Choosing the right bearings can stop many expensive problems. Industry data shows that picking the wrong bearing or size causes over 22% of failures.
You need to know the main sizes—inner diameter, outer diameter, and width—when picking roller bearing sizes. Size codes help you skip measuring by hand and avoid mistakes.
- Size codes for bearings:
- Give you exact facts about type, size, and features.
- Help you choose the right bearing for your job.
- Lower the chance of mistakes and make buying faster.
Key Takeaways
- Roller bearing size codes tell you the type, size, and special features. This helps you pick the right bearing fast and avoid mistakes.
- Always check the three main sizes: inner diameter, outer diameter, and width. Do this before you choose a bearing to make sure it fits.
- Learn how to read bearing codes by knowing prefixes, type symbols, size codes, bore diameter, and suffixes. This gives you all the details.
- Use size charts and manufacturer catalogs to match sizes and codes. Always check load and speed ratings so you do not have problems.
- If you are not sure about codes or features, ask your supplier for help. This helps you get the right bearing and keeps your machines working well.
Roller Bearing Sizes
Key Dimensions
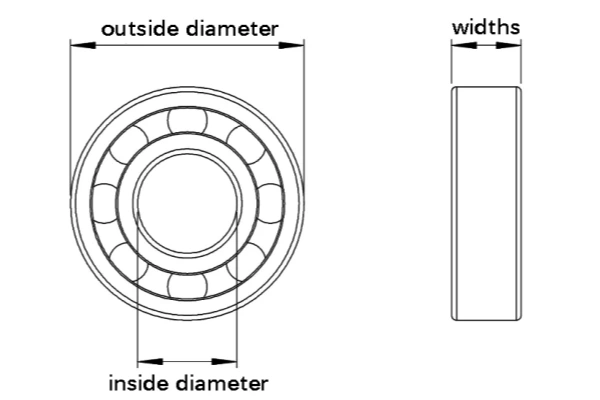
When you look at roller bearing sizes, you need to focus on three main measurements. These are the inner diameter, the outer diameter, and the width. The inner diameter is the hole in the center of the bearing. This is where the shaft fits. The outer diameter is the distance across the outside of the bearing. The width is how thick the bearing is from one side to the other.
You can see the typical size ranges for popular bearing series in the table below:
| Bearing Series | Inner Diameter Range (mm) | Outer Diameter Range (mm) | Width Range (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA Series (needle roller) | 4 to 13+ | 8 to 19+ | 8 to 17+ |
Tip: Always check all three dimensions before you choose a bearing. Even a small mistake can cause problems in your machine.
Common Series
You will find that roller bearing sizes come in many series. Each series has its own features and uses. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Needle Roller Bearings
- Series: TA, HK, NK, RNA, NA, K
- Features: Small cross-section, high load-carrying capacity. Ideal for applications where space is limited and radial loads are high.
- Example applications: Automotive transmissions, two-stroke engines, small gearboxes.
2. Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- Series: NU, NJ, NUP, N, NF, NH, NNU, NN
- Features: Support high radial loads. Certain designs (NJ, NUP) can also support limited axial loads.
- Example applications: Electric motors, machine tools, gearboxes, pumps.
3. Tapered Roller Bearings
- Series: 30200, 30300, 32000, 32200, 32900, and others
- Features: Designed to handle both radial and axial loads. The contact angle makes them suitable for combined load applications.
- Example applications: Vehicle wheel hubs, agricultural equipment, gear reducers.
4. Spherical Roller Bearings
- Series: 21300, 22200, 22300, 23000, 23100, 24000, 24100
- Features: Automatically compensate for shaft misalignment. Support heavy radial loads and some axial load in both directions.
- Example applications: Heavy machinery, mining equipment, paper mills.
You will see both metric and inch sizing systems for roller bearing sizes. Metric bearings use millimeters and are common worldwide. Inch bearings use inches and are mostly found in North America. You need to match the sizing system to your equipment. Many companies, like John Deere, have switched to metric sizing to make things easier and avoid confusion.
Size Code Structure
Code Elements
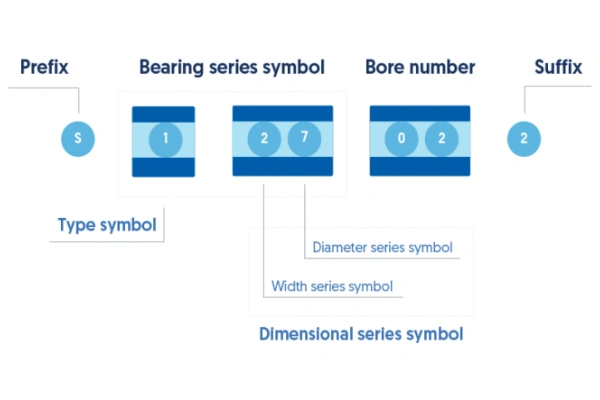
When you look at a roller bearing size code, you see a combination of letters and numbers. Each part of this code tells you something important about the bearing. You can break down a standard size code into several main elements:
- Prefix: This part shows if the bearing has special features or variations.
- Bearing Type Symbol: This symbol tells you what kind of bearing you have, such as deep groove ball, tapered roller, or needle roller.
- Bearing Size Code: This section gives you information about the width and outer diameter series.
- Bore Diameter Code: These digits show the size of the hole in the center. For most codes above 20 mm, you multiply the last two digits by 5 to get the bore size in millimeters.
- Suffix: This part describes extra details like internal clearance, cage design, or seals.
Note: Manufacturers around the world use standards from groups like ISO, ANSI, and ASTM. These standards help everyone use the same system, so you can compare and choose bearings easily, no matter where they come from.
You can see how the code structure works for different bearing types in the table below:
| Code Position | Meaning | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| First digit | Bearing type identifier | ‘2’ = Spherical roller, ‘3’ = Taper roller ‘NA’ = Needle roller, ‘NU’/’NJ’ = Cylindrical roller |
| Second digit | Bearing series (strength) | 0 = Extra light, 2 = Light, 3 = Medium, 4 = Heavy |
| Last two digits | Bore size (inner diameter) | Multiply by 5 for mm (e.g., ’04’ = 20 mm) |
Decoding Examples
You can use a simple formula to find the bore size from the code. Look at the third and fourth digits. For codes above ’03’, multiply these digits by 5 to get the bore in millimeters. For example:
| Bearing Code Digits (3rd & 4th) | Bore Size (mm) |
|---|---|
| 00 | 10 |
| 01 | 12 |
| 02 | 15 |
| 03 | 17 |
| 04 | 20 |
| 05 | 25 |
Let’s look at some real-world examples:
NA4903 – Needle Roller Bearing
- ‘NA’: Needle roller bearing (with inner ring)
- ’49’: Series 49 – light duty, full complement
- ’03’: Bore size = 17 mm
- Use: Compact applications requiring high radial load capacity.
NJ2205 – Cylindrical Roller Bearing
- ‘NJ’: Cylindrical roller bearing with one fixed rib
- ’22’: Medium series
- ’05’: Bore = 25 mm
- Use: Motors, gearboxes, where axial positioning is needed in one direction.
30206 – Tapered Roller Bearing
- ‘302’: Tapered roller bearing series
- ’06’: Bore = 30 mm
- Use: Automotive wheels, axles, industrial reducers (handles both radial and axial loads).
22208 – Spherical Roller Bearing
- ‘222’: Spherical roller bearing series
- ’08’: Bore = 40 mm
- Use: Applications with heavy loads and shaft misalignment, like mining and paper mills.
For tapered roller bearings, you see codes like 30205. The ‘3’ shows it is a tapered roller bearing. The ’02’ is the series. The ’05’ means a 25 mm bore. Needle roller bearings use codes like NA4905. The ‘NA’ prefix stands for needle roller, and the rest of the code gives size and design details. These codes focus more on roller dimensions and load ratings.
Tip: Always check the full code, including any suffixes. Suffixes can change the bearing’s features, such as adding seals or changing the cage type.
Manufacturers use these codes to make sure you get the right part every time. Standards from groups like ISO and ANSI help keep the codes the same across different brands and countries. This system started because companies needed a way to make sure parts would fit and work together, no matter who made them.
By learning how to read these codes, you can choose the right bearing for your job. You save time, avoid mistakes, and make sure your machines run smoothly.
Reading Bearing Sizes
Using a Size Chart
A size chart helps you match roller bearing codes to products. This makes it easier and saves time. Here are the steps you should follow:
- First, measure the inner diameter of the bearing. Use calipers for best results, or a ruler if you need to.
- Next, measure the outer diameter. Place the bearing between caliper jaws or use a ruler from one edge to the other.
- Then, measure the width of the bearing with calipers or a ruler.
- Find your measurements in a size chart. The chart shows which bearing series number matches your sizes.
- Check the suffix codes in the bearing number. These codes tell you about special features like seals or cage materials.
- Look up what the suffix means in the manufacturer’s guide. Suffixes can be different for each brand.
- Compare your measurements and codes with the manufacturer’s catalog. This helps you pick the right bearing for your needs.
A size chart also lists important things like load ratings and speed ratings. These numbers help you choose a bearing that fits your machine and works safely.
Avoiding Mistakes
Always check the main sizes: inner diameter, outer diameter, and width. These must fit your shaft and housing. Load ratings are important too. They show how much force the bearing can take. If you ignore these ratings, your machine could break early.
Some common mistakes buyers make are:
- Choosing a bearing just by the code, without checking the real measurements.
- Not looking at suffix codes, so they miss needed features.
- Forgetting to check load or speed ratings, which can cause breakdowns.
- Using the wrong sizing system, like metric instead of inch.
- Not thinking about clearance or tolerance, which affects how the bearing fits and works.
A size chart helps you avoid these mistakes. It gives you all the important details in one place. If you are not sure, you can ask supplier technical support for help. They have guides, catalogs, and advice to make things easier.
Knowing roller bearing size codes helps you choose the right part fast. This can stop you from making expensive mistakes. If you understand the codes, you can:
- Get the exact bearing you need. This saves time and stops errors.
- Make sure your bearing has special features, like seals or high precision. This helps your machine work better and have less downtime.
- Use size charts and catalogs to check every detail before buying.
Always check the whole code and any suffixes. Different brands use different systems. If you are not sure, ask your supplier for help. We TFL Bearings will also help you avoid problems and keep your machines working well.
FAQ
What do the numbers in a bearing code mean?
The numbers in a roller bearing code indicate the bearing type, series, and bore size. For example, in “30206,” “302” identifies it as a tapered roller bearing, and “06” means the bore is 30 mm (calculated by multiplying 6 × 5).
What happens if you use the wrong bearing size code?
If you use the wrong code, the bearing may not fit your machine. This can cause damage, noise, or early failure. Always check the code and match it to your equipment.
What is the difference between metric and inch bearing sizes?
Metric sizes use millimeters. Inch sizes use inches. You must match the sizing system to your machine. Mixing them can cause fit problems.
What do suffixes like “2RS” or “ZZ” mean in bearing codes?
Suffixes show extra features. “2RS” means rubber seals on both sides. “ZZ” means metal shields. These features help protect the bearing from dirt and moisture.
What should you do if you cannot find your bearing code in a catalog?
Ask your supplier for help. You can also measure the bearing and compare it to size charts. Suppliers often have guides or can suggest a replacement. At TFL, our team is ready to help—just send us your dimensions or photos, and we’ll quickly assist you with identifying or recommending a replacement bearing.




