Comparing Ceramic and Stainless Steel Bearings in Harsh Conditions
Explore key differences between ceramic and stainless steel bearings.
| Features | Ceramic Ball Bearings | Stainless Steel Ball Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Withstands up to 1200°C, maintains strength. | Effective up to 300°C, needs special grease. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and saltwater fully. | Good, resists rust in mild conditions. |
| Load and Speed | Ideal for high speed, moderate to high load. | Handles high load, moderate speed well. |
| Durability | Very high, lasts longer with less wear. | High, requires proper care and lubrication. |
| Maintenance Needs | Low, less lubrication and longer intervals. | Moderate, regular lubrication needed. |
| Cost | Higher upfront, lower total cost over time. | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance expenses. |
| Electrical Insulation | Yes, provides electrical insulation. | No, does not insulate electrically. |
| Weight | Lighter, less centrifugal force at speed. | Heavier, more heat and vibration. |
| Applications | Used in aerospace, wind energy, EVs. | Common in food, medical, marine industries. |
When you select bearings for extreme environments, ceramic ball bearings often offer superior reliability. Ceramic bearings, especially those made from silicon nitride, resist high temperatures, corrosion, and wear much better than steel bearings. Extreme environments include high temperatures, corrosive chemicals, high speeds, and heavy loads. Material choice is crucial because environmental conditions can reduce a bearing’s lifespan by up to 90%. The table below shows that ceramic bearings have lower density, higher hardness, and less thermal expansion than steel bearings, which results in better performance in demanding conditions.
| Material | Density (kg/m³) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10⁻⁶ K⁻¹) | Hardness (Rockwell Rc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Nitride | 3200 | 320 | 3.2 | 80 |
| AISI M-50 Steel | 7900 | 200 | 11.9 | 60 |
Key Takeaways
- Ceramic ball bearings handle extreme heat up to 1200°C and resist corrosion better than stainless steel, making them ideal for harsh environments.
- Stainless steel bearings offer strong corrosion resistance and hygiene, fitting well in food, medical, and moderate conditions.
- Ceramic bearings run cooler and smoother at high speeds with less maintenance, while steel bearings excel under heavy loads at moderate speeds.
- Though ceramic bearings cost more upfront, they last longer and reduce maintenance costs over time, providing better long-term value.
- Choose bearings based on your environment and needs: ceramic for extreme heat, corrosion, and speed; stainless steel for hygiene, moderate conditions, and heavy steady loads.
Extreme Environments
High Temperatures
You often face high temperature challenges when choosing bearings for demanding environments. Ceramic ball bearings, especially those made from silicon nitride, can handle much higher temperatures than stainless steel bearings. For example, silicon nitride bearings keep their strength above 350 MPa even at 1200°C. Stainless steel bearings, like those made from AISI 440C, usually work best up to 288°C. The table below shows typical temperature ranges for different bearing materials and lubricants:
| Temperature Range (°C) | Bearing Material | Lubrication Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 120 | Standard steel/ceramic | Conventional grease/oil | Normal operation |
| 150 to 350+ | High-temp ceramic/steel | High-temp grease, solid lubes | Special materials needed |
| Up to 1200 | Silicon nitride ceramic | Self-lubricating or dry running | Maintains strength at extreme temperatures |
Ceramic bearings give you better performance in high temperature settings because they resist heat and do not expand as much as steel.
Corrosive Conditions
Corrosive environments can quickly damage bearings. You need to consider how each material stands up to chemicals and moisture. Stainless steel bearings offer excellent corrosion resistance, especially in food, medical, or marine settings. Ceramic bearings, however, do not rust or corrode at all, even in harsh acids or salty water. The table below shows how corrosion rates are measured:
| Severity Level | Description | Copper Corrosion Rate (Å/month) |
|---|---|---|
| G1 (Mild) | Well controlled; corrosion not a factor | < 300 |
| G2 (Moderate) | Measurable corrosion; may affect reliability | < 1000 |
| G3 (Harsh) | High chance of attack; special equipment needed | < 2000 |
| GX (Severe) | Only special equipment survives | ≥ 2000 |
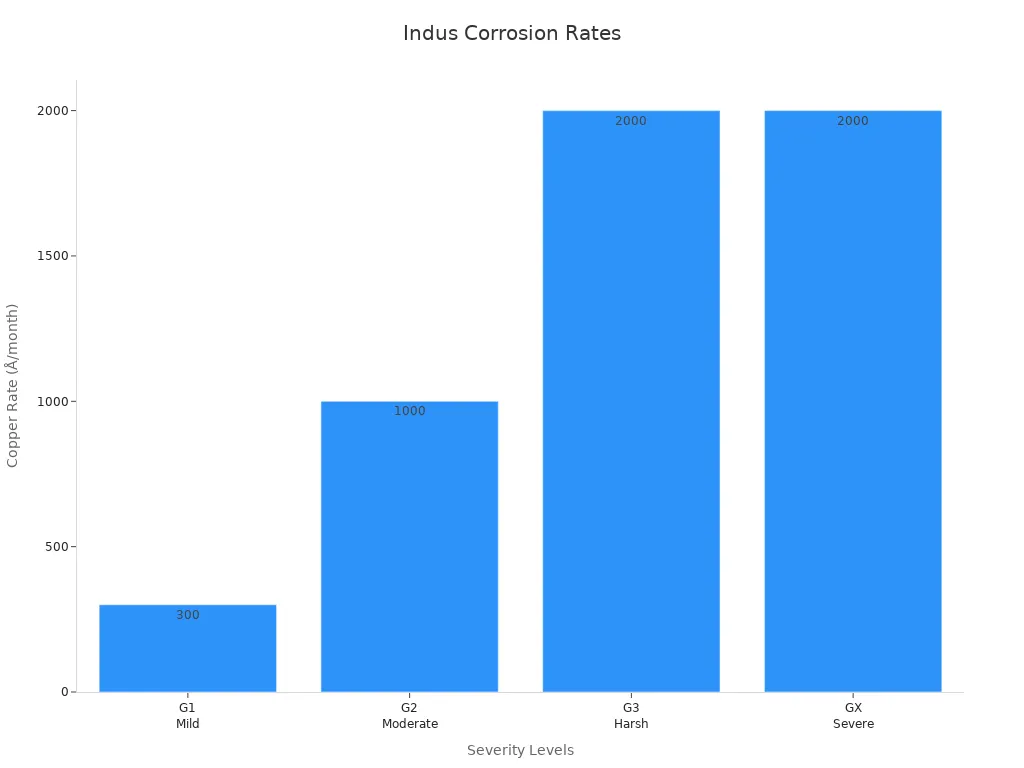
Ceramic bearings work best in the most severe corrosive conditions, while stainless steel bearings are a strong choice for moderate environments.
High Speed and Load
When you operate at high speed or under high load, bearing choice becomes even more important. Ceramic bearings have a lower density, so they generate less heat and vibration at high speed. This helps them last longer and run smoother. Stainless steel bearings can handle high load well, but they may wear out faster at very high speeds. Engineers use special tests, like root mean square (RMS) vibration and acceleration fault indicators, to check bearing health under these conditions. You can see that both types have strengths:
- Ceramic bearings: Best for high speed, less heat, and longer life.
- Stainless steel bearings: Good for high load and steady operation.
You should match the bearing type to your specific needs for speed and load to get the best results.
Ceramic Ball Bearings
Properties
When you compare ceramic ball bearings to stainless steel bearings, you notice several key differences. Ceramic bearings, especially those made from advanced ceramic materials like silicon nitride, have a much lower coefficient of friction. This means you get reduced friction and less heat during operation. You also benefit from high hardness and excellent wear resistance. Full ceramic bearings can handle temperatures up to 1200°C, while steel bearings start to lose strength above 300°C. These advanced ceramic materials do not rust or corrode, even in harsh chemicals or salty water. You also get electrical insulation, which protects your equipment from electrical damage.
Manufacturers use hot isostatic pressing (HIP) and gas pressure sintering (GPS) to make these ceramic bearings. These processes create dense, strong, and reliable bearing balls. The unique microstructure of silicon nitride gives you a product that is both tough and lightweight. Compared to steel, ceramic bearings have less than half the density, which means less centrifugal force and higher speeds.
Note: The lower coefficient of friction and self-lubricating properties of ceramic bearings help you achieve longer service life and less maintenance.
Applications
You find ceramic ball bearings in many extreme environments. They are common in applications within the automotive and aerospace industries, wind energy, and electric vehicles. In aerospace, ceramic bearings reduce weight and withstand rapid temperature changes. In wind turbines, they handle heavy loads and continuous rotation, improving reliability and reducing downtime. You also see ceramic hybrid bearings in high-speed machine tools and electric motors, where they prevent electrical corrosion.

Here is a table comparing performance metrics:
| Performance Metric | Ceramic Bearings | Steel Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Friction Reduction | Up to 80% less | Standard |
| Service Life | 3-10x longer | Standard |
| Max Operating Temp (°C) | 1200 | 300 |
| Weight | Less than half | Standard |
| Electrical Insulation | Yes | No |
The market for advanced ceramic materials continues to grow. Full ceramic zirconia bearings and ceramic hybrid bearings are now used in more industries. You see a steady increase in demand, especially as new energy and aerospace sectors expand.
Steel Ball Bearings
Properties
When you look at steel ball bearings, you see a strong focus on durability and versatility. Most steel bearings use stainless materials like AISI 440C, 304, or 316. Each grade offers unique benefits. AISI 440C gives you high hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy loads. AISI 304 and 316 provide excellent corrosion resistance, especially in wet or chemical-rich environments. You can use steel bearings in temperatures from -60°C up to 300°C, and with special cages, they can handle even higher temperatures.
Stainless steel bearings resist rust and corrosion, which is important in food, medical, and industrial settings. You can wash these bearings without worrying about rust. They also work well without lubrication at low speeds and loads. The hygiene of stainless steel bearings makes them a top choice where cleanliness matters.
Here is a table comparing the main stainless steel grades:
| Material Grade | Corrosion Resistance | Hardness & Wear Resistance | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Good (mild acids, moisture) | Moderate | Food, medical, light industry |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Excellent (marine, chlorides) | Moderate | Marine, chemical, pharmaceutical |
| 440C Stainless Steel | Moderate | High | Heavy load, abrasive environments |
Tip: You should choose the grade based on your environment and load needs.
Applications
You find steel ball bearings in many industries because of their reliability. Stainless steel bearings are essential in food processing, medical devices, and industrial machinery. Their corrosion resistance and hygiene help prevent contamination in sensitive environments. In the medical sector, you see them in imaging systems, surgical robots, and diagnostic tools. The food industry uses them for equipment that must stay clean and rust-free.

The global thin section bearing market, which relies heavily on stainless steel, is growing fast. It is expected to reach $2.1 billion by 2032. This growth comes from the need for durable, hygienic bearings in food, medical, and industrial applications. Studies show that stainless steel bearings can reduce E. coli by over 90% after 24 hours, which supports their use in hygiene-critical areas.
You also benefit from easy maintenance. Stainless steel bearings resist corrosion and last longer, even in harsh conditions. Field tests show that 440C stainless steel bearings have twice the fatigue life of regular steel bearings in corrosive environments. This means you spend less time and money on replacements and repairs.
Temperature Resistance
Ceramic Bearings
You can rely on ceramic bearings when you need top performance in extreme temperatures. These bearings, especially those made from silicon nitride, keep their strength and shape even when exposed to heat as high as 1200°C. You will notice that ceramic bearings do not expand much when heated. This low thermal expansion means they stay stable and precise, even during rapid temperature changes.
Laboratory tests show that ceramic bearings can handle both high and low temperatures. For example, in a high-temperature dynamic test, engineers ran bearings in a rotor system at temperatures up to 1500°C. The bearings kept working well, even with fast heating and in an oxidizing atmosphere. In another set of experiments, full ceramic bearings made of silicon nitride performed under heavy loads and high speeds. The temperature stayed stable around 55°C, even when the load reached 3900 N and the speed hit 10,000 rpm. This shows that ceramic bearings can manage heat buildup and keep running smoothly.
You also get great results in cold environments. Tests show that ceramic bearings work well in cryogenic conditions, down to 93 K (about -180°C). The friction torque changes as the temperature drops, but the bearings adapt and keep working. This makes ceramic bearings a smart choice for aerospace, wind energy, and electric vehicles, where you face both hot and cold extremes.
You can see from the data below that ceramic bearings have a much lower coefficient of thermal expansion than steel bearings. This means they resist changes in size and shape when the temperature shifts.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10^-6/K) | Corrosion Resistance Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Nitride | 20 – 30 | 3.2 – 3.5 | 9 |
| Bearing Steel | 30 – 50 | 12 – 13 | 5 |
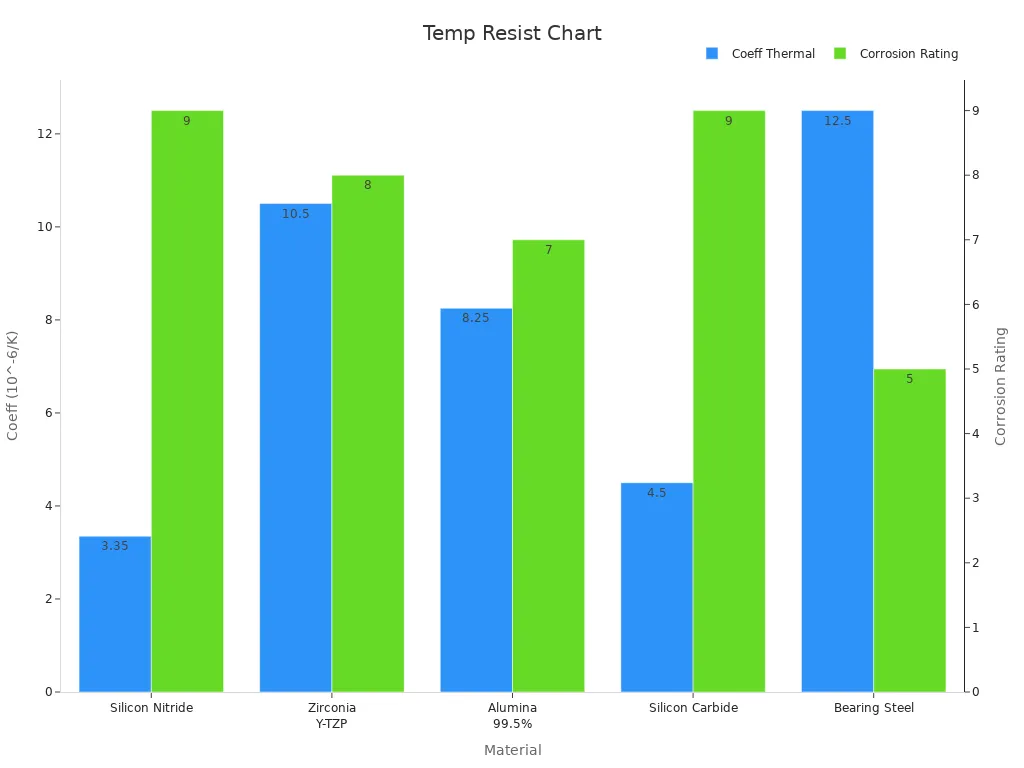
You also benefit from advanced coatings and cage materials. For example, SlipCoat coatings add a thin lubrication film, helping ceramic bearings resist heat and wear. PEEK and sheet metal cages last longer under high temperatures, while PTFE cages may fail early in dry running. These improvements make ceramic bearings even more reliable in harsh environments.
Note: Ceramic bearings often last longer and need less maintenance because they resist heat, wear, and corrosion better than steel bearings.
Steel Bearings
Steel bearings also offer good temperature resistance, but you will see some limits compared to ceramic bearings. Most stainless steel bearings, such as those made from AISI 440C, work best up to 300°C. With special cages and high-temperature grease, you can push this limit higher, but not as far as ceramic bearings.
In laboratory tests, steel bearings perform well under normal and moderately high temperatures. For example, a high-temperature dynamic test bench showed that steel bearings could handle temperatures up to 1500°C for short periods. However, you may notice changes in hardness and strength as the temperature rises. Steel bearings expand more than ceramic bearings when heated. This higher thermal expansion can lead to changes in fit and performance, especially in precision applications.
You will also find that steel bearings need more frequent lubrication at high temperatures. Without proper lubrication, they may wear out faster or even fail. In contrast, ceramic bearings can run dry or with minimal lubrication, making them better for environments where grease or oil is hard to use.
Steel bearings still provide reliable service in many industries. You can use them in food processing, medical devices, and industrial machinery, where temperatures stay within their safe range. Their ability to resist rust and corrosion also helps them last longer in wet or chemical-rich environments.
To sum up, you should choose ceramic bearings if you need the highest temperature resistance and stability. Steel bearings work well for most standard applications, but they may not match the performance of ceramic bearings in extreme heat.
Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic Ball Bearings
You will notice that ceramic ball bearings, especially those made from silicon nitride, stand out in harsh environments. These bearings show nearly 100% chemical inertness in many corrosive media. When you use them in acidic or salty conditions, they do not rust or corrode, even after long exposure. In laboratory tests, steel bearings developed rust within days in acidic solutions, but silicon nitride ceramic balls showed no corrosion at all. This means you can rely on ceramic bearings for a much longer service life in chemical plants or marine settings.
- Silicon nitride ceramic balls last up to three times longer than steel balls in chemical plant applications.
- You do not need to replace them as often, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
- Their thermal stability helps prevent micro-cracks and corrosion sites, even when temperatures change quickly.

You can see the difference in corrosion resistance by looking at standardized salt spray test results. This test exposes bearing materials to a 5% sodium chloride spray for 96 hours at 95°F. The table below shows how much of the surface rusts over time:
| Material Type | 8 hr | 16 hr | 24 hr | 48 hr | 72 hr | 96 hr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52100 Steel (plain) | 50% | 90% | 95% | 99% | 99% | 99% |
| 440C Stainless Steel | 10% | 10% | 25% | 60% | 70% | 88% |
| Chromed 52100 Steel | 0% | 0% | 1% | 10% | 23% | 63% |
| 52100 Steel (greased) | 25% | 75% | 90% | 99% | 99% | 99% |
| 440C Stainless (greased) | 0% | 1% | 5% | 20% | 25% | 43% |
| Chromed 52100 (greased) | 0% | 0% | 0% | 4% | 6% | 8% |
You can see that ceramic bearings do not appear in the table because they show no visible corrosion, even after extended testing. This makes them the top choice for the most aggressive environments, such as chemical processing, marine, or food industries where you need excellent corrosion resistance.
Tip: If you want to reduce maintenance and extend equipment life in corrosive environments, ceramic ball bearings are your best option.
Steel Ball Bearings
You will find that stainless steel ball bearings also offer strong protection against rust and chemical attack. Among the different grades, 440C stainless steel combines high hardness with good corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for humid, wet, or mildly corrosive environments. If you need even better protection, 316 stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich or marine settings, because of its molybdenum content. 304 stainless steel works well in food and medical applications where you need hygiene and moderate corrosion resistance.
- Stainless steel bearings resist rust and chemical attack better than chrome steel bearings.
- 440C stainless steel bearings keep their structure and performance under moderate shock and temperatures up to 300°C.
- You can use stainless steel bearings in wet or chemical-rich environments with less maintenance.
A comparative study tested 150 bearings made from AISI 440C stainless steel and AISI 52100 chrome steel in a moist carbon dioxide atmosphere with sodium chloride. The results showed that 440C stainless steel bearings had more than twice the corrosion resistance and fatigue life compared to 52100 steel bearings. This means you can expect longer service life and fewer replacements when you choose stainless steel bearings for harsh environments.
Note: While stainless steel bearings perform well in many corrosive settings, ceramic ball bearings still lead in the most extreme conditions.
Load and Speed
Ceramic Bearings
When you need to handle heavy loads or run at high speed, ceramic bearings give you clear advantages. These bearings have a lower density than steel bearings, so they create less centrifugal force. This means you can run machines faster and with less vibration. You also get less heat buildup, which helps the bearings last longer.
Ceramic bearings show excellent performance in endurance tests. For example, in high-speed durability tests, ceramic bearings run at speeds up to 9000 revolutions per minute for 8 hours. They handle axial loads from 382 to 7703 newtons and radial loads from 9 to 414 newtons. The temperature stays stable, usually between 27°C and 86°C. You can see how well ceramic bearings perform under these tough conditions in the table below:
| Test Type | Speed (r/min) | Duration (h) | Axial Load Range (N) | Radial Load Range (N) | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Durability | Up to 9000 | 8 | 382 – 7703 | 9 – 414 | 27.2 – 85.8 |
| Heavy-Load Durability | 3000 – 4000 | 1200 | 620 – 23076 | 259 – 593 | 19.6 – 67.8 |
You benefit from the high hardness and wear resistance of ceramic bearings. These properties help them resist surface damage and keep working even when you push them hard. You also get longer service life, especially when you use them in machines that run at high speed or carry heavy loads.
Tip: Ceramic bearings often need less lubrication, so you spend less time on maintenance.
Steel Bearings
Steel bearings also perform well under load, but you may notice some differences. These bearings have a higher density, so they create more centrifugal force at high speed. This can lead to more heat and vibration. You may need to check and maintain steel bearings more often, especially in demanding applications.
Steel bearings go through strict endurance tests to prove their strength. In heavy-load durability tests, steel bearings handle axial loads up to 23,076 newtons and radial loads up to 593 newtons. Testers use sample sizes of 20 to 30 bearings and run the tests long enough to see real failures. They use Weibull plots to check the life and reliability of the bearings.
Here are some steps used in endurance testing for steel bearings:
- Testers select random samples and run at least two full endurance tests.
- They use good lubrication to make sure the results focus on bearing strength.
- Load-to-capacity ratios are set between 1 and 3 to match real-world conditions.
- The test lasts long enough to see at least six failures for accurate analysis.
Steel bearings give you strong load capacity and good reliability. You can use them in many machines, but you may see more wear if you run them at high speed for long periods.
Note: You should choose steel bearings for steady, heavy loads and ceramic bearings for high speed or when you want less maintenance.
Durability
Ceramic Ball Bearings
When you look for the highest durability in extreme environments, ceramic ball bearings stand out. You can see their strength in real-world applications like satellites, jet engines, and Mars rovers. These bearings face vacuum, extreme temperatures, dust, and even radiation. Over five years, satellites using silicon nitride ceramic bearings reported zero failures in their reaction wheels. This shows you how well these bearings perform over time.

Ceramic ball bearings also work well in cryogenic conditions. Tests show that silicon nitride rings and balls keep their durability even at very low temperatures. A self-lubricating film forms on the surface, which helps reduce wear. However, the bearing cage may wear faster, so you should check this part if you use bearings in very cold places.
You also benefit from the high fatigue resistance and thermal stability of ceramic bearings. Dynamic fatigue tests prove that these bearings keep their strength up to 800°C. Even after long use, they show little change in flexural strength. This means you can trust ceramic bearings for both durability and longevity in harsh settings.
Tip: If you need bearings that last in space, deep cold, or high heat, ceramic ball bearings give you proven durability.
Steel Ball Bearings
Stainless steel ball bearings also offer strong durability, especially when you use advanced coatings. In accelerated life tests, uncoated AISI 440C bearings failed after about 40 hours under dry, high-speed conditions. When treated with SlipCoat, these bearings ran for 6,000 hours without visible damage. The raceways looked new, showing that coatings can greatly improve durability.
You should also pay attention to lubrication. Life tests show that bearings with enough grease last over 9,000 hours, while those without grease fail much sooner. Acoustic emission monitoring helps you spot early signs of failure, so you can replace bearings before they break.
Stainless steel bearings give you reliable durability in many industries. They work well in food, medical, and industrial machines. With proper care and the right coatings, you can expect long service life and good performance.
Note: Both ceramic and stainless steel ball bearings offer excellent durability, but ceramic bearings often lead in the most extreme environments.
Maintenance and Cost
Ceramic Bearings
When you look at maintenance and cost, ceramic bearings stand out for their long-term value. You pay more at first for ceramic bearings, but you save money over time. These bearings last longer and need less frequent replacement. You also spend less on lubrication because ceramic bearings can run with little or no grease. In many industries, you see these benefits add up quickly.
- In wind turbine gearboxes, switching from steel bearings to ceramic bearings increased the time between failures by almost 40%. This means you spend less time and money on repairs.
- In pharmaceutical factories, companies saw fewer shutdowns and less risk of contamination after using ceramic hybrid bearings. The savings became clear after about one year.
- Ceramic bearings often last twice as long as steel bearings. This longer life means you do not have to replace them as often.
- Many users find that the higher upfront cost pays off within two years because of lower maintenance needs.
You also benefit from less downtime. Machines keep running longer, which helps you avoid costly interruptions. If you want to reduce maintenance and get more value over time, ceramic hybrid bearings are a smart choice.
Steel Bearings
Steel bearings cost less when you buy them. You can find them in many machines because they are reliable and easy to get. However, you may spend more on maintenance over time. Steel bearings need regular lubrication to prevent wear and rust. You also have to replace them more often, especially in tough environments.
Steel bearings work well in many settings, but they may not last as long as ceramic bearings. If you use them in places with high heat or chemicals, you might see more frequent breakdowns. This means more time spent on repairs and more money spent on parts and labor.
When you compare the two, ceramic hybrid bearings give you lower maintenance costs and longer service life. Steel bearings offer a lower starting price, but you may pay more in the long run if you need to replace them often.
Summary Table
You need a clear overview when making a choice between ceramic and stainless steel ball bearings. The table below gives you a direct comparison between ceramic bearings and steel bearings across the most important factors. This helps you see which type fits your needs best.
| Factor | Ceramic Ball Bearings | Stainless Steel Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 1200°C | Up to 300°C |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (no rust, even in acids) | Good (resists rust, some limits) |
| Load & Speed | High speed, moderate to high load | High load, moderate speed |
| Durability | Very high (less wear, longer life) | High (with proper care) |
| Maintenance | Low (less lubrication needed) | Moderate (regular lubrication) |
| Cost | Higher upfront, lower over time | Lower upfront, higher over time |
| Applications | Aerospace, wind energy, EVs, chemical plants | Food, medical, marine, industry |
| Electrical Insulation | Yes | No |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Longevity | 2-10x longer than steel | Standard lifespan |
When you look at the comparison between ceramic bearings and steel bearings, you notice several key differences in performance. Ceramic bearings have a smoother and more uniform surface finish, which reduces rolling resistance. You also get lighter weight, greater hardness, and increased stiffness. These features mean less deflection under load and better results at high speeds. Ceramic bearings perform better in high-speed, high-load, and high-temperature environments. They also provide superior corrosion resistance.
- You can expect ceramic bearings to last longer and need less maintenance.
- Stainless steel bearings work well in many traditional applications and offer good durability with proper care.
Choose the bearing type that matches your environment and application needs for the best results.
Choosing Bearings
Selecting the right bearing for your application can make a big difference in performance and reliability. You need to look at your environment and decide which features matter most. Both ceramic and stainless steel ball bearings have strengths, but each works best in different situations.
Use this checklist to guide your choice:
- Temperature:
- If you work in very high temperatures (above 300°C), ceramic ball bearings are your best option.
- For moderate heat (up to 300°C), stainless steel bearings perform well.
- Corrosive Environments:
- Choose ceramic bearings if you face strong acids, saltwater, or harsh chemicals.
- Stainless steel bearings handle mild to moderate corrosion, like food processing or medical equipment.
- Speed and Load:
- For high-speed machines, ceramic bearings reduce heat and vibration.
- For heavy loads at moderate speeds, stainless steel bearings offer strong support.
- Electrical Insulation:
- Ceramic bearings provide electrical insulation, which protects sensitive equipment.
- Stainless steel bearings do not insulate against electricity.
- Maintenance and Cost:
- Ceramic bearings cost more at first but save you money over time with less maintenance.
- Stainless steel bearings have a lower upfront price and are easy to find.
Tip: Always match the bearing type to your specific needs. Think about temperature, chemicals, speed, and load before you decide.
Here is a quick comparison table to help you:
| Need | Best Choice |
|---|---|
| Extreme heat or corrosion | Ceramic Bearings |
| Hygiene and easy cleaning | Stainless Steel |
| High speed, low vibration | Ceramic Bearings |
| Heavy load, steady use | Stainless Steel |
| Electrical insulation | Ceramic Bearings |
You should talk to a bearing expert if you have special requirements. The right choice will help your machines last longer and work better. Always consider your environment and application before making a decision.
You have seen that ceramic ball bearings work best in high temperatures and corrosive environments, while stainless steel bearings excel in hygienic and moderate settings. Experts agree that you should always match bearing type to your specific needs, considering load, speed, and environment. Nearly one in five bearing failures result from poor selection. For the best results, talk with a specialist. TFL Bearings offers a wide range of ceramic and stainless steel options to help you find the right fit.
FAQ
What makes ceramic ball bearings better for high temperatures than stainless steel?
Ceramic ball bearings handle higher temperatures. You get stable performance up to 1200°C. Stainless steel bearings work well up to 300°C. If you need bearings for very hot places, ceramic is the better choice.
Are ceramic ball bearings always more expensive than stainless steel?
Yes, you usually pay more for ceramic ball bearings at first. Over time, you save money because they last longer and need less maintenance. Stainless steel bearings cost less to buy, but you may replace them more often.
Which bearing type resists corrosion better in harsh environments?
Ceramic ball bearings resist corrosion best. You can use them in acids, saltwater, or chemicals without worry. Stainless steel bearings resist rust in mild to moderate conditions, but they may not last as long in very harsh environments.
Do both bearing types work well at high speeds?
You get better results with ceramic ball bearings at high speeds. They weigh less and create less heat. Stainless steel bearings handle heavy loads well, but they may wear out faster if you run them very fast.
Can I use ceramic and stainless steel bearings in food or medical equipment?
You can use both types. Stainless steel bearings work well in food and medical equipment because they are easy to clean and resist rust. Ceramic bearings also work, especially if you need extra corrosion resistance or electrical insulation.




