using the right tapered roller bearings is important. Setting the correct preload helps with alignment. It also lowers noise and makes the main reducer last longer.
- Tapered roller bearings are better than ball and cylindrical roller bearings. They can hold more weight and last longer. This is true when there are heavy and mixed forces.
- Regular maintenance is needed for these bearings. Good lubrication and timely checks stop bearing failure. This keeps the main reducer working well and safely.
Main Reducer Role
Automotive Industry Applications
The main reducer is very important in cars. It is found in the middle of the transmission system. It changes fast engine spinning into slower spinning with more force. This helps cars use engine power better and safer. The main reducer works with gears and differentials. It helps send power smoothly to the wheels. Many transmissions need the main reducer to handle speed and load changes. Cars depend on this part for good performance every day. Special cars also need it for their transmissions. If the main reducer does not work, the transmission cannot give enough force for speeding up or going uphill.
Bearing Selection Factors
Picking the right bearings for main reducers is important. Engineers look at the types of forces the bearing will face. These include side and straight forces. They also think about speed, heat, shaking, and hits. The kind of oil or grease used matters a lot. It must work well with the bearing and gears. Seals keep dirt out and help lower rubbing. This helps the transmission last longer. Wetness and rust can make bearings wear out faster. Taking care of bearings and checking oil helps them last. Bearings must fit well for gears to work right. The type of bearing must match the job it needs to do. All these things help the main reducer work well in cars today.
Tapered Roller Bearings Structure
Geometric Design
Tapered roller bearings have a special shape. This shape makes them different from other bearings in main reducers. They use cone-shaped rollers and raceways. These parts help them hold both side and straight forces at once. Because of this, they can carry heavy loads. This makes them good for tough jobs in cars.
The shape of tapered roller bearings has many key parts. These parts decide how much weight the bearing can hold. They also help the bearing fit in the main reducer. The table below shows the most common shape parts:
| Geometric Parameter | Description / Significance |
|---|---|
| Roller-inner raceway contact angle (αi) | Influences axial load capacity. |
| Roller-outer raceway contact angle (αo) | Affects load distribution. |
| Roller-cone flange contact angle (αf or αR) | Important for roller guidance and load transfer. |
| Bearing pitch diameter (dm) | Critical for bearing sizing and fitment. |
| Large end diameter of the roller (Dmax) | Affects contact geometry and load capacity. |
| Small end diameter of the roller (Dmin) | Important for roller profile and stress distribution. |
| Roller length (lt) | Influences load carrying capacity and bearing stiffness. |
Tapered roller bearings can change their contact angle. This lets engineers adjust the bearing for special car needs. Some examples are wheel hubs or gearboxes. The line where the rollers touch the raceways spreads out the force. This helps the bearing last longer and hold more weight.
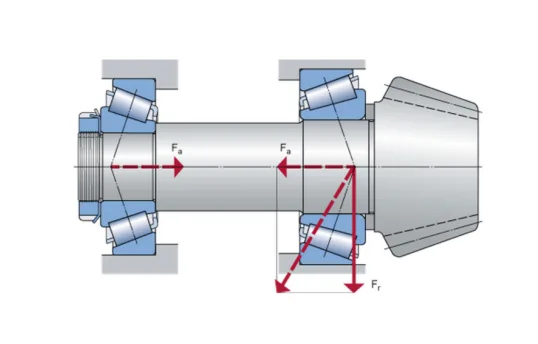
Handling Radial and Axial Loads
The shape of tapered roller bearings lets them hold big side and straight forces. Their cone-shaped rollers and raceways work together. They turn straight forces into side forces. This helps spread out the force and lowers stress on the bearing.
Being able to hold both types of force is a big plus in main reducers. The cup and cone shape, plus the cage that spaces the rollers, keeps the force even. It also helps the bearing spin smoothly. This setup gives the bearing strength and keeps it steady, even with heavy loads and shaking.
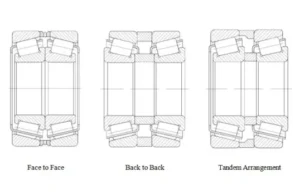
Note: Tapered roller bearings are often used in pairs in cars. This helps control movement and heat changes. It is important for the main reducer to work well.
The strong shape of tapered roller bearings lets them hold a lot of weight. This makes them good for wheel hubs, transmissions, and differentials. They keep working well and stay lined up, even when the load is hard. This means they last a long time and work well.
Tapered Roller Bearings in Automotive Gearbox
Load Distribution
Tapered roller bearings help spread out force in a car’s gearbox. Their cone shape lets them hold both side and straight forces at once. This shape helps the gearbox deal with heavy and changing loads from moving gears. The way these bearings share the force keeps the gearbox working well and stops damage.
- The cone shape lets tapered roller bearings hold both side and straight forces by spreading them along the sloped surfaces.
- Cylindrical roller bearings mostly hold side forces and do not work as well with straight forces.
- The cone shape makes a line where the rollers touch the raceways. This spreads the force out and lowers stress in one spot.
- In a car’s gearbox, gears make both side and straight forces. Tapered roller bearings hold these forces and help the gearbox run smoothly.
- Installers can change the space in tapered roller bearings when setting them up. This helps the bearing work well in different situations.
- Ball bearings touch at one point, so they can spin faster but cannot hold as much force. Tapered roller bearings touch in a line, so they are better for heavy mixed forces in gearboxes.
- Many gearboxes use two tapered roller bearings together. This setup holds straight forces in both ways, which is important for transmissions and wheel hubs.
- Tapered roller bearings spread out force better in gearboxes than cylindrical, ball, or needle roller bearings. Their shape lets them hold mixed forces and last longer.
Tapered roller bearings touch in a line between the rollers and raceways. This gives them more strength than ball bearings, which only touch at one point. Car gearboxes need this strength to handle heavy and mixed forces from gears. Tapered roller bearings help the gearbox work well and keep the car running smoothly.
Durability and Efficiency
Tapered roller bearings are strong and work well in car gearboxes. Their tough shape helps them last a long time, even when things get hard. The way they spread out force stops wear and keeps the gearbox working for many years. This is important for people who need their cars every day.
The table below shows how long tapered roller bearings usually last in car gearboxes:
| Operating Condition | Minimum L10 Life (Hours) |
|---|---|
| Intermittent operation, reliability important | 12,000 |
| Continuous 1 shift operation | 20,000 |
Tapered roller bearings also help lower rubbing inside the gearbox. Less rubbing means less heat and less wasted energy. This helps cars use less fuel and run more smoothly. The bearings keep the gears lined up and stop extra movement. This helps the gearbox stay quiet and work well for a long time.
Many car gearboxes use tapered roller bearings because they can hold heavy forces and last a long time. Their shape gives both strength and good performance for today’s cars. Drivers get a smoother ride and fewer gearbox problems when these bearings are used.
Advantages in Main Reducers
Reducing Friction and Heat
Tapered roller bearings help lower friction and heat in main reducers. Their special shape fixes problems seen in old bearing types. The rollers and raceways have slanted sides that fit together well. This lets the bearing hold both side and straight forces easily.
- The raceways’ lines meet at one spot. This helps the rollers move better and cuts down friction.
- The rollers touch the raceways in a line, not a point. This stops sliding and keeps oil in place to stop wear.
- Oil between the rollers and raceways lowers friction, noise, and heat.
- The cage keeps the rollers spaced out for smooth spinning and even force.
- A flange holds the rollers and cage together, even when spinning fast.
- Seals block water and dirt, so friction stays low.
All these parts work together to cut friction and heat. Less friction means the bearing lasts longer and wears less. The main reducer works better because it can handle heavy loads smoothly.
Low Torque and Fuel Efficiency
Tapered roller bearings help the main reducer need less force to turn. Their smooth rolling lowers wasted energy. This means the gears turn easier and use less fuel.
When the bearing spins well, it makes less heat. This keeps the main reducer cool and safe from harm. Some bearings have special coatings to lower friction more, especially in electric axles. Less friction and heat mean the car uses less energy. This helps cars save gas and pollute less.
Tip: Lower torque in the main reducer helps cars use less fuel and make fewer emissions.
Tapered roller bearings are strong and can hold both side and straight forces. This is important for moving force in cars. Even though they may make more friction than ball bearings at high speeds, their shape gives them strength and long life.
Alignment and Preload
Good alignment and preload help tapered roller bearings last longer in main reducers. These bearings often work in pairs to hold force both ways. This setup keeps the transmission parts lined up right.
- The usual preload torque is about 1.4 Nm (15 lb-in). This takes away loose movement but does not add too much stress.
- A little preload is better than none. It keeps the bearing stiff and lined up.
- Preload helps keep the main reducer’s shape and controls straight force.
- Too much preload makes heat and can wear out the bearing faster. The right amount is important.
Tapered roller bearings can also handle small mistakes in how they are set up. This lowers wear and makes them more reliable. Their strong build and good force control help them last a long time. The main reducer stays steady and accurate, which is needed for smooth power.
Note: The right preload and alignment help the bearing last longer and keep the main reducer quiet and working well.
Comparison with Other Bearings
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are used in cars when parts spin fast and carry light loads. These bearings have balls that touch the raceways at one point. This makes them spin smoothly but not hold heavy forces well. In main reducers, ball bearings cannot handle both side and straight forces like tapered roller bearings. If they get hit hard or carry heavy loads, ball bearings can bend or wear out fast.
The table below shows the main differences between tapered roller bearings and ball bearings in car main reducers:
| Feature | Tapered Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Type | Line contact, allowing higher load capacity | Point contact, suited for lighter loads |
| Load Capacity | High radial and axial load capacity | Limited heavy load capacity |
| Durability | More durable under heavy loads and shocks | Can deform under excessive loads |
| Typical Automotive Use | Wheel hubs, transmissions, main reducers | High-speed, lighter load applications (e.g., alternators) |
| Dynamic Load Rating | Up to 3 times higher than ball bearings of same size | Lower dynamic load rating |
| Bearing Life (L10) | Significantly longer under same load and speed | Shorter life under heavy load conditions |
| Sensitivity to Shock | More resistant | More vulnerable |
| Speed Capability | Lower than ball bearings | Higher speed capability |
Tapered roller bearings last longer and hold more force in main reducers. Ball bearings are better where spinning fast is more important than holding heavy loads, like in alternators or electric motors.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings have straight rollers that hold big side forces. These bearings do not hold straight forces well. In car main reducers, engineers use cylindrical roller bearings if most force comes from the side, not along the shaft. Their simple shape makes them easy to put in and good for fast spinning.
The table below compares tapered roller bearings and cylindrical roller bearings:
| Bearing Type | Load Handling Capability | Typical Automotive Applications | Suitability in Main Reducers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tapered Roller Bearing | Handles large radial and axial loads (axial in one or both directions when paired); contact angle affects thrust capacity | Automotive wheels, transmissions, differential pinion shafts; heavy-duty applications | Preferred when both axial and radial load support are needed in main reducers |
| Cylindrical Roller Bearing | Primarily supports large radial loads; limited axial load capacity; suitable for high-speed and shock loads | Motors, generators, gearboxes, machine tool spindles; applications with heavy radial loads but minimal axial loads | Chosen for high radial load capacity and ease of installation when axial loads are small or intermittent |
Tapered roller bearings are best for main reducers that need to hold both side and straight forces, especially when gears shift. Cylindrical roller bearings work best in systems with mostly side forces and little need for thrust support.
Applications
Real-World Examples
Tapered roller bearings are used in many car parts. Engineers pick them because they can hold side and straight forces. Trucks and trailers use these bearings to carry heavy things and handle hard bumps. These vehicles go far with big loads. The bearings must last long and work in tough places.
Cars use a different way. Many car makers use angular contact ball bearings in main reducers. This helps cars use less gas and make less noise. But some cars still need tapered roller bearings for more strength or longer life.
- Trucks and mining vehicles use strong tapered roller bearings for big loads and hard hits.
- Cars often use ball bearings for fast spinning and less friction, but sometimes use tapered roller bearings when needed.
- Tapered roller bearings are found in wheel hubs, transmissions, and differentials where both side and straight forces happen.
Performance Outcomes
Tapered roller bearings work well in main reducers. Trucks get longer life and break down less. These bearings keep working when loads change or roads get rough. Drivers have fewer repairs and spend more time driving.
Cars get smoother rides and use less gas when the right bearing is picked. Tapered roller bearings help keep gears lined up and lower shaking. This makes the car quieter and stops parts from wearing out fast.
Note: Picking the right bearing makes cars safer and more reliable.
Tapered roller bearings in main reducers help cars today work better. The right bearing gives good performance, lasts long, and costs less to fix.
Selection & Maintenance
Choosing the Right Bearing
Automotive engineers pick tapered roller bearings for main reducers by following some steps. First, they check if the bearing size fits in the main reducer. They use sizes from catalogs to help them choose. Engineers also think about how hot the bearing will get when the car runs. High heat can change how the bearing works. They look at the forces the bearing must hold, from the side and along the shaft. The roller angle helps decide how much force the bearing can take. Speed is important too. Tapered roller bearings work at different speeds than ball bearings. Engineers often use two bearings together to hold force both ways. They read catalogs and talk to experts to make sure the bearing will last. Tapered roller bearings can come apart, so engineers must set them up right. They need to keep the right space inside, especially when it gets hot.
- Make sure the bearing fits the space.
- Think about how hot the bearing will get.
- Check what forces the bearing must hold.
- Look at how fast the bearing will spin.
- Plan how to put in the bearings, often using two.
- Read catalogs and ask experts about bearing life.
- Set up the bearing with the right space inside.
Maintenance Best Practices
Taking care of tapered roller bearings helps them work well in main reducers. Lubrication is very important. Good grease lowers friction and stops wear. Checking the bearings often helps find problems early, like dirt or heat. Cleaning and fixing bearings helps them last longer and keeps the main reducer working.
- Check bearings for wear by moving and spinning the wheel.
- Use grease that meets car maker rules and pack it well.
- Set the preload right to stop early wear.
- Do not drive hard, hit potholes, or carry heavy loads.
- Change broken bearings fast to stop more damage.
- Keep tires at the right pressure, rotate, and balance them.
- Use the right tools to take out and put in bearings.
- Use enough good grease to lower friction and wear.
- Change how often you add grease based on car use. Heavy use needs more grease.
- Do not use sprays like WD40, as they do not protect bearings.
- Use good ways, like filling with grease or a supply system, for even grease.
- Check and add grease often to keep bearings working.
| Maintenance Challenge | Common Causes and Symptoms | Recommended Actions and Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Premature Bearing Failure | Not enough grease, metal touching metal, broken cage | Make sure there is enough grease and cooling |
| Overheating | Too much force, wrong oil level, blocked vent plug | Lower the force, keep oil at the right level, clean the vent plug |
| Loose Shafting | Shaft moves when checked | Plan to service the bearing |
| Oil Leakage | Too much oil, blocked vent, broken seals | Lower oil, clean vent, change seals |
| Loose Hardware | Bolts or fasteners are loose | Check and tighten bolts |
| Vent Plug Issues | Missing, blocked, or wrong vent plug | Put in and clean vent plugs the right way |
Good care helps bearings last longer and keeps the main reducer safe and working well.
Tapered roller bearings are very helpful in car main reducers. They can hold heavy side and straight forces. These bearings spread out force so it is even. They also work well if things are not lined up perfectly. Picking the right bearing keeps the system steady and strong. This helps the parts last longer and work better. Some big benefits are:
- They can hold a lot of weight and take hard hits.
- They work well in hot or cold, from -40 to 120℃.
- You can change how they are made for different jobs.
If you pick the right tapered roller bearings, they last longer and do not break early. TFL Bearings can help car engineers with good advice and strong products.
FAQ
What makes tapered roller bearings suitable for main reducers?
Tapered roller bearings can hold both side and straight forces. Their special shape spreads out the force. This helps main reducers run well and last a long time.
How often should technicians check tapered roller bearings in vehicles?
Technicians need to check bearings during regular car service or every 30,000 miles. Checking early helps find wear, dirt, or not enough grease.
Can tapered roller bearings reduce noise in automotive main reducers?
Yes. If installed right, tapered roller bearings keep gears lined up. This lowers shaking and noise in the drivetrain.
What lubrication works best for tapered roller bearings?
Good car grease or gear oil is best for these bearings. Lubrication stops metal from rubbing and cuts down friction. Always use what the car maker says.
Are tapered roller bearings easy to replace in main reducers?
Most tapered roller bearings come apart for easy checks and swaps. Mechanics can take them out and put them in with normal tools.