Comparing Roller and Ball Bearings: Features and Uses
Explore key differences and best uses of roller and ball bearings.

| Features | roller bearing | ball bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Element Shape | Cylindrical, tapered, needle, or spherical rollers | Spherical balls rolling between races |
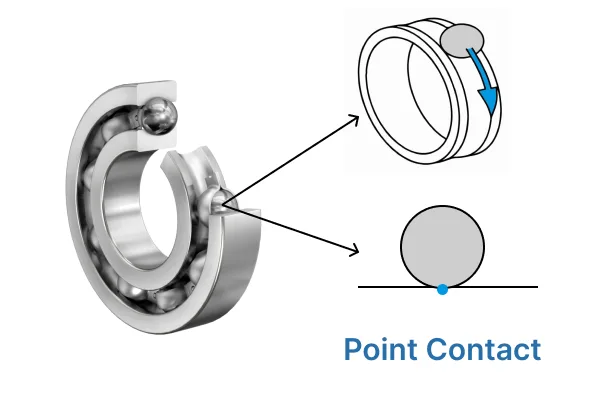
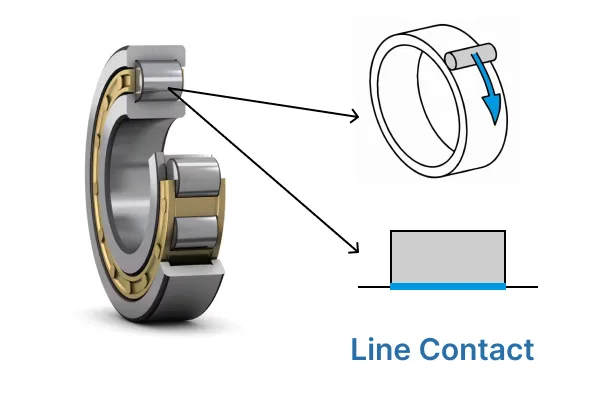
| Contact Type | Line contact with raceways | Point contact with raceways |
| Load Capacity | Handles heavy radial loads and shocks | Supports lighter radial and axial loads |
| Speed Suitability | Lower speed, some types run fast | High-speed applications preferred |
| Friction Level | Higher friction due to line contact | Lower friction from point contact |
| Misalignment Tolerance | Less tolerant, needs precise alignment | More tolerant to misalignment |
| Durability | Longer life under heavy loads | Good life, shorter under heavy stress |
| Typical Applications | Mining, construction, heavy machinery | Motors, bicycles, medical equipment |
| Maintenance | Some types easier to service | Easy to install and maintain |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lasts longer | Lower initial cost |
When you look at roller bearing vs ball bearing, you see a big difference in how they hold weight. Roller bearings touch in a line, so they can hold more weight. Ball bearings touch at one spot, so they move smoother and faster. Knowing these main differences helps you choose the best bearings for your job. Here is a quick chart:
| Aspect | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Speed | Higher | Lower |
| Friction | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Uses | Automotive, aerospace, machinery | Mining, construction, heavy machinery |
Picking the right roller bearing vs ball bearing helps your machines last longer and work better.
Key Takeaways
- Ball bearings use balls that touch at one point, making them spin fast and work well with light loads.
- Roller bearings use rollers that touch along a line, allowing them to hold heavy loads and handle shocks.
- Choose ball bearings for high-speed, smooth, and light-load jobs like motors and fans.
- Pick roller bearings for heavy-duty, slow-speed machines that carry big weights, like construction and mining equipment.
- Always match the bearing type to your machine’s load, speed, and environment to avoid breakdowns and save money.
Roller Bearing vs Ball Bearing Overview
Key Differences
When you look at roller bearing vs ball bearing, you see they work in different ways. Ball bearings have small balls inside. These balls touch the raceways at just one spot. This makes ball bearings spin fast and carry lighter loads. You can find them in things like electric motors and bikes. They are also in some medical machines.
Roller bearings use rollers that look like cylinders, needles, or spheres. These rollers touch the raceways along a line, not just a point. This lets roller bearings hold more weight and take more shock. You see roller bearings in big machines, mining tools, and construction trucks.
Tip: Think about how much weight your machine will carry and how fast it needs to go before you pick a bearing.
Here are the main differences between ball bearings and roller bearings:
- Ball bearings have round balls inside, but roller bearings use rollers shaped like cylinders, needles, or spheres.
- Ball bearings touch the raceways at one spot, while roller bearings touch along a line.
- Ball bearings are better for fast spinning and lighter loads.
- Roller bearings are good for heavy loads and can take more shock.
- Ball bearings can handle some misalignment, but roller bearings need to be lined up just right.
- You find ball bearings in electric motors and bikes. Roller bearings are in mining, construction, and heavy machines.
Quick Comparison Table
This table helps you see the main differences between roller bearing vs ball bearing:
| Aspect | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Element Shape | Spherical balls | Cylindrical, tapered, needle, or spherical rollers |
| Contact Type | Point contact with raceways | Line contact with raceways |
| Contact Area | Small contact area | Larger contact area |
| Load Capacity | Light to moderate radial, axial, and combined loads | Heavy radial loads, high shock resistance |
| Movement Capability | Rotates on multiple axes | Fixed axis of rotation |
| Speed Suitability | High-speed applications | Heavy load, shock-resistant applications |
| Misalignment Tolerance | More tolerant | Less tolerant, needs precise alignment |
| Typical Applications | Electric motors, bicycles, medical equipment, aerospace | Mining, construction, steel mills, power plants |
These differences help you pick the right bearing for your job. Ball bearings are good for speed and smooth movement. Roller bearings are strong and last longer in tough jobs. When you know the differences, you can choose the best bearing for your needs.
Ball Bearings
Design
Ball bearings are made with two rings. These are called the inner and outer race. Small, hard balls roll between these rings in a circle. A cage keeps the balls spaced apart. This setup lowers friction and helps things move smoothly. The table below shows how ball bearings and roller bearings are different in design:
| Feature | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Elements | Spherical balls that roll between inner and outer races. | Cylindrical or barrel-shaped rollers. |
| Components | Inner race, outer race, balls, cage to prevent ball contact. | Inner race, outer race, rollers, cage. |
| Contact Type | Point contact between balls and races, enabling smooth rotation but lower load capacity. | Line contact with larger area, supporting heavier loads but generally lower speeds. |
| Load Types | Handle both radial and axial loads. | Designed mainly for heavy radial loads. |
| Speed and Application | Suitable for high rotational speeds, precision instruments, micro-motors, gearboxes. | Used in heavy machinery, vehicle hubs, and applications requiring high load capacity. |
How They Work
Ball bearings use rolling balls to cut down on friction. Here is how they work: The balls roll between the two rings. Rolling makes less friction than sliding. The cage stops the balls from bumping into each other. Lubrication helps the balls roll better and last longer. The balls can hold both sideways and straight-on loads. This makes ball bearings useful in many ways.
This design helps machines use less energy and stay cooler. Machines run smoother and last longer with ball bearings.
Advantages
Ball bearings have many good points for machines:
- They spin fast and do not make much friction.
- Ball bearings can hold both sideways and straight-on loads.
- It is easy to take care of them because you can add oil easily.
- You can use them in many machines, like motors and skateboards.
- Sensors can help you find problems early and stop breakdowns.
- Ball bearings are great for jobs that need to be very exact and quiet.
The main good things about ball bearings are speed, smooth movement, and easy care.
Disadvantages
There are some things ball bearings cannot do well:
- Too much weight or not enough oil can make them break.
- Dirt or water can get inside and hurt the bearing.
- If you put them in wrong, they may not work right.
- Some types can break at very high speeds if they do not have a cage.
- Too much heat can make the oil bad and cause damage.
You should always put them in the right way and keep them clean and oiled to stop these problems.
Best Uses
Ball bearings are used in lots of places:
- Manufacturing: They help conveyor belts and assembly lines move.
- Robotics: They let robot arms move smoothly.
- Automotive: They are in wheel hubs, gearboxes, and transmissions.
- Medical: They are in surgery tools and scanners.
- Sports: They are in skateboards, bikes, and fishing reels.
- Home: They are in washing machines and swivel chairs.
- Aerospace: They are important for engines and controls.
- Marine: They are used in boat engines and parts.
Deep groove ball bearings are very popular. They can hold both sideways and straight-on loads and work well at high speeds. Ball bearings give smooth, strong, and steady performance in many jobs.
Roller Bearings
Design
Roller bearings look different from ball bearings. They use rollers, not balls. The rollers can be long, round, or shaped like needles. These rollers fit between two rings called races. A cage keeps the rollers spaced apart. Some roller bearings have covers to keep out dirt. This helps them last longer.
- Roller bearings touch in a line, not just one spot.
- The bigger contact area lets them hold more weight.
- There are many types for different jobs, like cylindrical, tapered, spherical, and needle roller bearings.
This design makes roller bearings bigger and stronger than ball bearings. They have more friction, but they can hold more weight and take more hits.
How They Work
Roller bearings work by rolling their rollers between two rings. The rollers touch the rings along a line. This spreads the weight over a bigger area. They can hold more weight and take more shock. The cage stops the rollers from rubbing together. Oil or grease helps them move better and last longer.
Here is a table to show how roller bearings and ball bearings work:
| Aspect | Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Type | Line contact between rollers and raceways | Point contact between balls and raceways |
| Rolling Element Shape | Cylindrical, spherical, tapered, or needle-shaped | Spherical balls |
| Load Capacity | Higher radial load capacity | Lower load capacity |
| Speed Capability | Lower speed, but some types can run fast | Higher speed capability |
| Shock and Misalignment | Better handling of shock and misalignment | More sensitive to misalignment and shock |
Advantages
Roller bearings have many good points. Here are the main ones:
- They can hold heavy loads.
- They last a long time and are strong.
- They can handle bumps and small mistakes in alignment.
- You can adjust them for easier care.
- They save space because of their shape.
These things make roller bearings great for hard jobs.
Disadvantages
Roller bearings have some downsides. They are bigger and heavier than ball bearings. They make more friction, so they may not spin as fast. Some types need extra care if they go fast. You must line them up right to stop problems.
Note: Even with these downsides, roller bearings are best for heavy loads and tough jobs.
Best Uses
You see roller bearings in many places. They work best where machines carry heavy things or face hard work.
- Construction machines like cranes and bulldozers.
- Mining tools such as crushers and conveyors.
- Wind turbines and energy machines.
- Car parts, including wheels and transmissions.
- Robots and machines in factories.
- Special machines in planes and chip factories.
Roller bearings help these machines work well and last longer. As more robots and electric cars are made, strong bearings are needed even more.
Key Differences in Performance
Load Capacity
Roller bearings and ball bearings handle weight in different ways. Roller bearings use rollers that touch the raceway in a line. This spreads the force over a bigger area. Because of this, roller bearings can hold more weight. Ball bearings use balls that touch at just one point. This means they cannot hold as much weight, especially if the load is heavy or there are shocks.
You can see the difference in test results:
| Parameter | Ball Bearings (Self-aligning) | Ball Bearings (Other) | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Maximum Contact Stress | 4600 MPa | 4200 MPa | 4000 MPa |
| Static Load Rating Basis | Permanent deformation limit | Permanent deformation limit | Permanent deformation limit |
| Fatigue Life Exponent (p) | 3 | 3 | 10/3 |
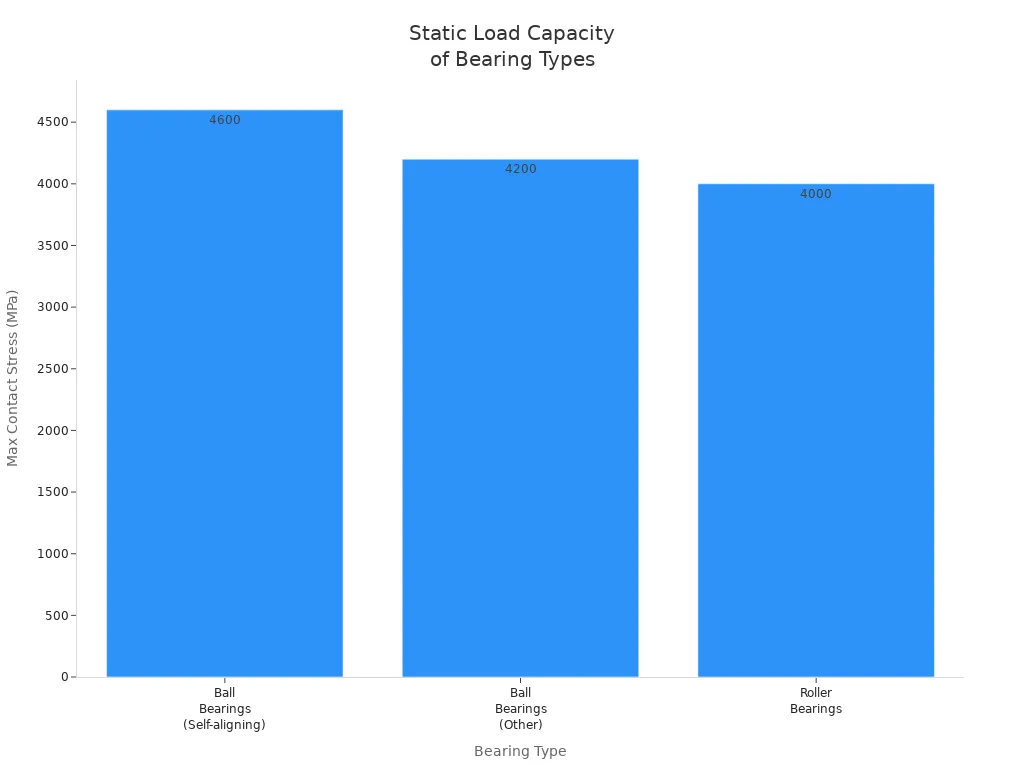
Ball bearings can take higher contact stress, but roller bearings last longer when used again and again with heavy loads. If you need a bearing for a heavy-duty machine, roller bearings are the best for holding weight.
Tip: For machines that carry heavy things or get bumped a lot, pick roller bearings for the best strength.
Speed
How fast a bearing can spin is important for many machines. Ball bearings are good for high speeds. They have low friction and only touch at one point. Roller bearings touch in a line, so they make more friction and heat. This can slow them down.
Here is a table with speed ratings from top brands:
| Bearing Type and Cage Design | Maximum Speed Rating (mm/min) |
|---|---|
| Deep Groove Ball Bearings | Up to 500,000 |
| Angular Contact Ball Bearings | Up to 450,000 |
| Cylindrical Roller Bearings (1 Piece Brass Cage) | Up to 600,000 |
| Cylindrical Roller Bearings (2 Piece Brass Cage) | Up to 550,000 |
| Tapered Roller Bearings (Pin Type Cage) | Around 400,000 |
| Tapered Roller Bearings (Brass Land Riding Cage) | Around 450,000 |
| Full Complement Roller Bearings | Around 170,000 |
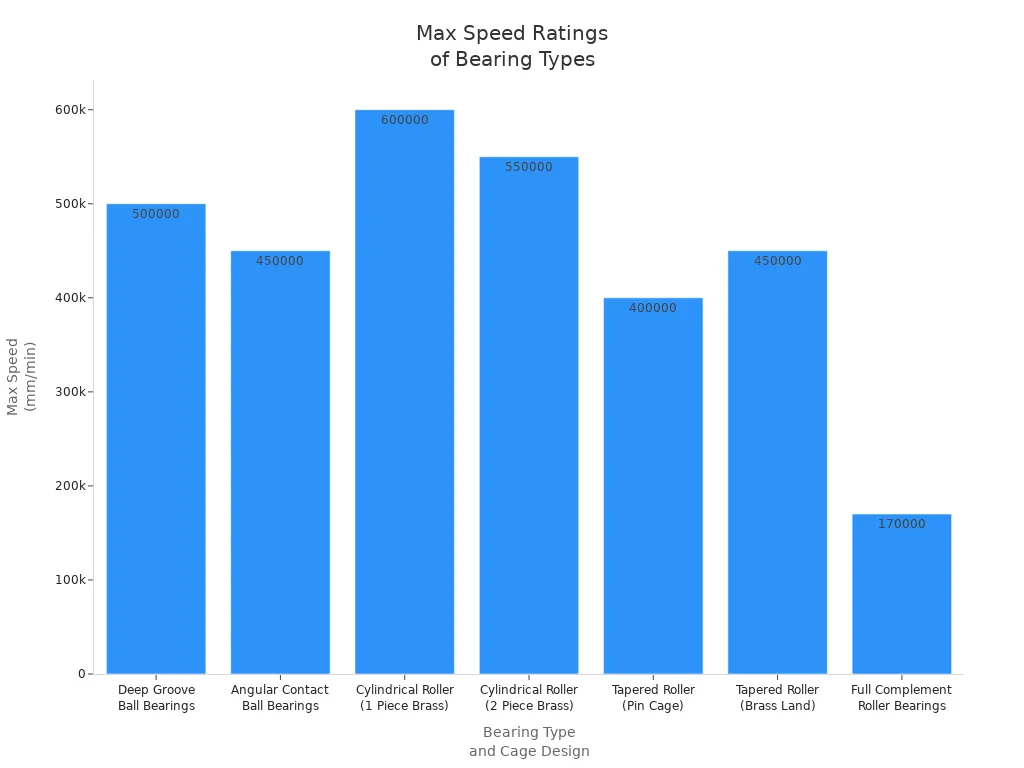
Ball bearings are usually better for fast spinning jobs, like in fans or motors. Some roller bearings can go fast if they have special cages. Most roller bearings are picked for their strength, not their speed. If you want high speed and less friction, ball bearings are the best choice.
Friction
Friction is how much a bearing slows things down and makes heat. Ball bearings have low friction because the balls only touch at one spot. This helps machines move easily and stay cool. Roller bearings touch in a line, so they have more friction. But this also lets them hold more weight.
Here is a table showing friction levels:
| Bearing Type | Friction Coefficient Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearing | 0.001 – 0.0015 | Lower friction due to point contact; suitable for high-speed, low-load applications |
| Roller Bearing | 0.002 – 0.004 | Slightly higher friction due to line contact; supports heavier loads but lower speeds |
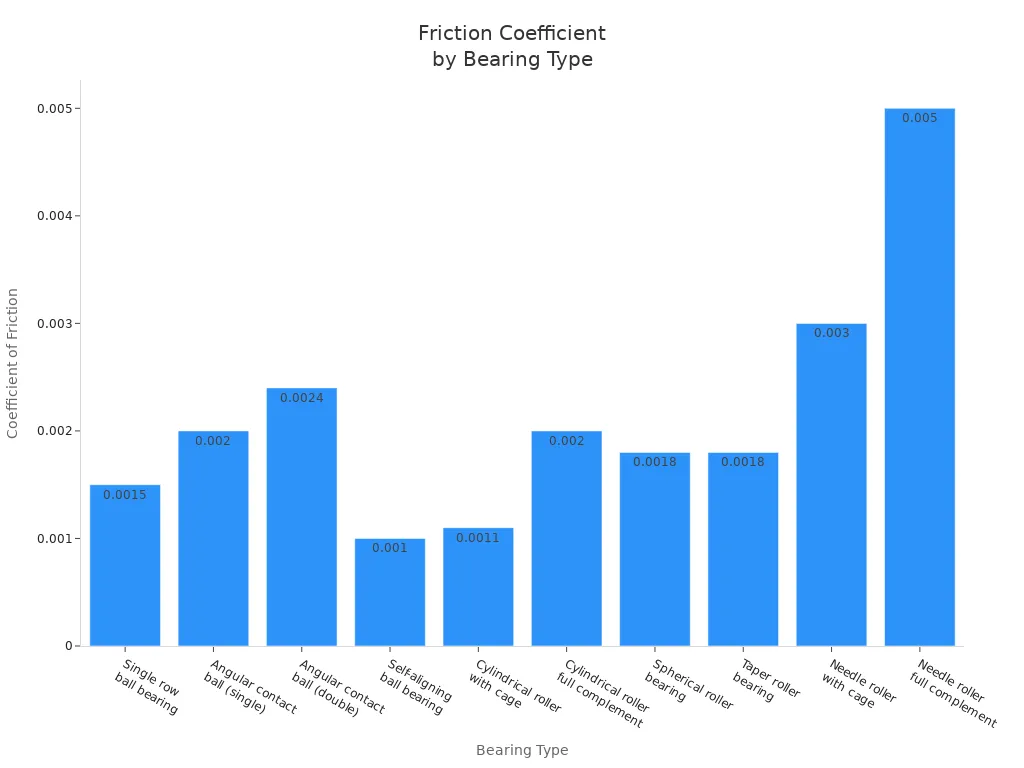
Ball bearings help machines use less energy and make less heat. If you want smooth and easy movement, ball bearings are a good pick. Roller bearings are still strong, but they focus on holding weight, not on low friction.
Durability
Durability means how long a bearing will last while working. Both roller bearings and ball bearings can last a long time if used right. Roller bearings often last longer in hard jobs. This is because they can handle more weight and have a special way to measure life.
Here is a table showing how long bearings can last:
| Operating Condition | Minimum L10 Life (Hours) |
|---|---|
| Intermittent operation, service interruptions allowed | ~8,000 |
| Intermittent operation, reliability important | ~12,000 |
| Continuous 1 shift operation | ~20,000 |
| Continuous 2 shift operation | ~40,000 |
| Continuous 24 hour operation | ~60,000 |
| Continuous 24 hour operation, reliability important | ~100,000 |
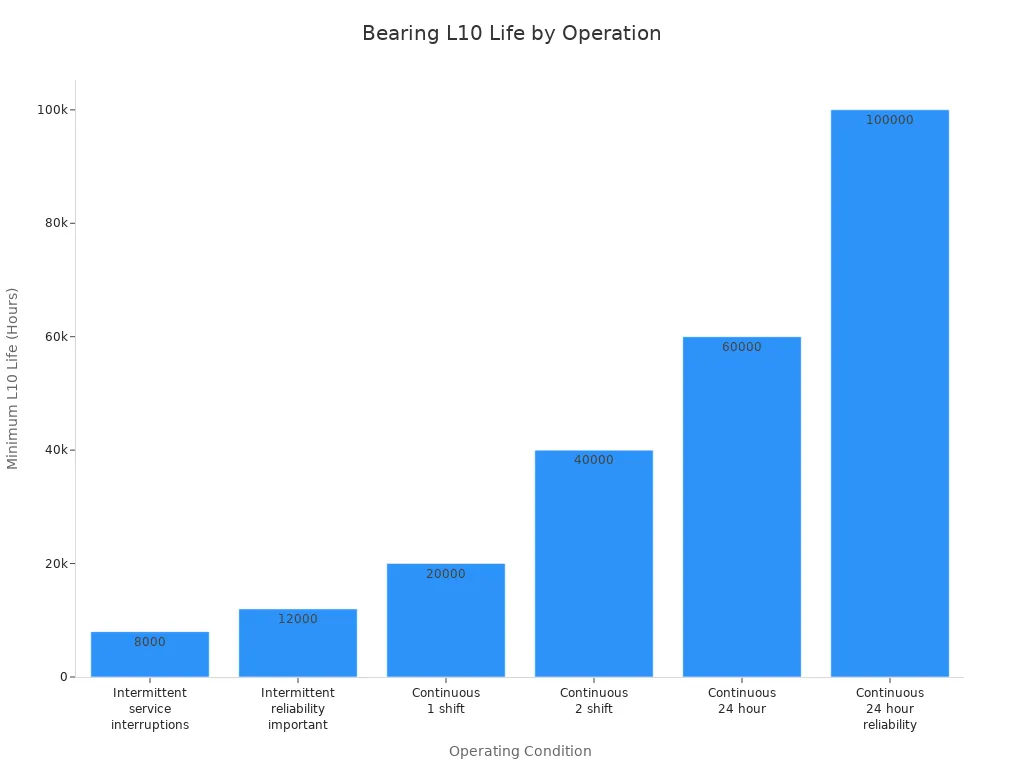
Roller bearings usually meet or beat these numbers, especially in tough jobs. Ball bearings also last a long time, but they may wear out faster if the job is hard. For the longest life in rough places, roller bearings are often the best.
Applications
You need to pick the right bearing for your job. Roller bearings and ball bearings each have jobs they do best.
- Roller bearings are great for heavy machines, mining, building, power plants, and factories. You find them in crushers, conveyors, and wind turbines. They are made for big loads and hard work.
- Ball bearings are best for fast and light jobs. You see them in motors, fans, bikes, and medical tools. They help things move smoothly and with less friction.
Some new types, like microtextured bearings, work better in special cases. For example, microtextures in angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings help lower friction when machines start and stop or move back and forth.
Note: Always think about where you will use the bearing, how much weight it will hold, and how fast it needs to go. Picking the right one helps your machine last longer and work better.
How to Choose
Decision Guide
Choosing the right bearings for your machine can make a big difference in how well it works and how long it lasts. You should look at several important factors before you decide. Here is a simple checklist to help you compare ball bearings and roller bearings:
| Criteria | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Load Type | Light to medium loads | Heavy loads |
| Speed | High-speed applications | Lower speed, high load |
| Precision | High accuracy needed | More rigidity needed |
| Misalignment | Some types allow misalignment | Spherical types handle misalignment |
| Maintenance | Easy to install and maintain | Some types easier to service |
| Environment | Good for clean, dry places | Good for dusty, wet, or harsh places |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, lasts longer |
You should ask yourself these questions:
- What kind of load will the bearing carry?
- How fast does the machine need to run?
- Does the machine need high accuracy or extra stiffness?
- Will the shaft move out of line sometimes?
- Is the area dusty, wet, or very hot?
- How often can you do maintenance?
- What is your budget for bearings?
Tip: Ball bearings work best for high-speed, light-load jobs like fans or motors. Roller bearings are better for heavy-duty machines that run slower but carry more weight.
Common Mistakes
Many people make mistakes when picking bearings. Using the wrong type can cause machines to break early. For example, if you use ball bearings in a heavy machine, they may wear out fast. If you use roller bearings in a high-speed fan, the machine may run slow or get too hot.
Sometimes, people think a bigger or stronger bearing will solve problems. This is not always true. Using the wrong size or type can lower speed ratings or cause other issues. In some factories, fake or wrong bearings have caused machines to stop and even put workers at risk. One plant had to shut down because a fake bearing failed, showing how important it is to choose the right one.
Note: Always follow the machine maker’s advice and use the correct bearing type. Changing the type without checking can lead to more problems.
If you need help choosing, I can help you find the best bearings for your job. Contact TFL Bearings for expert advice and reliable products.
You have learned the big differences between roller bearings and ball bearings.
- Ball bearings touch at one point. This makes them move smoothly and quickly. They work best with lighter loads.
- Roller bearings touch in a line. They can hold heavy loads and take more bumps. But they must be lined up carefully.
- Each type is good for certain jobs. Picking the right bearing for your machine helps stop early breakdowns and saves money on repairs.
If you are not sure what to pick or have a special problem, ask TFL Bearings for expert advice and the best answer.
FAQ
What is the main difference between roller bearings and ball bearings?
You will see that roller bearings use rollers for line contact, which lets them carry heavier loads. Ball bearings use balls for point contact, so they spin faster and work better with lighter loads.
Which bearing should you choose for high-speed machines?
You should pick ball bearings for high-speed machines. Ball bearings create less friction and heat. This makes them ideal for fans, motors, and other fast-moving parts.
Are roller bearings better for heavy-duty equipment?
Yes, you should use roller bearings for heavy-duty equipment. Roller bearings handle bigger loads and absorb more shock. You will find them in construction, mining, and large industrial machines.
Can you use ball bearings and roller bearings in the same machine?
You can use both types in one machine if different parts need different strengths. For example, use ball bearings for fast-moving parts and roller bearings for heavy-load areas.
How do you know which bearing type fits your application best?
Tip: Check your machine’s load, speed, and alignment needs. Ball bearings work best for speed and light loads. Roller bearings suit heavy loads and tough jobs. If you need help, ask TFL for expert advice.




