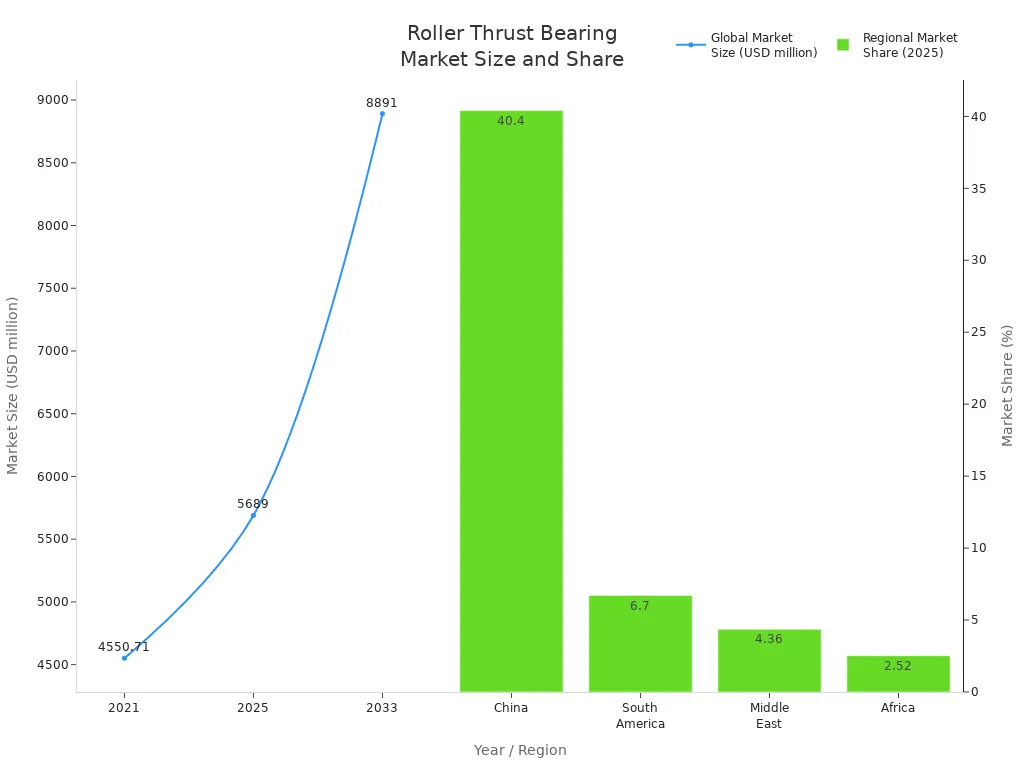
A roller thrust bearing holds up heavy loads that push in one direction. It uses rolling parts to lower friction between moving pieces. You can find thrust roller bearings in many machines. They are in things like car transmissions and industrial robots. These bearings stop metal parts from touching each other. They also take in shocks and spread out the weight. They can handle strong pushing forces and help machines last longer. This makes them very important for machines to work well. The market for thrust roller bearings is growing around the world. Asia Pacific is seeing the most growth, as you can see below:
Key Takeaways
- Roller thrust bearings help machines handle strong pushing forces in one way. They also lower friction so machines can work longer.
- There are different roller thrust bearings for different jobs. Needle rollers fit in small spaces. Cylindrical rollers hold up heavy straight-line forces. Tapered rollers handle both straight and sideways forces.
- A good bearing design uses strong rollers and cages. These parts keep everything lined up. They also help stop parts from wearing out fast. This makes machines work better.
- You should check bearings often and use the right oil or grease. This stops damage and helps machines last longer. It also helps you find problems early.
- Picking the right bearing material and type is important. It helps your machine carry loads well. It also helps your machine work smoothly, even when things get tough.
How Roller Thrust Bearings Work
Axial Load Support
You use thrust roller bearings when you need to hold up heavy forces that push along a shaft. These bearings have rolling parts, like cylindrical or tapered rollers. The rollers help spread the force over a bigger area. This makes the stress lower and cuts down on friction. It helps machines work better and last longer. The way the rollers move, based on the contact angle, lets these bearings handle bigger axial loads than other types.
Tip: If the contact area is bigger, the bearing can hold more weight and will not wear out as fast.
Here is a table that shows how different bearing types support thrust and axial loads:
| Bearing Type | Axial Load Support Characteristics | Comparison to Other Bearings | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Thrust Roller | Can hold high axial loads and is strong; made for axial loads only; not good for high speed | Holds more load and is stronger than ball bearings | Used in machine tool rotary tables and industrial equipment |
| Tapered Roller Thrust | Tapered rollers roll smoothly; can handle both axial and radial loads; holds more thrust than ball bearings | Has a bigger contact area than ball bearings; costs more to make | Used in car wheels and for two-way thrust |
| Spherical Roller Thrust | Can take both radial and axial loads; can fix shaft misalignment; holds the most load of all thrust bearings | Has the highest load rating among thrust bearings | Used in heavy machines and places with misalignment |
| Needle Roller Thrust | Has small rollers; good for high axial loads in small spaces | Fits in small spaces; holds high axial loads | Used in car transmissions and drive shafts |
| Thrust Ball Bearings | Made for low to medium axial loads; small and easy to put together | Holds less load and is less strong than roller types | Used in car transmissions, fans, and home appliances |
Thrust roller bearings are special because they can hold much heavier thrust than ball bearings. You see them in big machines, turbines, and gear sets where strong axial forces happen a lot.
Roller and Cage Design
The way the rollers and cages are made in thrust roller bearings is very important. The rollers can be cylindrical, tapered, or needle-shaped. They roll between two raceways. This rolling lowers friction and spreads the force across the bearing.
- Cages keep the rollers in place and guide them as they move. Most cages are made from strong stuff like steel or tough plastic. Some new designs use brass cages for even better roller control.
- The cage stops the rollers from tilting or moving sideways. This keeps the load even and stops too much wear.
- Cages also help oil get to the rollers, which lowers friction and helps the bearing last longer.
Note: If you use a cage instead of filling the bearing with rollers, it can spin faster and work better.
New thrust roller bearings use materials like ceramics and composites. These make the bearings lighter and stop rust. Some new bearings have sensors inside, so you can check how they are working right away. Better oil systems and careful engineering also help the bearings work better and last longer.
When you pick a roller thrust bearing, you get something made for hard work. Strong rollers and a good cage mean your machines can handle heavy thrust without breaking.
Key Components of Roller Thrust Bearings
Rollers
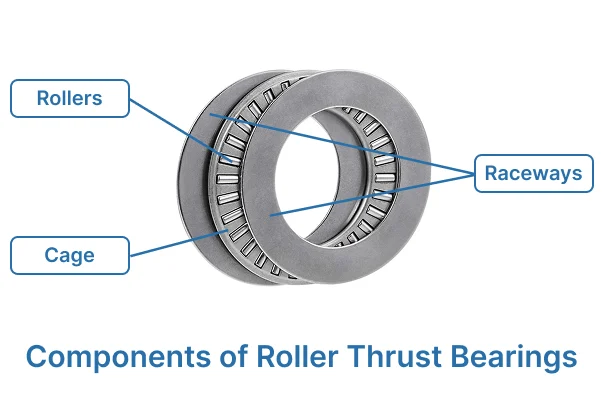
Rollers are the most important part of roller thrust bearings. These small cylinders carry weight and help things move smoothly. Rollers can be made from different materials. The material changes how well the bearing works. Here is a table that shows some common materials and what they do:
| Material Type | Characteristics and Treatment | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| High-alloy steel (e.g., GCr15 bearing steel) | Very hard, gets special heat treatment to make it stronger | Makes the bearing last longer; helps it handle heavy loads; lowers friction and heat; stops damage; keeps the bearing working well at high speeds |
| Advanced ceramic materials | Harder than steel, does not rust, good for tough places | Works well in hot, fast, or rough spots; makes the bearing strong and reliable; lowers shaking and noise; helps the bearing move smoothly |
High-alloy steel rollers help bearings last longer and work under heavy loads. Ceramic rollers are best for tough or fast-moving places.
Raceways
Raceways are the paths where rollers move. The way raceways are shaped helps bearings hold heavy loads. In tapered roller thrust bearings, the shaft washer has a cone-shaped raceway. This shape lets rollers touch the raceway in a long line. It spreads out the weight and keeps the bearing steady. The housing washer can be flat or cone-shaped. Tapered raceways and flanges help guide the rollers and let the bearing hold more weight. These features help bearings line up by themselves and work even if the shaft is not perfect.
- The shaft washer raceway is usually cone-shaped, which spreads out the load.
- Housing washers can be flat or cone-shaped, which helps hold more weight.
- Flanges and lips keep rollers in place and steady.
Cages
Cages keep rollers apart and help them move the right way. A good cage design helps bearings last longer. If the cage is weak or does not fit, it can break fast. If the cage is not lined up, goes too fast, or does not have enough oil, it can get damaged. Shaking and dirt can also hurt the cage. A strong cage stops rollers from slipping and helps them move smoothly. This makes bearings work better and last longer.
Tip: Always use enough oil and keep things clean to stop cage damage and help your bearings last longer.
Types of Thrust Roller Bearings
There are a few main types of thrust roller bearings. Each type has a special design for different loads. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right one.

Needle Roller Thrust Bearing
Needle roller thrust bearings have long, thin rollers. These rollers let the bearing fit in small spaces. They support a lot of weight for their size. This makes them good for small machines. You often find them in car transmissions and drive shafts. They work best at low speeds or when moving back and forth. These bearings do not handle both radial and axial loads well. They are made to support thrust in just one direction.
Tip: If you need a bearing for a tight spot but want it to hold a heavy thrust, needle roller thrust bearings are a good choice.
Cylindrical Roller Thrust Bearing
Cylindrical thrust roller bearings use thick, straight rollers. These rollers give strong support for axial loads in one direction. The big contact area spreads out the force. This helps the bearing wear less and last longer. You see these bearings in many heavy machines. Some places you find them are:
- Automotive transmissions
- Machine tools and textile machines
- Printing presses and paper mills
- Construction equipment like cranes and excavators
- Power plants, such as turbines and generators
- Oil and gas pumps and compressors
- Marine engines and steering systems
- Aircraft landing gear
- Robotics for careful movement
Cylindrical thrust roller bearings work well at slow or medium speeds. They can hold more thrust than needle roller thrust bearings. If your machine needs strong axial support, this type is a good pick.
Tapered Roller Thrust Bearing
Tapered roller thrust bearings use cone-shaped rollers and raceways. This design lets them handle both axial and radial loads. The contact angle spreads out the force. This helps the bearing last longer and run smoothly. You often see these bearings in car wheels and gearboxes. They are also used where the load changes direction.
Here is a table with some main advantages of tapered roller thrust bearings:
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved Load Distribution | The contact angle handles thrust well and lowers friction and wear. |
| Enhanced Rotational Stability | The shape keeps the rollers touching, so the bearing stays steady when loads change. |
| Superior Heat Dissipation | The design helps oil move, keeping the bearing cool and the oil fresh. |
| Exceptional Durability | Strong materials and smart design help the bearing last up to 40% longer than others. |
| Versatile Operating Conditions | Handles both thrust and combined loads in many places and speeds. |
Tapered roller thrust bearings are special because they handle both thrust and radial loads. You get a small solution that saves space and money. You do not need two bearings.
Tandem Tapered Roller Bearing
Tandem tapered roller bearings have more than one row of tapered rollers. All the rollers point the same way. You use this type when one row is not enough, but you cannot make the bearing bigger. Tandem tapered roller bearings give extra thrust support without getting larger. You often see them in gearboxes and heavy presses. They are also in machines that need to carry very high thrust.
Note: If you need more thrust support but cannot use a bigger bearing, tandem tapered roller bearings are the answer.
Comparing Needle, Cylindrical, and Tapered Designs
You might wonder how these types are different. Here is a table to help you see:
| Bearing Type | Load Capacity Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Needle Roller Thrust Bearings | High load for their size; fit in small spaces; best for heavy thrust in compact designs | Car transmissions, drive shafts, small machines |
| Cylindrical Roller Thrust Bearings | Handle very strong axial loads in one direction; large contact area; reduce wear | Heavy machinery, turbines, presses, construction equipment |
| Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings | Handle both axial and radial loads; load capacity depends on contact angle; manage changing forces | Car wheels, gearboxes, machines with combined or changing loads |
Needle roller thrust bearings are best for tight spaces with heavy thrust. Cylindrical thrust roller bearings give the most support for pure axial loads. Tapered roller thrust bearings are the most flexible. They handle both thrust and radial loads in one bearing.
Applications of Thrust Roller Bearings
Automotive
Thrust roller bearings are used in many car parts. They are important in gearboxes. When you drive, gears in the gearbox make strong pushing forces. Thrust roller bearings help hold these forces. They keep the gears working well. Tapered roller thrust bearings are good for this job. They can handle both pushing and sideways forces. Their shape spreads out the force and lowers friction. This helps keep the gearbox cool. It also makes it last longer. Needle roller thrust bearings fit in small spaces in gear parts. They can hold heavy forces even at high speeds. This is why they are great for new cars. You find these bearings where there is not much space but a lot of strength is needed.
Tip: Thrust roller bearings help your car run quietly and well by holding heavy loads in small spaces.
Heavy Machinery
Thrust roller bearings are used in big machines like diggers and mining trucks. These machines have to deal with strong pushing forces every day. The bearings help hold these forces. They also keep moving parts lined up. Here are some ways thrust roller bearings help big machines: They hold strong pushing forces in hard places. They keep spinning parts lined up. This lowers friction and wear. Cylindrical and spherical roller thrust bearings are used for big loads and when things do not line up right. They help machines last longer and work better. They also mean the machines need less fixing, even in tough places.
High-Load Equipment
Thrust roller bearings are used in machines that carry very heavy loads. These bearings must work well for a long time. They need to stay strong even when hit hard. Makers build them to last thousands of hours. Some can work up to 100,000 hours without stopping. The rating life tells you how long a bearing should last. Thrust roller bearings are very stiff and strong. You can pick from cylindrical, tapered, or spherical types. Cylindrical thrust roller bearings use brass cages to be extra tough. Spherical types can handle mistakes when putting them in or if the shaft bends. These things make thrust roller bearings a good pick for hard jobs in factories.
Advantages of Roller Thrust Bearings
High Load Capacity
You need bearings that can handle strong forces in your machines. Roller thrust bearings give you high axial load capacity. This means they can support heavy thrust in one direction without failing. The rollers spread the force over a large area. This design lets you use them in places where you need to hold up big weights. You often see these bearings in heavy machinery and automotive gearboxes. They work well when you need to manage both steady and peak thrust loads.
Tip: If your machine needs to carry a lot of weight in a small space, choose roller thrust bearings for their high axial load capacity.
Durability
You want your bearings to last a long time, even in tough places. Roller thrust bearings are built for durability. Several factors help them stay strong:
- The materials, like chrome steel or ceramics, resist wear and corrosion.
- Good lubrication reduces friction and heat, so the bearing does not wear out fast.
- Special seals keep out dirt and moisture.
- The design lets the bearing handle shocks and vibrations.
- Precision in the parts helps the bearing keep working under stress.
If you use the right grease, you protect your bearings from heat and damage. This means less maintenance and longer service life.
Compact Design
You often need to fit bearings into tight spaces. Roller thrust bearings have a compact design. This lets you use them in places where space is limited. The small size does not lower their strength or performance. You can install them in automotive transmissions or industrial machines without wasting space. The compact shape helps you design machines that are both powerful and efficient.
Note: Compact roller thrust bearings help you save space while still giving you the thrust support your machine needs.
Maintenance and Failure Symptoms
Inspection Tips
You need to check roller thrust bearings often to keep your machines running well. Regular inspections help you find problems early and avoid costly repairs. Here are some tips to guide you:
- Clean all bearing parts before you start. Remove dirt, old grease, and debris.
- Look for signs of wear, rust, or damage. If you see any, replace the damaged parts.
- Use the right amount of grease when you put the bearing back together. Too much or too little can cause trouble.
- Watch the temperature and load during operation. High heat or heavy loads can lead to early failure.
- Handle and store bearings with care. This prevents damage and keeps out moisture.
You should also follow a step-by-step process during inspections:
- Drain oil from the bearing housing and remove bolts.
- Support the end cap to avoid dropping or damaging it.
- Clean the housing inside and out. Remove old gasket material and oil buildup.
- Check each part for wear, alignment, and damage. Write down what you find.
- Reassemble the bearing with new seals and correct bolt torque.
Lubrication intervals depend on how you use the machine. Check the grease or oil based on hours of use and the type of lubricant. Always pick the right oil viscosity for your machine’s temperature and load.
Tip: Cleanliness and proper lubrication are your best tools for long-lasting bearings.
Common Issues
You may notice some warning signs when a roller thrust bearing starts to fail. Early detection helps you fix problems before they stop your machine. Watch for these common symptoms:
- Unusual temperature increases. Bearings that get too hot may have too much friction or not enough lubrication.
- Excessive vibration. This can mean damage, misalignment, or dirt inside the bearing.
- Strange noises. Squealing or grinding sounds often point to wear or broken parts.
- Dirty or contaminated lubricant. Dirt, water, or other particles can cause the bearing to wear out faster.
- Visible damage. Discoloration or marks on the bearing surface show that something is wrong.
- Lower performance. If your machine does not run as smoothly, check the bearings.
You can use tools like temperature probes and vibration analyzers to spot these issues early. Regular checks and quick action help prevent bigger problems and keep your equipment running longer.
Note: Good maintenance means checking for heat, noise, and vibration. This helps you avoid sudden breakdowns and keeps your machines safe.
Custom Thrust Roller Bearings
When Customization Is Needed
Sometimes, machines need custom thrust roller bearings. This happens when the machine faces hard or changing jobs. Standard bearings may not work if loads or speeds change a lot. Custom bearings help your machine work better and last longer.
Here are some times when you might need a custom bearing: Your machine has both steady and sudden load changes. You use things like turbochargers that must work with quick power changes. Your system sometimes runs outside normal limits, like during compressor surges. You want to balance how much weight it holds, lower friction, and keep it cool. You want to stop failures from tough or strange situations. You need a bearing that fits your oil system and cuts down on shaking. Custom thrust roller bearings use special shapes and materials. Engineers use computer models to pick the best size and shape for you. This helps your bearings work well, even in the hardest jobs.
Selecting the Right Bearings
Picking the right custom thrust roller bearing means looking at many things. You want the bearing to fit your machine and last a long time. The table below shows what to check for each type:
| Bearing Type | Key Features and Criteria | Benefits for Special Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Roller Thrust | Handles heavy and impact loads; saves space; easy to mount | Good for big loads and easy maintenance |
| Needle Roller Thrust | Fits in small spaces; uses strong cage; long service life | High stiffness in tight spots; lasts longer |
| Tapered Roller Thrust | Low friction; precise fit; handles heavy and peak loads | Smooth running; handles changing loads |
| Spherical Roller Thrust | Self-aligns; works at high speeds; handles both axial and radial loads | Very high load capacity; works even if misaligned |
You should also think about oil, material, and how the bearing fits. For fast speeds or heavy loads, use synthetic oils and strong materials like ceramics. Make sure the bearing can take heat and shaking. The right bearing keeps your machine safe and working well.
Roller thrust bearings have different types for different jobs. They are small, last a long time, and hold heavy loads. These bearings are important in cars, boats, and farms.
| Types | Key Advantages | Industrial Use |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical, Spherical, Needle, Tapered | Low friction, self-aligning, high load capacity | Automotive, machinery, aerospace |
Picking the right bearing and taking care of it stops big problems. This keeps your machines working well. If you want help or need a special bearing, you can ask TFL Bearings for advice.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a roller thrust bearing?
You use a roller thrust bearing to support heavy forces that push along a shaft. This bearing helps reduce friction and keeps machine parts moving smoothly under strong axial loads.
What types of machines use roller thrust bearings?
You find roller thrust bearings in cars, trucks, heavy equipment, and industrial machines. These bearings work well in gearboxes, turbines, presses, and other places where strong pushing forces happen.
What signs show a roller thrust bearing might fail?
You might notice more noise, heat, or vibration. The machine may not run as smoothly. If you see dirty grease or damaged parts, the bearing could be wearing out.
Tip: Regular checks help you spot problems early and avoid bigger repairs.
What should you look for when choosing a roller thrust bearing?
You should check the load capacity, size, speed rating, and material. Make sure the bearing fits your machine and can handle the forces it will face.