NU and NUP cylindrical roller bearings are different in some ways. They handle axial loads differently and have different designs. NU cylindrical roller bearings only support radial loads. NUP cylindrical roller bearings can support both radial and some axial loads. This is because they have a special collar ring. Engineers must know these differences. Picking the right cylindrical roller bearings helps machines run well. It also helps them last longer. Using the wrong bearing can cause expensive problems.
Key Takeaways
- NU bearings can hold heavy side loads. They let the shaft move back and forth. This is good for machines that get hot or are not lined up right.
- NUP bearings can hold heavy side and end loads. They keep the shaft in one place. This is best for big machines that need the shaft to stay still.
- Picking the right bearing stops machine damage. It helps the machine work better and last longer. The bearing must match the load and movement needed.
- NU and NUP bearings are not the same. You must pick the right one. Choose based on if the shaft should move or stay still when working.
- Taking care of bearings is important. Use the right oil and seals. This stops problems like getting too hot, wearing out, or getting dirty.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings Overview
Structure and Function
Cylindrical roller bearings are important in many machines. They use cylindrical rollers to help things move. The rollers are between an inner ring and an outer ring. A cage keeps the rollers spaced out. This design lets the rollers touch the raceways in a line. Because of this, they can hold heavy radial loads. The rings can come apart, so it is easy to put them in or take them out.
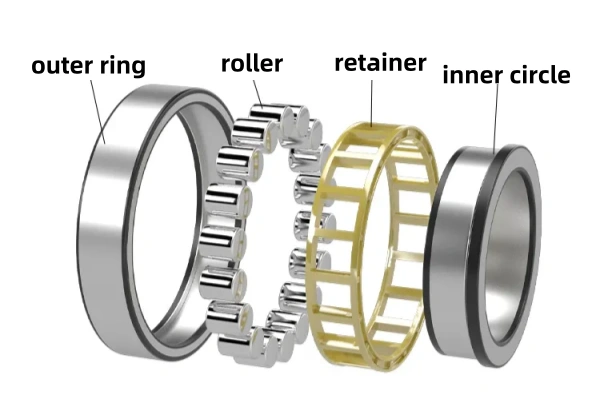
Key structural features include:
- Cylindrical rollers placed between the inner and outer rings
- A cage that keeps the rollers spaced out
- Fixed lips or collar rings that guide the rollers
- Special shapes on rollers and raceways for better oil flow and pressure
Single-row cylindrical roller bearings are used the most. These bearings can hold heavy radial loads. They also work well when things move fast. But they do not support much axial load. They also cannot fix misalignment well. Ball bearings are different because they use balls. Ball bearings can handle other loads.
Common Uses
Cylindrical roller bearings are used in many industries. They work well when things move fast or carry heavy loads. Some common uses are:
- Machine tool spindles
- Traction motors
- Conveyor systems
- Automotive transmissions and suspensions
- Gearboxes, pumps, and compressors
Single-row cylindrical roller bearings are used in machine tool spindles and conveyor systems. NU-type bearings are good for high-speed jobs. NUP-type bearings are best for tough jobs like steel and mining. Engineers pick cylindrical roller bearings because they are strong and reliable. They also work well in hard conditions.
NU Type Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Design Features
NU type cylindrical roller bearings have a special structure. The outer ring has two shoulder lips. The inner ring does not have any lips. This design lets the shaft move back and forth. The rollers sit between the rings. The outer ring shoulders guide the rollers. A cage keeps the rollers in place and spaced out. Some brands like INA and SKF make stronger types. These have bigger and longer rollers for more strength. The bearings come apart easily. This makes them simple to put in or take out. Cages can be made from steel, brass, or polyamide resin. These materials help the bearing work in many machines.
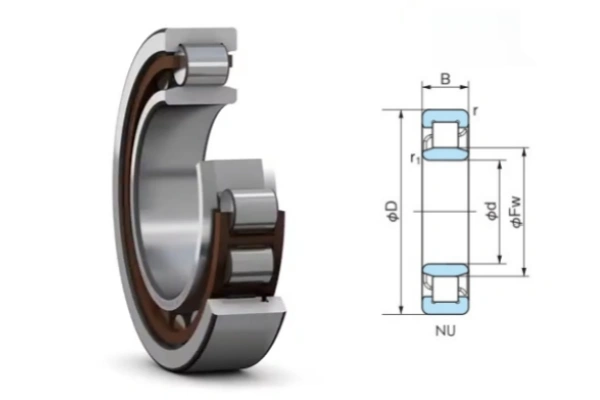
Note: NU type cylindrical roller bearings are best for electric motors, gearboxes, and machines where heat or misalignment can happen.
Radial Load Capacity
NU type cylindrical roller bearings can hold heavy radial loads. The rollers touch the raceways in a straight line. This spreads out the force and makes them stronger. For example, the NU 230 ECJ model can hold up to 114,750 pounds-force for moving loads. It can also hold 135,000 pounds-force for still loads. This high strength makes these bearings good for tough jobs.
Axial Displacement
NU type cylindrical roller bearings let the shaft move both ways. The two shoulder lips on the outer ring help with this. The inner ring does not have lips. This makes the bearing act like a floating bearing. It can handle changes in length from heat or misalignment. The shaft can move while the outer ring stays still. This helps protect machines from damage when parts get bigger or move during use.
NUP Type Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Structure and Collar Ring
NUP type cylindrical roller bearings have a special design. The outer ring has flat ribs. The inner ring has one fixed rib and a loose collar ring. This collar ring is also called a loose thrust collar. It fits next to the inner ring and gives extra support. The table below shows how NU and NUP types are different:
| Bearing TypeOuter Ring RibsInner Ring RibsAxial Movement Capability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NU | Double ribs | No ribs | Lets the shaft move both ways; rings can slide |
| NUP | Flat ribs (single rib) | Single rib + loose rib washer | No movement between rings; stops shaft from sliding; holds shaft in place both ways |
This design lets NUP type cylindrical roller bearings hold the shaft in place both ways. They are good for jobs where the shaft must stay in one spot.
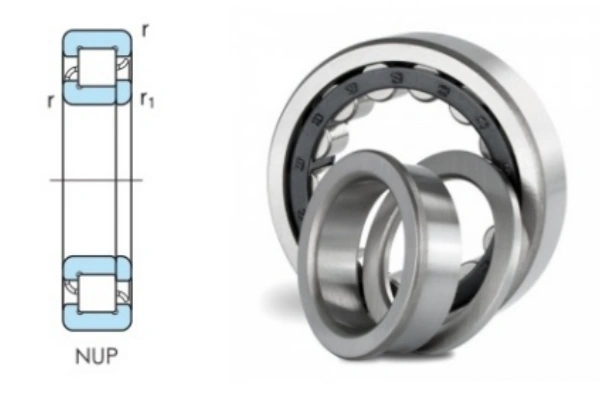
Axial Load Support
The collar ring in NUP type cylindrical roller bearings is very important.
- The collar ring works with the fixed rib to help hold loads from both sides.
- This makes NUP type cylindrical roller bearings better at holding axial loads than NU types.
- You can take the inner ring out of the outer ring, so it is easy to put together or take apart.
- These bearings help guide the shaft and are good for machines that need to be exact.
For example, the NUP 2328E model can hold up to 180.0 kN of axial load and 1,380 kN of static load. This high strength makes NUP type cylindrical roller bearings good for heavy and exact jobs.
Application Scenarios
NUP type cylindrical roller bearings are best when the shaft must not move sideways. Big machines, gearboxes, and rolling mills need this control. These bearings are also used in:
- Machines like conveyor systems, lathes, and milling machines
- Car parts such as engines, transmissions, and wheel hubs
- Airplane and defense parts, like landing gear and turbine engines
- Lifting machines, pumps, and compressors
Engineers pick NUP type cylindrical roller bearings when they need to hold both radial and axial loads. They also use them when the shaft must stay in one place for safe and good work.
Choosing the right bearing is very important for machines. NU, NUP, and N type cylindrical roller bearings each have special features. Knowing how they are different helps engineers pick the best one for the job.
Comparison Table
| Bearing Type | Structure | Axial Displacement Capability | Axial Guidance Function | Load Capacity | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NU | Outer ring with two ribs, inner ring without ribs | Lets the shaft move both ways | Non-locating | Handles heavy radial loads | Electric motors, gearboxes, conveyor systems |
| N | Inner ring with two ribs, outer ring without ribs | Lets the shaft move both ways | Non-locating | Handles heavy radial loads | Pumps, compressors, high-speed machines |
| NUP | Outer ring with two ribs, inner ring with one fixed rib and one loose collar ring | Does not let the shaft move | Locating (guides shaft both ways) | Handles heavy radial and some axial loads | Gearboxes, rolling mills, heavy-duty machines |
Note: Cylindrical roller bearings without ribs on the inner or outer ring, like NU and N types, let the shaft slide back and forth. This makes them good as free end bearings. NUP type cylindrical roller bearings stop the shaft from moving and guide it both ways, so they act as locating bearings.
Key Differences Explained
Structure
- NU type cylindrical roller bearings have two ribs on the outside ring and none on the inside ring. This lets the shaft slide both ways.
- N type cylindrical roller bearings have two ribs on the inside ring and none on the outside ring. This also lets the shaft move both ways.
- NUP type cylindrical roller bearings have two ribs on the outside ring, one rib on the inside ring, and a loose collar ring. This stops the shaft from sliding and helps guide it.
Axial Load Handling
- NU and N type cylindrical roller bearings do not hold axial loads. They let the shaft get longer or shorter when it gets hot or cold.
- NUP type cylindrical roller bearings can hold axial loads both ways. The collar ring and ribs keep the shaft in place. This is good when the shaft must stay in one spot.
- NJ type cylindrical roller bearings hold the shaft in one direction. NUP type bearings guide the shaft both ways.
Load Capacity
- All three types can hold heavy radial loads. NU and N type cylindrical roller bearings are best when the shaft needs to move and the load is heavy.
- NUP type cylindrical roller bearings can hold both heavy radial and some axial loads. This makes them good for tough jobs.
- Double-row bearings can hold even more load and are more stable. Single-row cylindrical roller bearings are used for lighter jobs.
- Full complement bearings do not use a cage. They can hold more load but may not work as fast.
Typical Use Cases
- NU type cylindrical roller bearings are used in electric motors, gearboxes, and conveyor systems where the shaft must move.
- N type cylindrical roller bearings are used in pumps, compressors, and fast machines that need the shaft to move.
- NUP type cylindrical roller bearings are used in gearboxes, rolling mills, and big machines where the shaft must stay still.
- Engineers use single-row bearings for medium loads and speeds. Double-row and full complement bearings are for bigger loads and harder jobs.
Additional Notes
- NU bearings with L-section rings can partly stop the shaft from moving on one side.
- NJ type cylindrical roller bearings and NF type cylindrical roller bearings give other ways to guide the shaft. NJ type holds the shaft one way. NF type gives similar help.
🛠️ Tip: Always pick the bearing that matches the machine’s load and movement needs. Using the wrong bearing can break the machine or stop it from working.
Choosing the Right Bearing Type
Selection Criteria
Picking the right bearing type helps machines work well and last longer. Engineers need to think about a few key things when picking between NU, NUP, and N type bearings. The table below shows the main points:
| Criteria | NU Type | N Type | NUP Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial Load Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Axial Load Support | No | No | Yes (both directions) |
| Axial Displacement Capability | Allows both directions | Allows both directions | No (fixes shaft axially) |
| Typical Use | Free-end bearing | Free-end bearing | Fixed-end bearing |
| Shaft Expansion Accommodation | Yes | Yes | No |
Engineers should pick the bearing type based on how the load pushes and if the shaft needs to move. NU and N types are best when the shaft must get longer or shorter, like in machines that get hot or cold. NUP type bearings keep the shaft in one spot and can hold loads from both sides, so they are good for places where the shaft should not move.
Note: Always check how much load the bearing will hold and if the shaft needs to move before picking a bearing. Doing this stops problems like parts not lining up or breaking early.
Application-Based Tips
Different machines and places need special bearing features. These tips help engineers choose the right one:
- For radial loads, NU and N types give strong support and let the shaft move. These are good for conveyor systems and pumps.
- For axial loads, NUP type bearings keep the shaft steady and in place. Use these in gearboxes and rolling mills.
- If you have both radial and axial loads, you need bearings that can handle both. NUP type bearings are good for this.
- If the shaft moves because of heat or parts not lining up, use bearings that let it move. NU and N types are best for this.
- Fast-moving machines need bearings with cages and the right oil. This helps stop too much rubbing and keeps them cool.
- If there is not much space or you need a special fit, you might need single-row or double-row bearings. Always check the space before picking.
🛠️ Tip: Using the right oil and seals keeps dirt and water out of the bearing. This helps the bearing last longer and need less fixing.
Common Mistakes
Picking the wrong bearing can cause big problems. Here are some common mistakes and what happens:
- Using a bearing that cannot hold the load makes it wear out fast and break.
- Not matching the bearing to how the shaft moves causes parts to not line up and shake.
- Not following speed rules makes the bearing get too hot and break, especially in fast machines.
- Not using enough oil makes the bearing rub too much and not last long.
- Letting dirt or water in the bearing makes it rust and get damaged inside.
- Putting too much weight on the bearing or fitting it wrong can crack or bend it.
- Not checking how tight or loose the bearing is can make it too wobbly or too tight.
⚠️ Alert: Always follow the rules for your job and check everything before putting in a bearing. Mistakes can stop machines and cost a lot to fix.
NU and NUP cylindrical roller bearings are not the same. NU bearings let the shaft move and only hold radial loads. NUP bearings keep the shaft in place and hold both radial and some axial loads. Picking the right bearing stops early breakdowns and saves money on repairs. It also helps machines work longer without stopping. Engineers often want to know about how much load each type can hold and if they can swap types. TFL Bearings gives expert help and connects people to more resources. Choosing the right bearing helps machines run well and last longer.
| Frequently Asked Question | Summary of Answer |
|---|---|
| How to choose the right type? | Use NU for radial loads and movement. Use NUP for radial and axial loads when you need to keep the shaft in one spot. |
| Which type for high axial loads? | NUP bearings are better for higher axial loads. |
| Are types interchangeable? | Not always. You must pick based on what the machine needs. |
| How to select N or NU types? | Pick by how much the shaft and seat can grow or shrink. Neither type holds axial loads. |
🛠️ Engineers can get help and advice from TFL Bearings and other trusted partners in the industry.
FAQ
What is the main difference between NU and NUP cylindrical roller bearings?
NU bearings let the shaft slide back and forth. NUP bearings keep the shaft still and hold loads from both sides. This happens because their rings and collars are made differently.
Can engineers use NU and NUP bearings interchangeably?
Engineers should not swap these bearings. NU bearings are for when the shaft needs to move. NUP bearings are for when the shaft must stay in one spot. Always pick the bearing that matches how the machine works.
Which bearing type handles higher axial loads?
| Bearing Type | Axial Load Support |
|---|---|
| NU | No |
| NUP | Yes (both ways) |
NUP bearings can hold more axial load. NU bearings only hold radial loads.
When should engineers choose N type cylindrical roller bearings?
N type bearings are good when the shaft needs to move and only radial loads are there. These bearings are used in pumps, compressors, and fast machines that need the shaft to slide.
How does temperature affect bearing selection?
High heat can make shafts get bigger. NU and N type bearings let the shaft move when this happens. NUP bearings do not let the shaft move, so use them only if you need to guide the shaft.





