A cylindrical roller bearing uses cylindrical rollers to hold heavy loads. It does this with very little friction. This bearing has a special structure. The rollers touch the raceway in a line. This helps it carry more weight. It also lets it work at high speeds. Cylindrical roller bearings are used in many places. The automotive industry uses over 35.9% of these bearings. They are used in vehicles and machines. People all over the world want more of these bearings. You can see this in the table below:
| Year / Period | Market Size (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 25.8 | N/A | Base year estimate |
| 2025 | 29.29 | N/A | Estimate for 2025 |
| 2025-2034 | 51.27 | 6.42 | Forecast period |
Knowing about the structure and performance of cylindrical roller bearings helps people choose the right one for their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Cylindrical roller bearings have long rollers. They help carry heavy loads with little friction. This makes them good for machines with big radial forces.
- These bearings come in many types and materials. Each type is made for a special job, speed, or load. This helps them work better and last longer.
- They work well at high speeds. They last a long time if you install, oil, and care for them right. This helps machines run well and use less energy.
- Cylindrical roller bearings are used in many industries. You can find them in cars, wind turbines, and trains. They help because they hold heavy loads and work in hard places.
- Picking the right bearing depends on the load, speed, and alignment. The environment matters too. Ask experts and follow the maker’s rules for the best results.
Cylindrical Roller Bearing Structure
Main Components
A cylindrical roller bearing has several important parts. These parts help it carry heavy loads and lower friction. The main parts are:
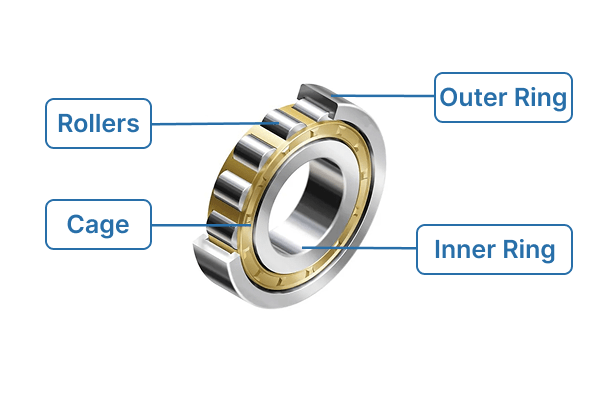
- Inner ring: This ring goes on the shaft. It gives the rollers a smooth place to move.
- Outer ring: This ring stays in the housing. It keeps the rollers in the right spot.
- Cylindrical rollers: These rollers are longer than they are wide. They roll between the rings. This spreads out the weight and keeps things moving smoothly.
- Cage (retainer): The cage spaces the rollers apart. It stops them from touching each other. This lowers friction and wear.
The outer ring connects to the housing. The inner ring fits on the shaft that turns. When the rings line up right, the bearing works better and lasts longer. The design lets it handle big radial forces and stay stiff. Some bearings have holes or seals for oil or grease. This helps them work better and last longer.
Tip: The cage is very important. It keeps the rollers in the right place. This helps the bearing work well and last longer.
Here is a table that lists the main parts and what they do:
| Component | Function | Material/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inner ring | Holds the shaft, gives rollers a track | High-quality steel, made with care |
| Outer ring | Holds rollers, supports weight, stays in housing | High-quality steel |
| Cylindrical rollers | Help things turn smoothly, spread out the load | Steel, longer than wide |
| Cage | Spaces rollers, lowers friction and wear | Steel, brass, or strong plastics |
Types and Variations
Cylindrical roller bearings come in many types. Each type is made for a special job. The main types are single row and double row cylindrical roller bearings. The flanges on the rings decide how each type works.
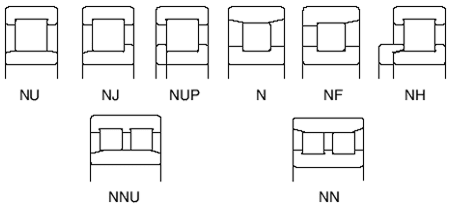
- N type: The inner ring has two flanges. The outer ring has none. This type lets the shaft move one way and holds big radial loads.
- NU type: The outer ring has two flanges. The inner ring has none. It lets the shaft move back and forth.
- NJ type: The outer ring has two flanges. The inner ring has one. It can hold some force in one direction.
- NUP type: The outer ring has two flanges. The inner ring has one fixed and one loose flange. It can hold force both ways and is used to keep things in place.
- NF type: The inner ring has one flange. The outer ring has two. It can hold some force in one direction.
- NN and NNU types: These have two rows of rollers. This makes them stronger and able to carry more weight. They are used in big machines that need to go fast and carry heavy loads.
- Full complement cylindrical roller bearing: This type has no cage. It uses more rollers. It can carry more weight but may get hotter and have more friction.
| Bearing Type | Structural Features | Axial Load Capability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| NU | One row, no ribs on inner ring, outer ring has no flanges | No axial load | Heavy industry, mining, machine tools |
| NJ | One row, flange on outer ring, no flange on inner ring | Some, one direction | General machinery |
| NUP | Two flanges on outer, fixed/loose flange on inner ring | Both directions | Fixed end, keeps things in place |
| N | Flanges on both sides of inner ring, none on outer ring | Some, one direction | General machinery |
| NF | Flange on inner ring, none on outer ring | Some, one direction | General machinery |
| NN, NNU | Two rows, more rollers, can carry more weight | Some axial, high radial load | Big, fast machines |
Some cylindrical roller bearings have more than one row. Double or four-row types can carry even more weight and are very stiff. These are used in rolling mills and other big machines.
Precision grades like P0, P6, P5, P4, and P2 show how exact the bearing is made. Higher grades mean the bearing is made with tighter rules. This makes it run smoother and last longer.
Materials and Cages
Special materials make cylindrical roller bearings strong and tough. The rings and rollers often use Cr4Mo4V alloy steel. This steel has chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, and carbon. These make the bearing strong, hard to wear out, and able to carry heavy loads.
Cages can be made from different things. Each kind has its own good points:
| Cage Material | Operational Characteristics | Best For | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strong, reliable, not expensive, works in high heat | General industry, high heat | Strong, low cost, reliable |
| Brass | Takes shock, very tough, good for vibration and heavy loads | High-vibration, heavy-duty machines | Tough, lasts long, takes shock |
| Nylon 6/6, PEEK | Light, low friction, tough, resists chemicals | Precision, high-speed machines | Light, low friction, resists chemicals |
Steel cages are good for most factories. Brass cages are best for machines with heavy loads and lots of shaking. Nylon or PEEK cages are good for fast or very exact machines because they are light and lower friction.
The cage material changes how the bearing handles speed, weight, and heat. New ways of making bearings, like CNC machines and heat treatment, make the parts harder and more exact. This helps the bearing last longer and work better.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings Performance
Load Capacity
Cylindrical roller bearings are good at holding heavy radial loads. The rollers touch the raceway in a line, not just at one point. This gives a bigger area to spread out the weight. It helps the bearing handle more stress and last longer. The way the rollers are set up helps share the load. This means less wear and less chance of damage. Bearings with more rows can hold even more weight and last longer.
| Design Feature | Contribution to Load-Bearing Capability |
|---|---|
| Line contact via cylindrical rollers | Gives a bigger area to spread out the weight, so the load is shared better. |
| Geometry and roller arrangement | Helps the load get shared evenly, so there is less wear. |
| Multi-row roller structure | Lets the load spread over more rollers, so each one has less stress and the bearing lasts longer. |
Cylindrical roller bearings are used when machines need to carry heavy loads. Some types can also take a little bit of force from the side, depending on the flange. But most are made to hold big radial loads. This makes them great for motors, gearboxes, and big machines.
Speed and Friction
Cylindrical roller bearings can spin fast and do not make much friction. This helps machines work better and use less energy. The rollers help things turn smoothly. But because the rollers touch in a line, there is a bit more friction than with ball bearings. This happens because of how the rollers touch the ribs and how oil moves inside.
Ball bearings have less friction, so they are better for very fast spinning.
- Cylindrical roller bearings have a little more friction, but they can hold more weight.
- These bearings can still spin pretty fast and are often used with high-speed ball bearings in spindles.
- Ball bearings are best for low friction at high speeds, but cylindrical roller bearings are better for heavy loads.
Even though they have a bit more friction, cylindrical roller bearings still work well at high speeds. Good oil and careful making help them run smooth and last longer.
Durability and Maintenance
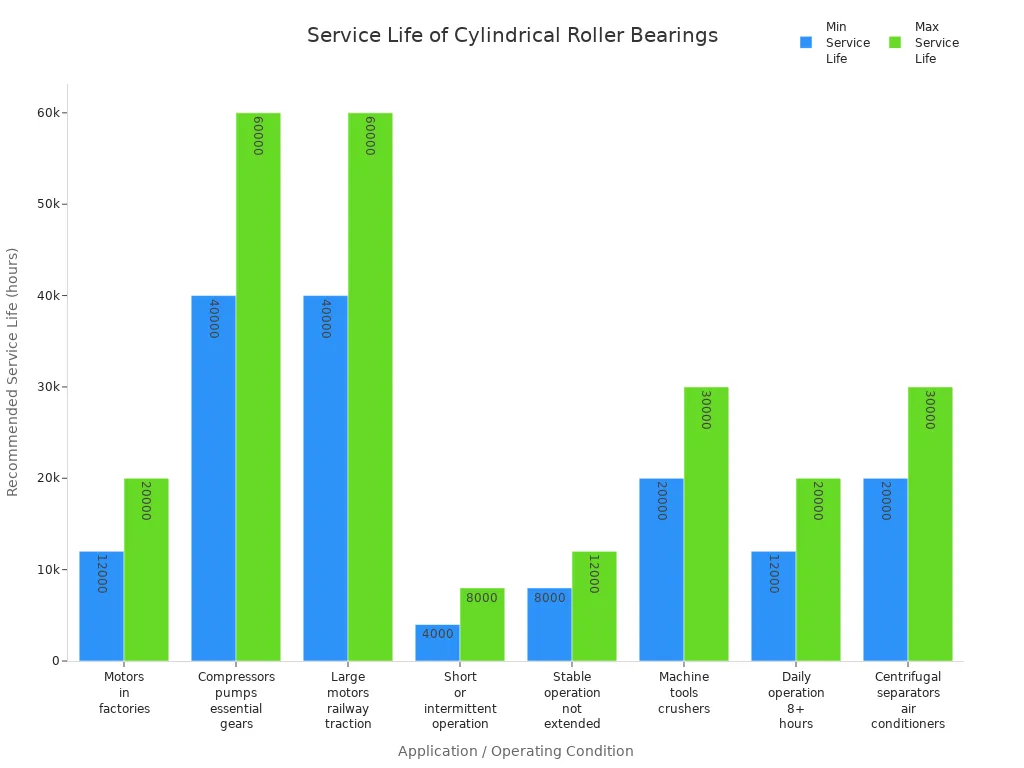
Cylindrical roller bearings are strong and last a long time. They work well even in tough places. How long they last depends on how they are used and where they are used.
| Application / Operating Condition | Recommended Service Life (hours) |
|---|---|
| Motors used in factories, general gears | 12,000 – 20,000 |
| Compressors, pumps, essential gears | 40,000 – 60,000 |
| Large motors, railway rolling stock traction motors | 40,000 – 60,000 |
| Short or intermittent operation (e.g., household appliances) | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| Not extended duration but stable operation (e.g., air conditioners) | 8,000 – 12,000 |
| Machine tools, crushers | 20,000 – 30,000 |
| Daily operation more than 8 hours or continuous extended operation (e.g., escalators) | 12,000 – 20,000 |
| Centrifugal separators, air conditioners, passenger coach axle journals | 20,000 – 30,000 |
To help bearings last, you need to take care of them. Here are some important steps:
- Check for noise, shaking, or damage often.
- Put them in the right way with the right tools.
- Use the right oil or grease and the right amount.
- Keep the bearing and area clean.
- Watch the temperature to catch problems early.
- Store bearings in clean, dry, cool places.
- Fix old bearings if you can.
- Teach workers how to put in and care for bearings.
Doing these things helps bearings work well and not break early. This keeps machines running and makes bearings last longer.
Limitations
Cylindrical roller bearings are great for heavy radial loads, but they have some limits. They cannot hold much force from the side. Most types need extra parts to keep them in place. The table below shows the main limits:
| Limitation Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Axial Load Capacity | Not made to hold much side force; need extra help to stay in place. |
| Axial Location Requirement | Tight fits are not enough; need other ways to keep them from moving. |
| Misalignment Tolerance | Only good for small errors in lining up; big mistakes can cause damage. |
| Rib Support | Ribs must be fully supported or they can break. |
| Seating Surface Tolerances | Need very exact sizes for the shaft and housing. |
| Axial Guidance Function | Not made to guide things from side to side. |
If the bearing is not lined up right, it can wear out fast. Even small mistakes can make the load uneven and cause more friction. This can break the cage or make the bearing not last as long. It is very important to put the bearing in the right way.
Note: Always follow what the maker says for putting in and lining up the bearing. This helps stop early problems and keeps the bearing working well for a long time.
Bearing Applications
Industrial Uses
Cylindrical roller bearings are used in many industries. They help machines carry heavy loads. These bearings work well in electric motors and gearboxes. They also work in other machines that spin fast. Their shape lets them hold big radial loads. They can also spin at high speeds. Factories use these bearings in wind turbines and railway axleboxes. They are also in machines that move materials. The automotive industry puts them in transmissions and differentials. Pumps and compressors in oil, gas, and water plants use them too. These bearings help machines run smoothly and save energy.
| Industry | Machinery Types / Applications |
|---|---|
| Electric Motors & Generators | Electric motors, generators (high radial loads, high speeds) |
| Automotive | Transmissions, differentials, other components requiring high radial load support |
| Industrial Gearboxes | Gearboxes for power transmission and operational reliability |
| Wind Turbines | Main shafts of wind turbines (high radial loads, harsh conditions) |
| Railway | Axleboxes of locomotives and rolling stock (robustness, shock absorption) |
| Material Handling Equipment | Conveyors, hoists, lifting equipment (smooth motion, high load capacity) |
| Pumps and Compressors | Pumps and compressors in oil & gas, water treatment, manufacturing (precision, efficiency) |
These uses show why engineers pick cylindrical roller bearings. They are a good choice for many machines.
Selection Criteria
Engineers think about many things when picking these bearings. They check the kind and size of the load. They look at both radial and axial forces. Precision class is important for machines that need to spin just right. Speed ratings help match the bearing to how fast the machine goes. Temperature changes can affect the bearing and its oil or grease. Rigidity matters for machine tool spindles. Friction torque shows how smooth the bearing will run. Engineers also check the size to fit the shaft and housing. They pick the right cage design to stop misalignment with heavy loads. Good care and oiling help the bearings last longer.
Taking care of bearings with oil and checks keeps them working well and stops early problems.
Real-World Examples
Many companies do better by using cylindrical roller bearings. For example:
- A cement company fixed dirt problems and saved over $200,000 by making bearings work better.
- A steel company made pipe forming rolls last longer by using better bearing setups.
- In mining, strong steel bearings fought off dirt on conveyor pulleys. This made the bearings last longer in tough places.
| Industry/Application | Description | Challenges Identified | Outcomes/Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dust Extraction Fan (Ore Preparation Plant) | Bearings on a 60 mm shaft at about 1485 rpm failed often. | Dirt, high heat | Better reliability and fewer failures. |
| Hot Strip Mill | Four-row tapered roller bearings lasted only 1,400 hours in hard conditions. | Tough working conditions | Bearings lasted longer with new types. |
| Pipe Forming Roll | Used double-row cylindrical and needle thrust bearings from other brands; wanted longer life. | Hard setup, heavy loads | Bearings lasted longer and worked better. |
| Continuous Casting Machine | Roll segment cylindrical roller bearings lasted only 1-2 months; cooling and oiling were hard. | Oiling problems, heavy loads | Bearings lasted much longer. |
These stories show how cylindrical roller bearings help tough jobs. They also help companies save money and stop machines from breaking down.
Bearing Comparison
Cylindrical vs. Ball Bearings

Cylindrical roller bearings and ball bearings do different jobs. Cylindrical roller bearings have long rollers that touch in a line. Ball bearings use small balls that touch at one spot. This makes them handle loads and speed in different ways.
| Feature | Cylindrical Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Element | Cylindrical rollers (line contact) | Spherical balls (point contact) |
| Load Capacity | High radial load, limited axial load | Handles both radial and axial loads, lower radial capacity |
| Speed Capability | Moderate to high speeds under heavy load | Very high speeds, low friction |
| Durability | Highly durable, ideal for heavy-duty setups | Good for moderate loads and speeds |
| Design Flexibility | Separable, easy maintenance | Compact, fits tight spaces |
Cylindrical roller bearings are best for gearboxes and wind turbines. They also work well in steel mills. Ball bearings are good for electric motors and fans. They fit lighter machines too. Ball bearings can handle misalignment better. They also spin faster and have less friction.
Tip: Use cylindrical roller bearings for heavy radial loads. Pick ball bearings for high speed and lighter loads.
Cylindrical vs. Spherical Bearings

Both cylindrical roller bearings and spherical roller bearings carry heavy loads. Spherical roller bearings can line up by themselves. This helps them deal with shaft misalignment and shaking. Cylindrical roller bearings need to be lined up just right. They give higher speed and more precision.
- Spherical roller bearings can take shock and work in rough places.
- Cylindrical roller bearings are stiffer and good for fast, precise machines.
- Spherical roller bearings need more space and careful oiling.
| Aspect | Cylindrical Roller Bearings | Spherical Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment | Needs precise alignment | Self-aligning, handles misalignment |
| Load Capacity | High radial, limited axial | High radial and some axial |
| Speed | High-speed capability | Lower speed due to design |
| Environment | Controlled, clean | Harsh, vibration, contamination |
Choosing the Right Bearing
Picking the right bearing depends on a few things:
- Heavy radial loads need cylindrical roller bearings. If there are both radial and side loads, use spherical roller bearings.
- Fast machines should use cylindrical roller bearings or ball bearings.
- If the shaft might not line up, use spherical roller bearings.
- Dirty or shaky places are better for spherical roller bearings.
- Cylindrical roller bearings are easy to put in and take out.
- Ball bearings fit in small spaces. Spherical roller bearings need more room.
- Think about price, how long it lasts, and how much care it needs.
Note: Always pick the bearing that matches the machine’s needs. This helps it work well and last longer.
Cylindrical roller bearings help hold up heavy loads and work in hard places.
Advantages include:
- They can hold a lot of radial load.
- They work well when machines go fast or carry heavy things.
- They last a long time, even in rough spots.
- They help new machines and technology work better.
Limitations include:
- They do not work well if they do not get enough oil.
- Shaking can make them wear out faster.
- Fake products can cause problems.
To pick the right bearing:
- Make sure the bearing fits the job’s weight and speed.
- Look at how good the maker is and how fast they can send it.
- Check if the bearing meets the right rules before buying.
- Work with companies that have good results over time.
For the best outcome, always think about what your machine needs and talk to experts in the field.
FAQ
What makes cylindrical roller bearings different from ball bearings?
Cylindrical roller bearings have rollers that touch in a line. Ball bearings have balls that touch at one spot. This lets cylindrical roller bearings hold more weight from the side. Ball bearings can hold both side and up-and-down loads, but not as much weight.
What industries use cylindrical roller bearings most often?
Many industries use these bearings in their machines. Cars, wind turbines, trains, and big machines all use them. Factories and power plants use them in motors, gearboxes, and pumps.
What does the bearing precision grade mean?
Precision grade tells how exact the bearing is made. Higher grades like P4 or P2 mean the parts fit together better. These grades help machines work smoother and last longer.
What is the main advantage of using a cage in cylindrical roller bearings?
The cage keeps the rollers apart and in place. This lowers friction and stops the rollers from rubbing. It also helps the bearing spin fast and smooth.
What should engineers check before choosing a cylindrical roller bearing?
Engineers need to check the load, speed, and size needed. They should also look at where the bearing will be used. The cage material and oil or grease are important too. Picking the right bearing helps it last long and work well.




