Tapered roller bearings are special because of their cone shape. This shape helps them hold both side and up-and-down loads. The design lets tapered roller bearings work well in tough places. Engineers use these bearings to get the best results in hard jobs. The rollers and raceways line up exactly in tapered roller bearings. This makes sure they work well every time. Knowing these design parts helps people pick the right tapered roller bearing for great results.
Key Takeaways
- Tapered roller bearings have a cone shape. This shape lets them hold side and straight loads. They are strong and work well in hard jobs.
- The contact angle in these bearings is important. It controls how much load the bearing can hold. Steeper angles help the bearing hold more axial force.
- Engineers pick materials like high-carbon steel, stainless steel, or ceramic. They choose the best one for strength, rust resistance, or speed.
- Good assembly and the right preload settings help bearings last longer. These steps lower friction and stop too much wear.
- Tapered roller bearings are used in cars, machines, and heavy equipment. Their design helps machines work better and last longer.
Tapered Roller Bearing Design
Geometry

The shape of a tapered roller bearing makes it different from other bearings. It has a cone-shaped design. The inner and outer ring raceways look like cones. The rollers are also shaped like cones. Each part lines up with the bearing’s axis. This helps the bearing hold heavy loads. The raceways and rollers are made for smooth movement. Engineers use this shape to spread out the load. The shape helps lower friction and gives more strength. Tapered roller bearings use this shape to hold both radial and axial forces. The design also saves space in machines. The geometry of a taper roller thrust bearing is made to hold axial loads. This design lets the bearing work well in tough jobs.
Note: The special shape of tapered roller bearings helps them work better in many machines.
Contact Angles
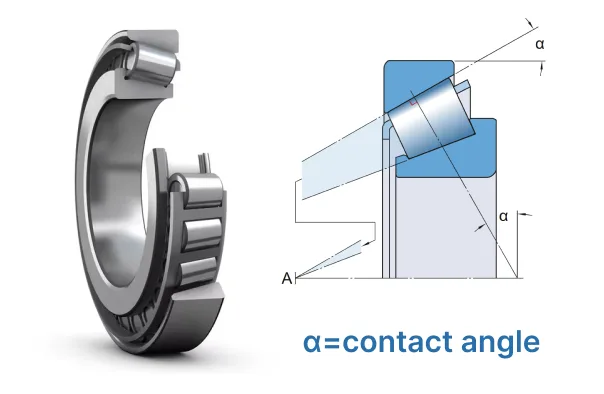
Contact angles are very important in tapered roller bearings. The angle is between the roller and the raceway. This angle changes how the bearing holds loads. A bigger contact angle lets the bearing hold more axial load. Engineers change the angle to make the bearing work better. The angle also changes how strong the bearing is. Tapered roller bearings with a steep angle are good for high axial forces. The contact angle helps move the load the right way. Tapered roller bearings use this to balance both radial and axial loads. Taper roller thrust bearings have a very steep contact angle. This design gives the bearing more strength for thrust jobs.
| Contact Angle | Load Support | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Small | Radial | Gearboxes |
| Medium | Mixed | Automotive wheel hubs |
| Large | Axial | Taper roller thrust bearing |
Assembly
Putting together a tapered roller bearing has many good points. The design lets you take apart the inner ring, outer ring, and rollers. This makes it easier to put together and fix. Engineers can change the preload during assembly to make it work better. Changing the preload helps the bearing get stronger. The design also makes it easier to install in small spaces. Tapered roller bearings use this to cut down on repair time. Taper roller thrust bearings are also easy to put together and take apart. This helps the bearing last longer and work better. The way it is put together makes sure the bearing is strong enough for each job.
Tip: Putting the bearing together the right way and setting the preload helps the bearing last longer and work better.
Materials
Common Choices
Engineers pick materials for tapered roller bearings very carefully. Steel is the most used material. High-carbon chromium steel makes the bearing strong and hard. This helps the bearing work well in tough jobs. Stainless steel is used in some bearings too. It does not rust and works in wet places. Sometimes, ceramic materials are used instead of steel. Ceramics are lighter and make less friction. This is good for fast machines. Some bearings have special coatings. These coatings protect the surface and help the bearing last longer.
A table below shows common materials and their main features:
| Material | Main Feature | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| High-carbon steel | High strength | Automotive, industry |
| Stainless steel | Corrosion resistance | Food processing, marine |
| Ceramic | Low weight, low friction | High-speed, precision |
Note: Picking the right material helps the bearing work better for each job.
Durability Factors
How long a bearing lasts is very important. The material changes how long the bearing will work. Heat treatment makes steel even stronger. This helps the bearing not crack. A smooth surface also helps the bearing work better. It lowers friction and helps the bearing last longer. Engineers think about load, speed, and temperature. They pick the best material for these needs. Lubrication keeps the bearing safe from wearing out. Good lubrication stops heat and friction. Keeping the bearing clean during assembly is important. This keeps dirt out and helps the bearing last longer.
- Key durability factors for making bearings last:
- Good heat treatment
- Smooth surface
- Right lubrication
- Clean assembly
Engineers always try to make bearings last longer and work better. Doing the right things helps the bearing stay strong and work well.
Load Capacity
Radial Loads
Tapered roller bearings are made to hold heavy side loads. The rollers and raceways work together to support weight. Engineers try to make the bearing hold more weight while moving. This is called dynamic capacity. A good design helps the bearing hold more load. Engineers test how much load the bearing can take. They use these tests to pick the right bearing for each job. The best design and dynamic capacity help the bearing last longer and work better.
Axial Loads
Axial loads push straight along the bearing’s axis. Tapered roller bearings are shaped to handle these forces. Engineers work to make the bearing stronger for axial loads. The contact angle in the bearing helps guide the force. Taper roller thrust bearings have a steep angle for more strength. Engineers change the design to get better results in hard jobs. They check the dynamic capacity for every use. They use this to make sure the bearing can handle the force. The right design and dynamic capacity keep the bearing strong.
Combined Loads
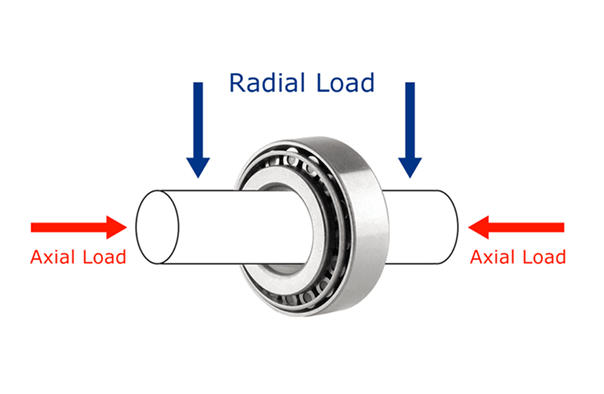
Some machines need bearings that hold both side and straight loads. Tapered roller bearings are made for this job. Engineers work to balance dynamic capacity for both load types. The bearing must have high dynamic capacity to work well. Engineers use tests to pick the best bearing for each job. They look at the design and check the dynamic capacity. The table below shows how much optimization and dynamic capacity matter for each load type:
| Load Type | Needed Optimization | Dynamic Capacity Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Radial | High | High |
| Axial | High | High |
| Combined | Very High | Very High |
The best results come from good design and high dynamic capacity. Engineers always try to get the best performance by focusing on these things.
Tip: Always check the dynamic capacity and use optimization to match the bearing design to the job.
Taper Roller Bearings Applications
Automotive
Tapered roller bearings are very important in cars and trucks. Engineers put them in wheel hubs, transmissions, and differentials. These parts need to handle side and straight loads. The special design gives strong support and helps them last longer. In each car part, engineers use optimization to match the bearing to the job. For example, wheel hubs need to be tough and spin smoothly. Engineers pick the best contact angle and preload for each use. This helps the bearing work well on all kinds of roads.
Note: Good optimization in cars can make them quieter and safer.
Industrial
Factories use taper roller bearings in many machines. Gearboxes, conveyor belts, and electric motors all need these bearings. Each job needs the right optimization for load, speed, and heat. Engineers change the shape and material to get the best results. For gearboxes, the bearing must hold heavy loads and spin fast. Optimization helps balance these needs. In conveyor belts, engineers try to lower friction and wear. They use optimization to help the bearing last longer and need less fixing.
A table below shows where these bearings are used and what engineers focus on:
| Application | Optimization Focus |
|---|---|
| Gearboxes | Load & speed balance |
| Conveyor systems | Friction reduction |
| Electric motors | Heat management |
Heavy Machinery
Big machines like rolling mills and construction tools need tapered roller bearings to work well. These machines face heavy loads and tough jobs. Optimization is very important for each use. Engineers use special ways to pick the right size, material, and oil. For rolling mills, optimization helps the bearing take shocks and keep working. In construction tools, engineers want the bearing to last and be easy to fix. The right optimization keeps machines working longer and stops breakdowns.
Tip: Checking optimization often helps big machines stay safe and work better.
Tapered roller bearings have a special shape. This shape lets them hold both side and straight loads. The design helps many machines work better. Engineers use optimization to pick the best bearing. Optimization means matching the bearing to each job. When optimization is done well, machines work better and last longer. Engineers check optimization at every step. They use it to set preload and pick materials. Optimization also helps when putting the bearing together and fixing it. Engineers always look at optimization to keep things working well. Careful optimization makes sure the bearing works in every machine.
If you need to purchase and related assistance, TFL offers high-quality tapered roller bearings and professional purchasing advice. Contact us anytime to get the latest quotations.
FAQ
What makes tapered roller bearings different from other bearings?
Tapered roller bearings have rollers and raceways shaped like cones. This shape lets them hold both side and straight loads. Most other bearings can only hold one kind of load.
How do engineers set the preload in tapered roller bearings?
Engineers move the rings to set the preload when putting it together. Setting the right preload helps the bearing last longer. It also helps the bearing work better.
Where do people use tapered roller bearings most often?
| Application Area | Example Use |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Wheel hubs |
| Industrial machines | Gearboxes, conveyors |
| Heavy equipment | Rolling mills |
Why is lubrication important for tapered roller bearings?
Lubrication helps stop friction and heat. It keeps the bearing safe from wearing out. Good lubrication makes the bearing last longer and run smoothly.