A needle roller bearing has long, thin rollers. These rollers help lower friction between moving parts. These bearings are important in machines and vehicles. They help things work better and last longer. Many industries use them more each year. Automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing need small and strong parts. These parts go in engines, transmissions, and other equipment.
Picking the right bearing helps machines work better and longer.
| Metric | Value (USD Billion) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size (2024) | 8.24 | Estimated global market size |
| Market Size (2034) | 13.19 | Projected market size by end of period |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate | 4.82% | CAGR for 2025-2034 |
Common uses include:
- Engines and transmissions in cars
- Industrial robots and conveyors
- Aircraft engines and landing gear
- Household appliances and medical devices
Key Takeaways
- Needle roller bearings have long, thin rollers. They can hold heavy loads in small spaces. This helps machines become smaller and stronger.
- Their small size and strong load ability help machines work well. They also help machines last longer. This is important in cars, planes, and big machines.
- There are different needle roller bearing types for different jobs. Some save space, like drawn cup types. Others hold more weight, like full complement types.
- Taking care of bearings is important. Use clean oil or grease. Install them the right way. This helps bearings last longer and machines work better.
- Picking the right needle roller bearing type and size is important. It helps machines work better and last longer in many jobs.
Overview
Needle Roller Bearing Structure
A needle roller bearing uses several key parts to deliver strong performance in a small package. The main components include the rolling elements, cage, inner ring or shaft, and outer ring. Each part plays a special role in how the bearing works.
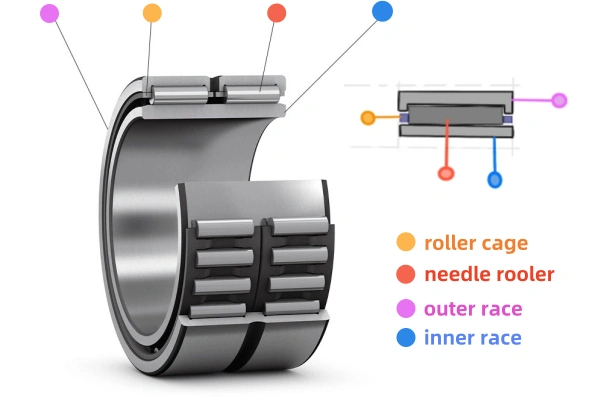
| Structural Component | Description and Contribution to Performance |
|---|---|
| Rolling elements (needle-shaped rollers) | Long, thin rollers with a high length-to-diameter ratio. They give the bearing a small cross-section and allow it to carry heavy radial loads in tight spaces. |
| Cage | Holds the rollers in place, guides them, and keeps them from touching each other. This reduces friction and wear. |
| Inner ring or shaft | Serves as a raceway for the rollers. Sometimes, the shaft itself acts as the raceway, but it must be very hard and smooth. |
| Outer ring | Provides the outer raceway. It can be a solid ring for strength or a thin drawn cup for saving space. |
| Variants (drawn cup, solid ring) | Drawn cup bearings use a thin, deep-drawn outer ring for compactness. Solid ring bearings use a solid outer ring for more strength and speed. |
This structure makes the needle roller bearing compact, lightweight, and able to handle high loads. The cage keeps the rollers spaced evenly, which helps the bearing run smoothly and last longer.
How They Work
A needle roller bearing works by letting the needle-shaped rollers move between the inner and outer rings. These rollers have a large contact area with the raceways, which means they can support heavy radial loads even in small spaces. The cage keeps the rollers from rubbing against each other, which lowers friction and helps the bearing last longer.
Unlike ball bearings, which use balls with point contact, needle roller bearings use long rollers with line contact. This design gives them a higher load capacity and makes them ideal for machines that need to fit bearings into tight spots. Many needle roller bearings can use the shaft or housing as a raceway, which saves even more space. This unique setup allows them to work well in applications where both size and strength matter.
Features
Compact Design
A needle roller bearing is small and light. The rollers inside are thin and long. This helps the bearing fit in tight spots. Other bearings might not fit there. Most needle roller bearings are thinner than ball bearings. This shape saves space and makes machines lighter.
- Drawn cup needle roller bearings have a thin outer ring. This makes them even slimmer.
- The small size makes them easy to put in tight places.
- Designers can make machines smaller and lighter. The machines still stay strong.
The small size of needle roller bearings helps make machines smaller. It also helps machines work better.
High Load Capacity
Needle roller bearings are small but very strong. They can hold heavy loads. The long rollers touch more of the raceways. This spreads the weight out. It makes the bearing stronger. The rollers are much longer than they are wide. This helps the bearing hold more weight than ball bearings of the same size.
Full complement needle roller bearings do not use a cage. They can hold more rollers. This makes them even stronger. But these bearings are not good for heavy side loads. They also do not work well if the shaft and housing are not lined up right.

| Bearing Type | Load Capacity (Relative to Size) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Needle Roller Bearing | Very High | Tight spaces, heavy radial load |
| Ball Bearing | Moderate | General use |
| Tapered Roller Bearing | High | Combined radial and axial load |
Stiffness and Precision
Needle roller bearings are stiff and move very accurately. There are many rollers inside. This makes the bearing strong and steady. It is good for machines that need to move just right, like gearboxes and machine tools.
- The cage keeps the rollers spaced apart. This lowers friction and wear. It helps the bearing last longer.
- Many needle roller bearings use very clean steel, like GCr15. This makes them more accurate and tough.
- Special grinding and heat treatments make the bearing work better. It helps the bearing handle heavy loads and fast speeds.
Bearings need oil or grease to keep working well. This helps them last longer and not wear out.
Engineers pick needle roller bearings for small spaces and strong support. Good materials and smart design help these bearings work well in tough jobs.
Needle Roller Bearing Types
Needle roller bearings come in several main types. Each type has special features that make it useful for different jobs. The most common types include drawn cup, thrust, caged, and full complement needle roller bearings.
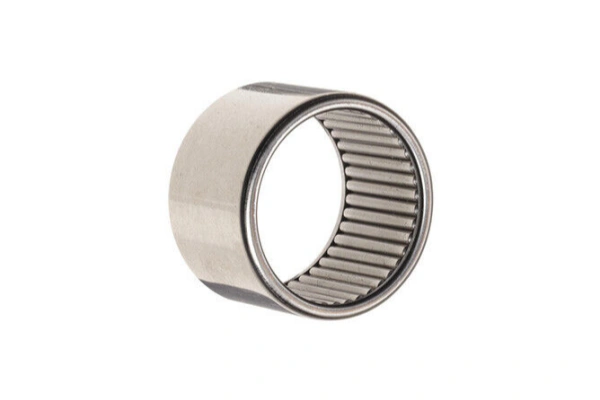
Drawn Cup Needle Roller Bearing
Drawn cup needle roller bearings have a very thin outer ring. This design makes them compact and lightweight. The thin steel cup allows the bearing to fit into places with very little space. These bearings often run directly on the shaft, so they do not need an inner ring. They support high radial loads and work well at high speeds. Drawn cup bearings are easy to install and do not need extra parts to hold them in place. They come in open and closed end designs. Many engineers use them in cars, power tools, and industrial machines where space is tight and strength is important.
Drawn cup bearings help save space and lower costs in many machines.
Thrust Needle Roller Bearing
Thrust needle roller bearings handle forces that push along the shaft, not just around it. Most needle roller bearings support radial loads, but thrust types are made for axial loads. These bearings use special parts like shoulders or snap rings to keep them in place. Without these parts, regular needle bearings cannot handle much axial force. Thrust needle roller bearings work well in gearboxes and pumps where parts push against each other along the shaft.
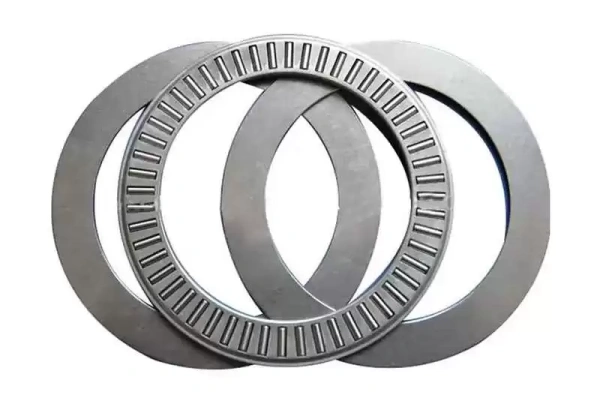

Caged Needle Roller Bearing
Caged needle roller bearings use a cage to keep the rollers spaced apart. The cage helps the rollers move smoothly and stay in the right place. This design allows the bearing to run at higher speeds than full complement types. The cage also helps oil or grease reach all the rollers, which lowers friction and wear. Caged bearings are common in high-speed machines like planetary gears. The strong cage material stands up to heavy use and helps the bearing last longer.
Full Complement Needle Roller Bearing
Full complement needle roller bearings have no cage. They fill the space with as many rollers as possible. This design gives the bearing a very high load capacity. Full complement bearings work best in slow-moving machines where heavy loads matter more than speed. They are often used in construction equipment and presses. However, they do not run as fast as caged types because the rollers touch each other and create more friction.
| Bearing Type | Key Feature | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Drawn Cup | Thin outer ring, compact | Tight spaces, automotive, tools |
| Thrust | Handles axial loads | Gearboxes, pumps |
| Caged | High speed, good lubrication | Planetary gears, high-speed machines |
| Full Complement | Maximum load capacity | Heavy loads, slow-moving equipment |
Choosing the right type of needle roller bearing helps machines work better and last longer.
Applications
Automotive
Needle roller bearings are very important in cars. Many car parts need these bearings to work well and last longer. You can find them in engines, steering, torque converters, and rocker arm pivots. These parts must handle heavy loads and move fast. Needle roller bearings help by lowering friction. They also support forces from different directions. Because they are small, engineers can put them in tight spots inside cars.
- Engines
- Steering systems
- Torque converters
- Rocker arm pivots
Many car parts use needle roller bearings because they are strong, last long, and work well at high speeds.
Industrial Machinery
Big machines in factories do hard work and need strong parts. Needle roller bearings help pumps, compressors, and gearboxes work better. They hold heavy loads and run smoothly at fast speeds. This lowers friction and saves energy. Their small size helps make machines smaller and saves space. These bearings also help machines last longer and need less fixing. Many factories use them in motors, conveyors, and presses.
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pumps | Smooth, efficient operation |
| Compressors | High load support |
| Gearboxes | Reliable, long-lasting motion |
Aerospace
Airplanes and spacecraft need every part to work really well. Needle roller bearings are good for this because they are small and strong. They come in types that handle loads in different ways. Caged types lower friction and let parts move faster. This is important in engines and landing gear. Full complement types hold more weight for slow-moving parts. Special materials help these bearings work in very hot or cold places and at high speeds.
Other Uses
Engineers use needle roller bearings in many things besides cars and planes. Robotic arms and medical tools need to be stiff and exact. These bearings help with that. Their small size lets them fit in tiny spaces, like inside appliances and small motors. Some types, like the SKF NA 4900, work in fast machines. Companies also make special bearings for robots and precision tools. New materials, like light metals and ceramics, help these bearings work even better in new projects.
Advantages
Space Efficiency
Needle roller bearings help machines save space. Their rollers are thin and long. This lets them fit in tight places. Other bearings might not fit there. Designers pick these bearings when space is small. The small shape works well in engines and tools.
Ball bearings can be even smaller in very tight spots. Ball bearings use point contact. This means they can be tiny and still work fast. Needle roller bearings use line contact. They need a little more room but can hold more weight.
- Ball bearings are small and good for fast machines.
- Roller bearings, like needle roller bearings, hold more weight but need more space.
- In very tight spaces, ball bearings save more space than needle roller bearings.
Needle roller bearings are a good mix of size and strength. This makes them a smart pick for many machines.
Some features help needle roller bearings fit in small spaces:
- The height is very small, set by the roller size.
- Flat washers take up less space.
- Rollers have rounded ends to stop damage.
- Bearings can run on the shaft or housing if they are hard and smooth.
- Shafts and housings must fit well for smooth work.
Durability
Needle roller bearings last a long time if used right. How long they last depends on use, load, and how they are made. Good materials and careful work make them strong.
| Operating Condition | Minimum L10 Life (hours) |
|---|---|
| Intermittent operation, service interruptions OK | 8,000 |
| Intermittent operation, reliability important | 12,000 |
| Continuous 1 shift operation | 20,000 |
| Continuous 2 shift operation | 40,000 |
| Continuous 24 hour operation | 60,000 |
| Continuous 24 hour operation, reliability important | 100,000 |
Many things change how long a bearing lasts:
- How big the load is and which way it goes
- How fast it spins
- How good the oil or grease is
- How good the material is
- The temperature and where it is used
- How well it is put in place
Makers do many steps to make needle roller bearings strong:
- They pick strong steel that meets rules.
- They cut and grind the steel to the right shape.
- They trim rollers to the right size.
- They heat the parts to make them tough.
- They put the parts together with cages.
- They add oil or grease to lower friction.
- They test each bearing to check quality.
Good materials, careful building, and the right oil or grease help needle roller bearings last longer and work better.
Versatility
Needle roller bearings work in many machines and jobs. Their design lets them hold heavy loads and fit in small spaces. They also run smoothly. Engineers use them in cars, planes, factory machines, and medical tools.
Some reasons why they are so useful:
- They hold a lot of weight for their size
- They can use the shaft or housing as a raceway to save space
- They run smoothly with little friction
- They last a long time if cared for
- They work well with small space for both radial and axial clearance
These things make needle roller bearings a top choice for many uses. They help machines work better, last longer, and use less space.
Needle roller bearings are strong, small, and useful in many machines. When picking one, you must think about the load, speed, how parts line up, and where it will be used. Some people think all bearings work the same or that using more oil or grease is always best. These ideas are not true and can cause trouble. Picking the right needle roller bearing helps machines work better and last longer. If you need help, TFL Bearings gives expert advice and quick support for every project.
FAQ
What makes needle roller bearings different from ball bearings?
Needle roller bearings have long, thin rollers inside. Ball bearings have small balls instead. Needle roller bearings can hold more weight in small spaces. Ball bearings are better when things need to spin very fast.
Where do engineers use needle roller bearings most often?
Engineers put needle roller bearings in cars, machines, and planes. These bearings fit where there is not much room. They also help carry heavy things. Many tools and home appliances use them too.
How do you know when to replace a needle roller bearing?
You should change a bearing if it gets noisy or feels rough. If you see damage, it is time to replace it. Engineers look for heat, shaking, or leaks. Checking often helps stop machines from breaking.
Can needle roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads?
Most needle roller bearings hold up radial loads. Some special types, like thrust needle roller bearings, can take axial loads. Engineers pick the right kind for the way the force pushes.
Do needle roller bearings need special care?
Needle roller bearings need clean oil or grease to work well. Cleaning and adding oil or grease helps them last longer. Engineers keep out dirt and water so the bearings stay good.




